 PDF(2694 KB)
PDF(2694 KB)


Research progress on the effects of forest fire on forest ecosystem C-N-P ecological stoichiometry characteristics
SUN Long, DOU Xu, HU Tongxin
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2) : 1-9.
 PDF(2694 KB)
PDF(2694 KB)
 PDF(2694 KB)
PDF(2694 KB)
Research progress on the effects of forest fire on forest ecosystem C-N-P ecological stoichiometry characteristics
 ,
,

Forest fires can change the ecological stoichiometry of elements in forest ecosystems, reflecting the pattern of biogeochemical cycle change of the forest ecosystem environment after the fire. Clarifying the ecological stoichiometrics characteristics of carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in forest ecosystems under forest fire disturbances is essential for understanding the response mechanisms of forest ecosystems to forest fire disturbances. By consulting a large number of relevant documents, the author summarizes and analyzes the impact pattern of forest fire disturbance on forest ecosystem C-N-P ecological stoichiometry and on plant, litter and soil C-N-P ecological stoichiometry characteristics. It is believed that the forest ecosystem C-N-P ecological stoichiometric characteristics were mainly affected by fire factors (i.e., fire intensity, fire frequency, recovery years after fire), type of vegetation and soil properties in three aspects. To address the scientific problems that need to be solved urgently in the study of forest fires on the ecological stoichiometry of forest ecosystems, prospects were made from three aspects, including exploring the influence of the mechanism of forest fire disturbance on the internal stability of plant ecological stoichiometry, comprehensively clarifying the study of multi-element ecological stoichiometry under forest fire disturbance, and establishing the ecological stoichiometric relationship of plant-litter-soil complex systems under forest fire disturbance. These are important for a deep understanding of the nutrient cycle and balance of forest ecosystems within the context of global climate change, for the rational formulation of forest fire management measures, and for further exploring the impact mechanism of plant growth, litter decomposition, and biogeochemical cycles in forest ecosystems after fire disturbance in China, to provide a reference for promoting the development of this field.
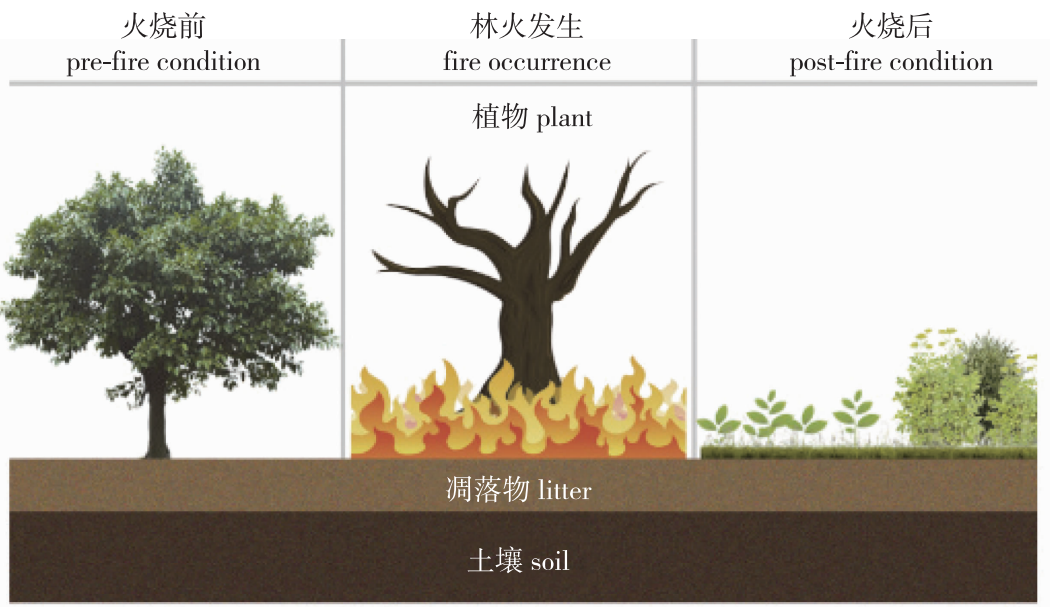
forest fire / forest ecosystem / ecological stoichiometry / litter / soil nutrient
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
赵一娉, 曹扬, 陈云明, 等. 黄土丘陵沟壑区森林生态系统生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2017,37(16):5451-5460.
|
| [3] |
张亨宇. 火干扰对大兴安岭北方森林土壤性质和碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[D]. 沈阳:沈阳师范大学, 2019.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
孙骞, 王兵, 周怀平, 等. 黄土丘陵区小流域土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的空间变异性[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020,39(3):766-774.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
遆萌萌. 火烧和氮添加对气候过渡带针阔混交林叶片功能性状的影响[D]. 开封:河南大学, 2019.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
黄铄淇, 胡慧蓉, 韩钊龙, 等. 林火对昆明人工林凋落物和表层土壤碳氮的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2014,32(1):18-22.
|
| [29] |
杨新芳, 鲍雪莲, 胡国庆, 等. 大兴安岭不同火烧年限森林凋落物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016,27(5):1359-1367.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
程瑞梅, 王娜, 肖文发, 等. 陆地生态系统生态化学计量学研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2018,54(7):130-136.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
孔健健, 杨健. 火烧对中国东北部兴安落叶松林土壤性质和营养元素有效性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013,32(11):2837-2843.
|
| [38] |
谷会岩, 金屿淞, 张芸慧, 等. 林火对大兴安岭偃松-兴安落叶松林土壤养分的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016,38(7):48-54.
|
| [39] |
孔健健, 张亨宇, 于龙, 等. 林火干扰后大兴安岭森林土壤磷的变化特征[J]. 沈阳师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019,37(2):149-154.
|
| [40] |
李炳怡, 刘冠宏, 李伟克, 等. 不同火强度对河北平泉油松林土壤有机碳及土壤养分影响[J]. 生态科学, 2018,37(4):35-44.
|
| [41] |
曾素平, 刘发林, 赵梅芳, 等. 火干扰强度对亚热带四种森林类型土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020,40(1):233-246.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
胡海清. 林火生态与管理[M].修订版. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2005.
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
孙龙, 赵俊, 胡海清. 中度火干扰对白桦落叶松混交林土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2011,47(2):103-110.
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
耿玉清, 周荣伍, 李涛, 等. 北京西山地区林火对土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2007,5(5):66-70.
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
张婷婷, 刘文耀, 黄俊彪, 等. 植物生态化学计量内稳性特征[J]. 广西植物, 2019,39(5):701-712.
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |