 PDF(2340 KB)
PDF(2340 KB)


Interpretation of environmental factors affecting β diversity and its components in plant communities on the northern slope of Changbai Mountain
CONG Mingzhu, LIU Qijing, SUN Zhen, DONG Chunchao, QIAN Nipeng
JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 99-106.
 PDF(2340 KB)
PDF(2340 KB)
 PDF(2340 KB)
PDF(2340 KB)
Interpretation of environmental factors affecting β diversity and its components in plant communities on the northern slope of Changbai Mountain
【Objective】This study explored the patterns and environmental factors that drived β diversity and its components in plant communities on the northern slope of Changbai Mountain, to provide a theoretical basis for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem management in the area.【Method】The betapart package of R was used to decompose the components (turnover and nestedness) of β diversity. The generalized dissimilarity modelling (GDM) was used to explore the environmental factors that drived β diversity and its components.【Result】Decomposition of the β diversity components revealed that the β diversity of the plant communities was dominated by the turnover, indicating that species replacement leads to differences in species composition among communities. The results of GDM analysis showed that 13 environmental variables explained 32.63%-66.52% of the β diversity and the turnover components of the plant communities. The mean annual air temperature significantly influenced the arbor β diversity. The arbor β diversity was significantly affected by the annual precipitation and soil bulk density when they reached values higher than 710.00 mm and 1.07 g/cm3, respectively. The turnover components of arbor β diversity were primarily affected by the mean annual air temperature, soil bulk density, and slope. The turnover rate increased with an increase in the values of the predictive variables once the threshold was surpassed. The growth rate of shrub β diversity and its turnover components exhibited a downward, constant and upward trend, respectively, for shrub plants following an increase in air temperature seasonality, slope and mean annual air temperature. However, in response to the major determinants, the gradient changes in the β diversity of herbs and its turnover components increased with altitude, decreased with rising isothermality, and initially increased and then decreased following an increase in soil organic carbon.【Conclusion】Altogether, the findings revealed a turnover pattern in the species composition of plant communities in the northern slope of Changbai Mountain, indicating that biodiversity conservation efforts should focus on multiple species and at multiple regions. The β diversity patterns are primarily affected by environmental factors. The arbor β diversity and its turnover components are primarily affected by the mean annual air temperature, while those of shrub plants are mainly affected by seasonal variations in air temperature, and those of herbs are primarily limited by the altitude.
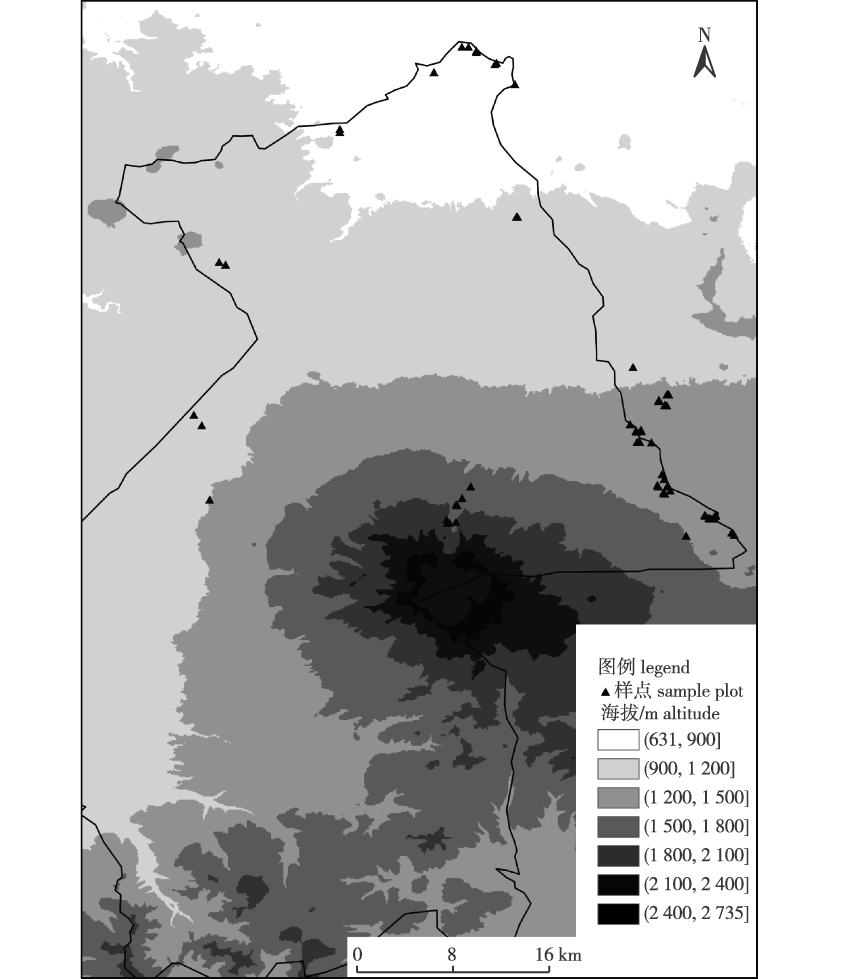
β diversity / turnover / nestedness / generalized dissimilarity modelling (GDM) / environmental heterogeneity
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
李明家, 吴凯媛, 孟凡凡, 等. 西藏横断山区溪流细菌beta多样性组分对气候和水体环境的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12):1570-1580.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
郝占庆, 代力民, 贺红士, 等. 气候变暖对长白山主要树种的潜在影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(5):653-658.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
姜小蕾, 孙振元, 郝青, 等. 崂山次生林群落β多样性格局及其组分的驱动因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(10):3211-3220.
|
| [23] |
杨美华. 长白山的气候特征及北坡垂直气候带[J]. 气象学报, 1981, 39(3):311-320.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
赵淑清, 方精云, 宗占江, 等. 长白山北坡植物群落组成、结构及物种多样性的垂直分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(1):164-173.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
韩铭, 李华, 蔡体久. 黑龙江太平沟国家级自然保护区森林群落植物多样性特征[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (5): 40-47.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
张沛健, 徐建民, 卢万鸿, 等. 基于生长过程的海南桉树纸浆林土壤理化性质和植物多样性分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(5):82-92.
|
| [31] |
汤靖文, 李晨晞, 彭政淋, 等. 氮磷钾肥对水曲柳雌雄株叶片光合生理及化学计量特征的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (2): 30-38, 46.
|
| [32] |
高璐鑫, 兰天元, 赵志霞, 等. 中国中亚热带北部灌丛群落植物空间周转及其驱动因素[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(11):1411-1421.
|
| [33] |
张剑, 王利平, 谢建平, 等. 敦煌阳关湿地土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(9):2455-2464.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
长白山国家级自然保护区管理局提供科研调查条件,研究生徐振招、郑东升、胡博,邓发昌、刘文婷、张潇、宋超杰、曾伟等参加野外调查。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |