 PDF(1722 KB)
PDF(1722 KB)


Evaluating forest ecosystem restoration ability of natural forest in northern Greater Khingan Mountains by a structural equation model
SA Rula, WANG Zirui, HUA Yongchun, HU Richa, LIU Lei, GAO Minglong, YU Xiaoyu
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 196-204.
 PDF(1722 KB)
PDF(1722 KB)
 PDF(1722 KB)
PDF(1722 KB)
Evaluating forest ecosystem restoration ability of natural forest in northern Greater Khingan Mountains by a structural equation model
【Objective】This study aimed to investigate the dynamic changes of forest ecosystem structure, function, climate and site type factors during the restoration of natural forest ecosystems in northern Greater Khingan Mountains, screen out the key influencing factors, and use scientific methods to scientifically evaluate its forest ecosystem restoration capacity. This study provides a reference for exploring effective management measures to improve the ecological function of Greater Khingan Mountain natural forest. 【Method】Based on field survey data, discriminant validity test was used to determine the evaluation index system of forest ecosystem restoration capacity, and a structural equation model for forest ecological restoration capacity evaluation was established according to the conduction mechanism to determine the index weights. Based on K-means cluster analysis and the equidistant division method, a classification standard for the forest ecological restoration capacity in Greater Khingan Mountains was established. 【Result】The weights of four criterion factors in the evaluation index system of forest ecological restoration capacity in Greater Khingan Mountains-forest productivity, stand structure, climate factor and site type are 0.339, 0.192, 0.256 and 0.213 respectively; The comprehensive scores of the ecological restoration capacity evaluation of the two kinds of forest in the study area are in the range of 1.70 to 3.53, and the distribution of restoration capacity grades conformed to a normal distribution. The restoration capacity grades were mainly concentrated in difference, poor and good states. Overall, the ecological restoration capacity grades of the two forest types were as follows: mixed forest > pure forest. 【Conclusion】The forest ecosystem restoration capacity is mainly affected by forest productivity, whereas stand structure, climate factors and site types have relatively little impacts on ecological restoration capacity, and the ecological restoration capacity of some areas of the Greater Khingan Mountains is still poor.
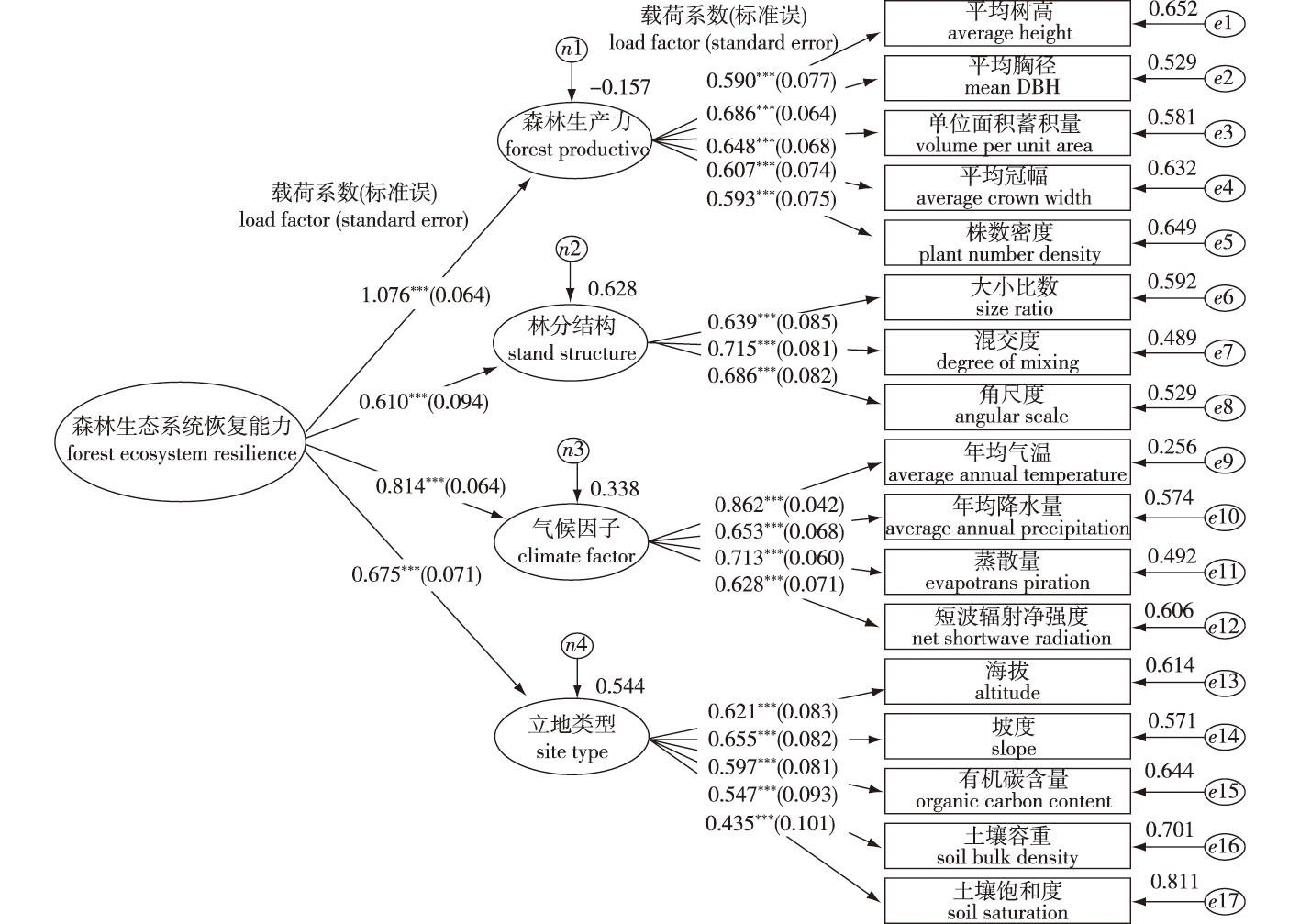
forest ecological restoration capacity / structural equation model / index weight / northern Greater Khingan Mountains
| [1] |
赵其国, 黄国勤, 王礼献. 中国南方森林生态系统的功能、问题及对策[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2015, 35(4):289-296.
|
| [2] |
徐欢, 李美丽, 梁海斌, 等. 退化森林生态系统评价指标体系研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(24) : 9034-9042.
|
| [3] |
刘国华, 傅伯杰, 陈利顶, 等. 中国生态退化的主要类型、特征及分布[J]. 生态学报, 2000, 20(1) : 13-19.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
王丽艳, 孙志华, 林小凡, 等. 江西德兴地区阔叶林生态系统恢复评价[J]. 南方林业科学, 2018, 46(1):9-12.
|
| [7] |
战金艳, 闫海明, 邓祥征, 等. 森林生态系统恢复力评价:以江西省莲花县为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2012, 27(8):1304-1315.
|
| [8] |
甘敬, 张振明, 余新晓, 等. 森林健康监测与评价研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2006, 13(3):177-180.
|
| [9] |
王长义, 王大鹏, 赵晓雯, 等. 结构方程模型中拟合指数的运用与比较[J]. 现代预防医学, 2010, 37(1):7-9.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
董灵波, 刘兆刚. 森林健康评价及其多尺度转换方法[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(3):206-216.
|
| [12] |
李冰. 大兴安岭兴安落叶松林健康评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2009.
|
| [13] |
吴嘉禹. 基于结构方程模型的私立医院消防安全绩效考核研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2021.
|
| [14] |
委霞. 基于结构方程模型的福寿林场三种典型林分健康评价[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2021.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
姜帆. 山地退化森林生态系统恢复效果评价[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2009.
|
| [17] |
曹小玉, 李际平, 闫文德. 杉木林改造前后的土壤肥力对比分析及综合评价[J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(5):1231-1237.
|
| [18] |
甘敬. 北京山区森林健康评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2008.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
李俊清. 森林生态学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
魏安然, 张雨秋, 谭凌照, 等. 抚育采伐对针阔混交林林分结构及物种多样性的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(5):148-158.
|
| [23] |
刘世荣, 温远光, 蔡道雄, 等. 气候变化对森林的影响与多尺度适应性管理研究进展[J]. 广西科学, 2014, 21(5):419-435.
|
| [24] |
王姮, 李明诗. 气候变化对森林生态系统的主要影响述评[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(6):167-173.
|
| [25] |
汤孟平, 娄明华, 陈永刚, 等. 不同混交度指数的比较分析[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(8):46-53.
|
| [26] |
陈亚南, 杨华, 马士友, 等. 长白山2种针阔混交林空间结构多样性研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(12):48-58.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
苏棣坤, 李保军, 袁俊, 等. 火力楠混交林早期生长效果分析[J]. 林业与环境科学, 2018, 34(4):54-57.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |