 PDF(2075 KB)
PDF(2075 KB)


Effects of C, N and P additions on soil respiration in woodland under Cd stress
SUN Jinwei, WANG Shengyan, FAN Diwu, ZHU Yongli
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 140-146.
 PDF(2075 KB)
PDF(2075 KB)
 PDF(2075 KB)
PDF(2075 KB)
Effects of C, N and P additions on soil respiration in woodland under Cd stress
【Objective】 Artificial standard soil was used to investigate the potential stimulatory effects of low-dose C, N, and P additions on soil respiration and Hormesis under heavy metal stress. 【Method】The four treatments were: GC (glucose), NP (nitrogen and phosphorus), GC+NP (glucose, nitrogen and phosphorus), and, no additions (CK). The soil samples were inoculated with soil microorganisms from forest land to determine the potential Hormesis effect of exogenous addition of glucose, N and P on soil respiration under Cd stress. 【Result】In the case of the NP and GC+NP treatments, the soil respiration rate was significantly higher than that of the control at Cd doses of 0.02, 0.10, 0.40, 2.50, and 13.00 mg/kg, respectively. There was a significant alternating phenomenon of multiple hormetic effects with stimulation amplitudes between 66.6% and 262.6%. When there was no Cd added to the soil, the sum of the soil respiration rates in the GC and NP treatments was greater than that in the GC+NP treatment. The interaction between C source and NP addition on soil respiration showed an antagonistic effect. When the Cd dose was 0.01 to 0.20 mg/kg, the sum of soil respiration rates in GC and NP treatments was lower than the corresponding rates in GC+NP treatments, and the effects of C source and NP additions on soil respiration showed a synergistic effect. Synergistic and antagonistic effects appeared alternately when the Cd dose was over 0.20 mg/kg. 【Conclusion】The Cd-induced soil respiration rate had a significant Hormesis effect under exogenous NP addition. With increasing Cd stress, the interaction between the C source and NP addition on soil respiration changed from antagonistic to synergistic effects.
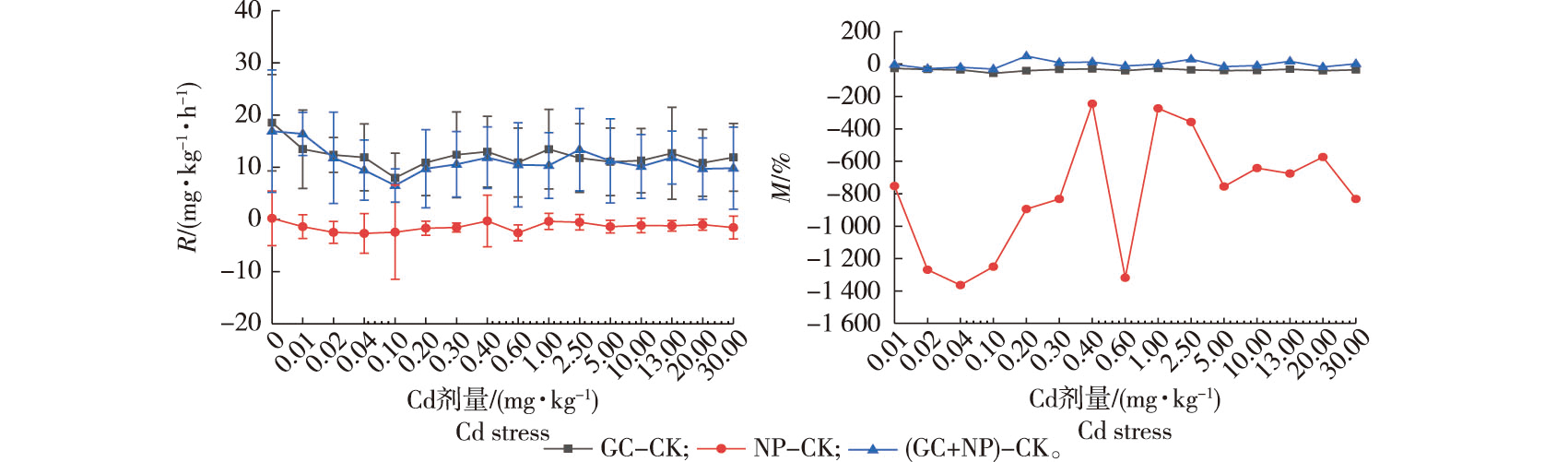
soil respiration / cadmium stress / hormesis / artificial standard soil / glucose / nitrogen and phosphorus addition
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan. Environmental quality standards for soil pollution[S].[2022-04-18]. www.env.go.jp/en/water/soil/sp.html, 2011.
|
| [20] |
王国庆, 邓绍坡, 冯艳红, 等. 国内外重金属土壤环境标准值比较:镉[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2015, 31(6):808-821.
|
| [21] |
王小庆, 马义兵, 黄占斌. 痕量金属元素土壤环境质量基准研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2013, 44(2):505-512.
|
| [22] |
USEPA United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ecological soil screening levels[R/OL]. [2022-04-18]. http://www.epa.gov/ecotox/ecossl, 2011.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
周涵君, 于晓娜, 秦燚鹤, 等. 施用生物炭对Cd污染土壤生物学特性及土壤呼吸速率的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2017, 23(6):61-68.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |