 PDF(2639 KB)
PDF(2639 KB)


A comparative study on leaf characters between diploid and tetraploid of Cyclocarya paliurus
LIU Xialan, SONG Ziqi, HU Fengrong, SHANG Xulan
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 76-84.
 PDF(2639 KB)
PDF(2639 KB)
 PDF(2639 KB)
PDF(2639 KB)
A comparative study on leaf characters between diploid and tetraploid of Cyclocarya paliurus
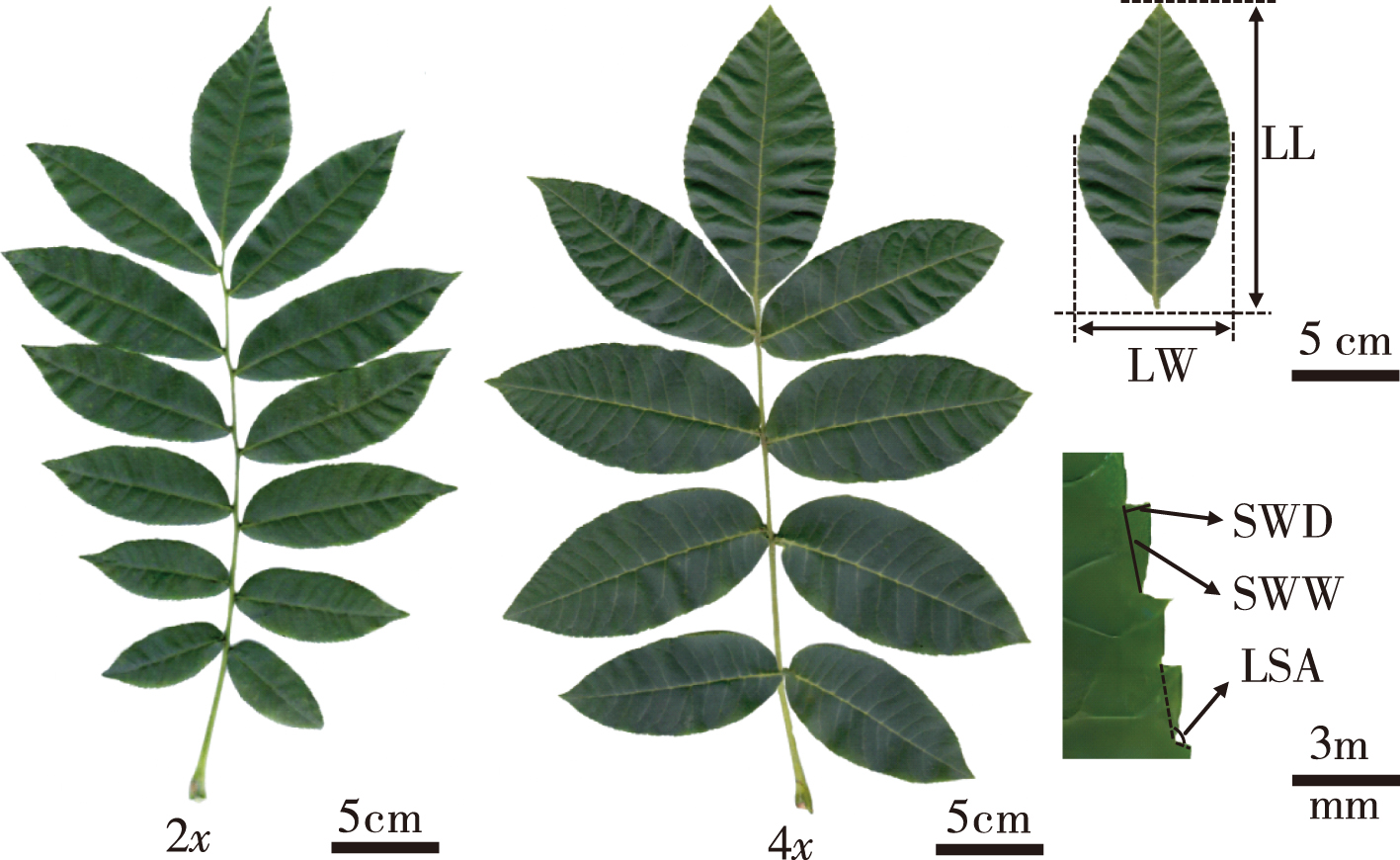
【Objective】To compare the differences in leaf phenotypes characters, anatomical structures and stomatal characteristics between diploid and tetraploid Cyclocarya paliurus, we obtained data on the leaf characteristics of C. paliurus with different ploidy.【Method】Diploid and tetraploid seedlings of C. paliurus were used as study materials, and 32 leaf traits were measured. Independent samples t-tests, a correlation analysis, and principal component analysis (PCA) were conducted.【Result】There were no significant differences between diploid and tetraploid seedlings for sawtooth width and the position of the maximum leaf width of the middle leaflet. For the other 30 leaf traits, there were significant or extremely significant differences between diploid and tetraploid seedlings. Among them, the number of leaflets of tetraploids was significantly less than that of diploids, while the area and specific leaf weight of compound leaves of tetraploids were significantly greater than those of diploids. The length, width and area of the terminal and middle leaflets of tetraploids were significantly greater than those of diploids, while the leaf shape index was significantly smaller than that of diploids. The sawtooth density of tetraploids was significantly smaller than that of diploids. The leaflet thickness, the upper epidermis thickness, lower epidermis thickness, palisade tissue thickness, and sponge tissue thickness of tetraploids were all significantly higher than those of diploids, while the ratio of palisade tissue to sponge tissue and cell tense ratio were significantly smaller than those of diploids. The stomatal length and width of tetraploids were significantly greater than those of diploids, while the stomatal density was significantly smaller than that of diploids. The correlation analysis results indicated that there were broad and significant correlations between the phenotypic characteristics, anatomical structure, and stomatal characteristics of C. paliurus. The indicators reflecting the differences of leaf characteristics between diploid and tetraploid C. paliurus were extracted by a PCA, including leaflet width, leaflet area, leaf shape index, sponge tissue thickness, stomatal length, palisade tissue thickness and cell tense ratio.【Conclusion】There were significant differences in leaf traits between diploid and tetraploid C. paliurus, and leaf phenotypic characteristics, such as leaflet width, leaflet area, and leaf shape index, can be used for the preliminary screening of diploid and tetraploid C. paliurus.
Cyclocarya paliurus / polyploid / phenotypic characters / anatomical structure / stomatal characteristics
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
袁静, 周冰莹. 植物叶缘锯齿发育调控的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(26):24-31.
|
| [4] |
晁亚琮, 武荣花, 蒋卉, 等. 同源多倍体化对植物侧生器官形态建成影响的研究进展[J]. 河南农业科学, 2021, 50(5):1-6.
|
| [5] |
方升佐. 青钱柳产业发展历程及资源培育研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):115-126.
|
| [6] |
方升佐, 尚旭岚, 洑香香. 青钱柳种子生物学研究[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2017.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
肖岩, 马博稷, 李冰涛, 等. 青钱柳醇提物中化学成分的UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(16):196-204.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
陈絮蒙, 王雅靖, 陈靓, 等. 青钱柳活性物质及其代谢调节作用的研究与应用进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2023, 49(12):336-344.
|
| [11] |
聂小华, 吴聪聪, 林胜利, 等. 青钱柳中活性物质及其功能特性研究进展[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2022, 50(2):222-227.
|
| [12] |
田力, 徐骋炜, 尚旭岚, 等. 青钱柳药用优良单株评价与选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1):21-28.
|
| [13] |
徐展宏, 朱莹, 金慧颖, 等. 不同叶色青钱柳叶片色素、多酚含量及光合特性的差异[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2):103-110.
|
| [14] |
吴玲利, 韩航, 曾艳玲, 等. 青钱柳组织培养及快速繁殖[J]. 植物生理学报, 2019, 55(1):61-68.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
熊中人. 中国花楸属复叶组植物叶特征及其分类学意义[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2019.
|
| [19] |
郭燕, 张树航, 李颖, 等. 燕山板栗种质资源叶片表型性状多样性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8):1673-1688.
|
| [20] |
曹林青, 钟秋平, 邹玉玲, 等. 油桐种质资源叶片结构变异及与环境因子的关系[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):95-102.
|
| [21] |
郭素娟, 武燕奇. 板栗叶片解剖结构特征及其与抗旱性的关系[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(9):51-59.
|
| [22] |
孙清荣, 孙美娟, 孙洪雁, 等. 梨(Pyrus communis L.)多倍体新种质表型变异多样性研究[J]. 果树学报, 2016, 33(1):1-7.
|
| [23] |
陶抵辉. 植物多倍体的研究与应用[J]. 生物技术通报, 2010(7):22-27.
|
| [24] |
唐军荣, 李斌, 朱丽娜, 等. 滇杨多倍体苗期叶片形态及光合生理比较分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2016, 29(1):103-109.
|
| [25] |
刘金霞, 刘盼, 米娜瓦尔·亚森, 等. 南疆地区枣二倍体及其同源四倍体表型性状比较[J]. 西北农业学报, 2022, 31(5):595-602.
|
| [26] |
温国, 孙皓浦, 党江波, 等. 多倍体与二倍体枇杷叶片特征及抗旱性初步分析[J]. 果树学报, 2019, 36(8):968-979.
|
| [27] |
祁传磊, 靳春莲, 李开隆, 等. 不同倍性大青杨的光合特性及叶片解剖结构比较[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2010, 46(9):917-922.
|
| [28] |
张源源, 郭涵, 袁红章, 等. 橡胶树不同倍性的气孔性状差异研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(3):389-394.
|
| [29] |
余文迪, 刘娟旭, 余义勋, 等. 桂中报春苣苔四倍体诱导及鉴定[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2023:1-12.(2023-02-10). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230210.1133.004.html.
|
| [30] |
李娟娟, 邓伟, 许泽楠, 等. 黄连木多倍体诱导及鉴定[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(10):18-22.
|
| [31] |
张石虎, 古敏, 周玮, 等. 黄梁木多倍体离体诱导及其性状变异[J]. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(7):2372-2383.
|
| [32] |
徐鹏飞, 杨艳红, 张毓婷, 等. 毛竹四倍体诱导及初步鉴定[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(8):55-62.
|
| [33] |
郗连连, 李嘉宝, 朱凯琳, 等. 花楸属3种植物的基因组大小与叶气孔特征分析[J]. 植物科学学报, 2020, 38(1):32-38.
|
| [34] |
徐斌, 彭莉霞, 杨会肖, 等. 杜鹃红山茶叶片主要性状的遗传多样性分析[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(5):730-734.
|
| [35] |
林祺英, 李芳, 蔡汝鹏, 等. 海南荔枝资源叶片性状多样性分析[J]. 热带生物学报, 2023, 14(6):628-635.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |