 PDF(4196 KB)
PDF(4196 KB)


Carbon dynamic simulation based on Biome-BGC model in mixed coniferous and broadleaved forest of Fengyang Mountain, Zhejiang Province
HUANG Luyao, DU Shanfeng, JI Xiaofang, GUAN Xin, LIU Shenglong, YE Limin, JIANG Jiang
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 11-20.
 PDF(4196 KB)
PDF(4196 KB)
 PDF(4196 KB)
PDF(4196 KB)
Carbon dynamic simulation based on Biome-BGC model in mixed coniferous and broadleaved forest of Fengyang Mountain, Zhejiang Province
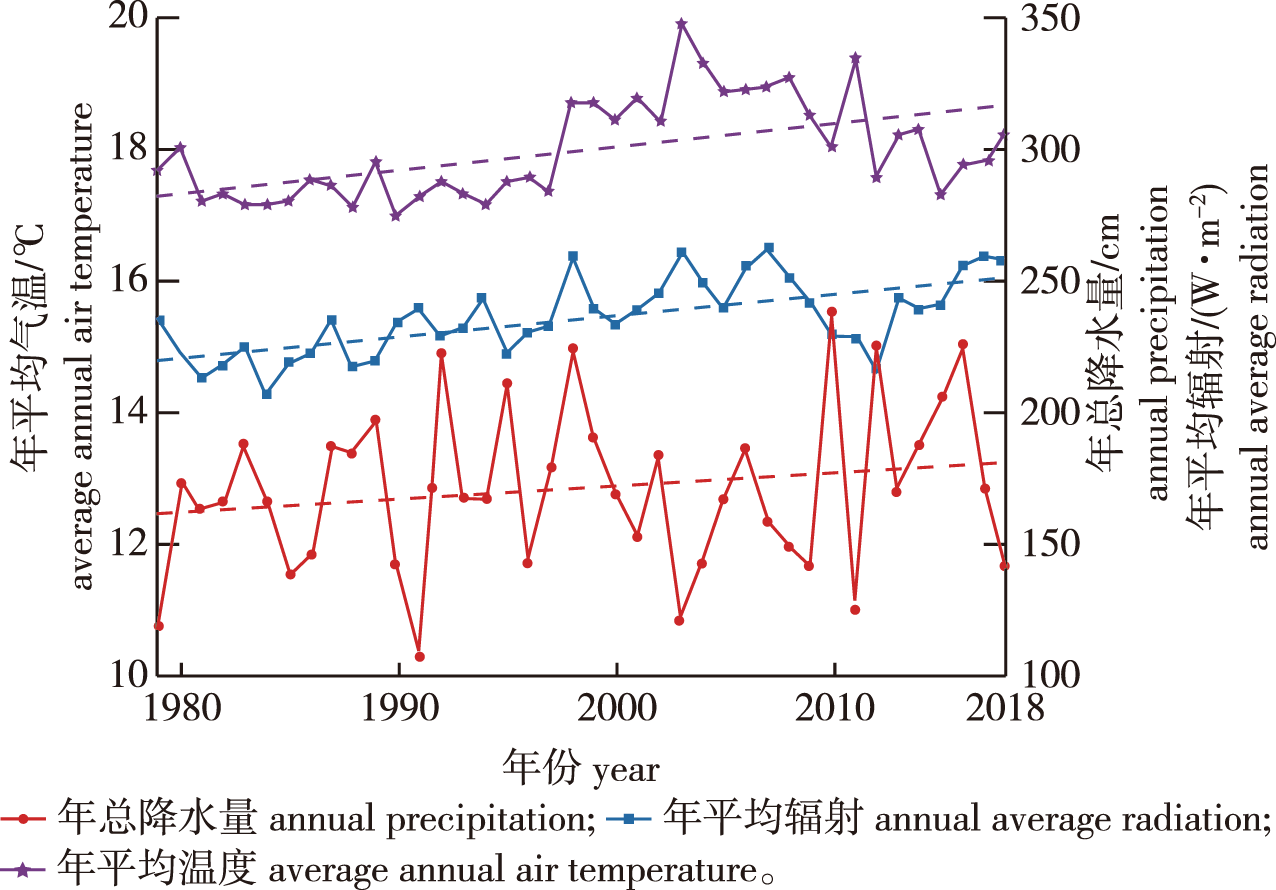
【Objective】This study aims to investigate the carbon dynamics of subtropical mixed coniferous and broadleaved forests in Fengyang Mountain, Zhejiang Province and their response to climate change. 【Method】The Biome-BGC model was used to simulate the net primary productivity (NPP), gross primary productivity (GPP), and net ecosystem productivity (NEP) in Fengyang Mountain from 1979 to 2018, to investigate the relationships between climate factors and NPP at different time scales. Pearson correlation analysis and quadratic function fitting were performed between climate factors and NPP at different temporal scales to explore the relationship and response patterns between NPP and major climate factors, and finally, different climate scenarios were applied to predict the carbon cycling trends in Fengyang Mountain in the next 100 years. 【Result】The average values of GPP, NPP and NEP of mixed coniferous and broadleaved forests in Fengyang Mountain for 40 years were 1 392.94, 451.25 and 16.21 g/(m2·a), respectively. Except for 1984, 2002, 2005, 2008 and 2010, which were carbon sinks and showed that the sensitivity of NPP to temperature change was the highest, and the increase of temperature in summer had a positive effect on the increase of NPP, while the increase of temperature in winter had a negative effect on NPP. To a certain extent, winter rainfall showed a positive effect on NPP, while summer precipitation showed a negative effect on NPP. The gross primary productivity of Fengyang Mountain forests in RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP6.0 scenarios will keep increasing in the 21st century, and by 2100, the GPP of the studied forests in Fengyang Mountain under RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP6.0 scenarios will reach 1 552.73, 1 660.30 and 1 960.41 g/(m2·a), respectively, and get increased 1.38%, 8.41% and 28.00% relative to the GPP in 2018. 【Conclusion】Overall, the forest ecosystem of Fengyang Mountain exhibited carbon sinks under normal conditions, but the cloudy and rainy summer weather in the mountainous area inhibited the increasing effect of temperature on carbon sinks to some extent. The future warming, increased rainfall and higher CO2 concentration simultaneously will favor the vegetation growth of mixed coniferous forests in Fengyang Mountain.
mixed coniferous and broadleaved forest / Biome-BGC model / carbon dynamics / climate change / Fengyang Mountain of Zhejiang Province
| [1] |
沈永平, 王国亚. IPCC第一工作组第五次评估报告对全球气候变化认知的最新科学要点[J]. 冰川冻土, 2013, 35(5):1068-1076.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
李媛. 陆地植被净初级生产力估算及影响因素研究现状[J]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 39(4):362-366.
|
| [4] |
刘国华, 傅伯杰, 方精云. 中国森林碳动态及其对全球碳平衡的贡献[J]. 生态学报, 2000, 20(5):733-740.
|
| [5] |
韩其飞, 罗格平, 李超凡, 等. 基于Biome-BGC模型的天山北坡森林生态系统碳动态模拟[J]. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31(3):375-382.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
黄国贤. 基于CBM-CFS3模型的江西省森林生态系统碳动态模拟[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2016.
|
| [8] |
温永斌, 韩海荣, 程小琴, 等. 基于Biome-BGC模型的千烟洲森林水分利用效率研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(4):69-77.
|
| [9] |
曾攀儒, 张福平, 冯起, 等. 祁连山地区不同植被生态系统固碳价值量估算及时空演变分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2019, 41(6):1348-1358.
|
| [10] |
李传华, 韩海燕, 范也平, 等. 基于Biome-BGC模型的青藏高原五道梁地区NPP变化及情景模拟[J]. 地理科学, 2019, 39(8):1330-1339.
|
| [11] |
李旭华, 于大炮, 代力民, 等. 长白山阔叶红松林生产力随林分发育的变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(3):706-716.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
范敏锐, 余新晓, 张振明, 等. 北京山区油松林净初级生产力对气候变化情景的响应[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2010, 38(11):46-48.
|
| [14] |
张文海, 吕锡芝, 余新晓, 等. 气候和CO2变化对北京山区油松林NPP的影响[J]. 广东农业科学, 2012, 39(6):4-7.
|
| [15] |
纪小芳, 龚元, 郑翔, 等. 凤阳山森林生态系统碳交换及其物候特征[J]. 地球环境学报, 2020, 11(4):376-389.
|
| [16] |
孟苗婧, 郭晓平, 张金池, 等. 海拔变化对凤阳山针阔混交林地土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(19):7057-7065.
|
| [17] |
孟苗婧, 张金池, 郭晓平, 等. 海拔变化对黄山松阔叶混交林土壤有机碳组分的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(6):106-112.
|
| [18] |
赵友朋, 孟苗婧, 张金池, 等. 不同林地类型土壤团聚体稳定性与铁铝氧化物的关系[J]. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(4):75-81,86.
|
| [19] |
赵友朋, 孟苗婧, 张金池, 等. 凤阳山主要林分类型土壤团聚体及其稳定性研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(5):84-90.
|
| [20] |
张洋. 浙江凤阳山不同林分土壤有机碳矿化研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2015.
|
| [21] |
田月亮. 凤阳山主要林分类型结构特征及其改土效应[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2012.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
朱再春, 刘永稳, 刘祯, 等. CMIP5模式对未来升温情景下全球陆地生态系统净初级生产力变化的预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(1):31-39.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
董艳辉, 李国敏, 郭永海, 等. 应用并行PEST算法优化地下水模型参数[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(1):140-144.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
《第三次气候变化国家评估报告》编写委员会. 第三次气候变化国家评估报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 213-231.
Committee for The Preparation of The Third National Assessment Report on Climate Change. Third national assessment report on climate change[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 213-231.
|
| [31] |
何学兆, 周涛, 贾根锁, 等. 光合有效辐射总量及其散射辐射比例变化对森林GPP影响的模拟[J]. 自然资源学报, 2011, 26(4):619-634.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
张越, 刘康, 张红娟, 等. 基于Biome-BGC模型的秦岭北坡太白红杉林碳源/汇动态和趋势研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2019, 27(3):235-249.
|
| [34] |
张凤英, 张增信, 田佳西, 等. 长江流域森林NPP模拟及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1):175-181.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
李亮, 何晓军, 胡理乐, 等. 1958—2008年太白山太白红杉林碳循环模拟[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(9):2845-2855.
|
| [37] |
侯英雨, 柳钦火, 延昊, 等. 我国陆地植被净初级生产力变化规律及其对气候的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(7):1546-1553.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |