 PDF(4018 KB)
PDF(4018 KB)


Variation and correlation analysis of leaf traits of three Acer species in different growth periods in the Xiaoxing’an Mountains of northeast China
PENG Zhongtao, GUO Jiaxing, WANG Yixuan, WANG Lei, JIN Guangze, LIU Zhili
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 131-139.
 PDF(4018 KB)
PDF(4018 KB)
 PDF(4018 KB)
PDF(4018 KB)
Variation and correlation analysis of leaf traits of three Acer species in different growth periods in the Xiaoxing’an Mountains of northeast China
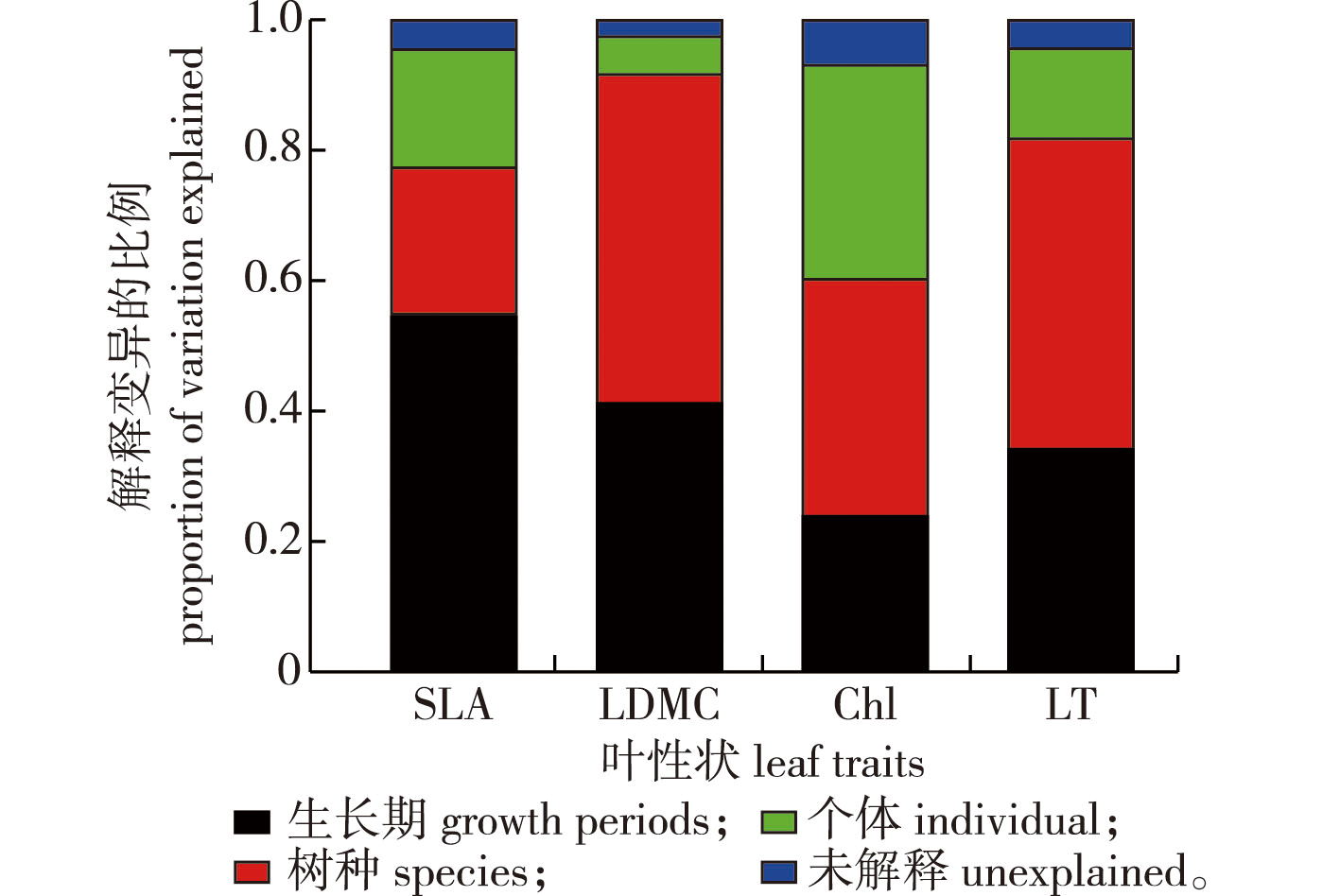
【Objective】 Leaf traits play important roles in plant resource acquisition and photosynthetic capacity. Therefore, plants can adapt to different leaf-growth periods by adjusting their leaf traits. 【Method】Acer ukurunduense, A. tegmentosum and A. pictum subsp. mono, three typical Acer species in the Xiaoxing’an Mountains of northeast China were selected as the objects of the study. During the three growth periods of leaf expansion (early June), leaf stabilization (mid-July), and leaf senescence (early September), the specific leaf area, leaf dry matter content, chlorophyll, and leaf thickness were measured. Additionally, the growth dynamics of the leaf traits and the correlations between traits were analyzed. 【Result】 Significant differences existed in leaf traits among different Acer species in different growth periods, and the leaf thickness in the leaf expansion period and leaf dry matter content in the leaf stabilization period were significantly higher than the other two periods. The correlation between leaf traits varied significantly with different growth periods. Three Acer species exhibited the “quick investment-return” strategy in the leaf expansion period and the “slow investment-return” strategy in the leaf stabilization and leaf senescence periods. Leaf traits and their correlations were significantly different at the species level. 【Conclusion】Plants adapt to different growth periods through leaf trait variations and different combinations of leaf traits, and finally form various survival strategies.
Acer species / specific leaf area / leaf dry matter content / chlorophyll / leaf thickness / survival strategy / Xiaoxing’an Mountains
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
刘晓娟, 马克平. 植物功能性状研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2015, 45(4):325-339.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
张林, 罗天祥. 植物叶寿命及其相关叶性状的生态学研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(6):844-852.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
徐丽娜, 金光泽. 小兴安岭凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地:物种组成与群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(4):470-481.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
金明月, 姜峰, 金光泽, 等. 不同年龄白桦比叶面积的生长阶段变异及冠层差异[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(9):18-26.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
盘远方, 陈兴彬, 姜勇, 等. 桂林岩溶石山灌丛植物叶功能性状和土壤因子对坡向的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(5):1581-1589.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
田俊霞, 魏丽萍, 何念鹏, 等. 温带针阔混交林叶片性状随树冠垂直高度的变化规律[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(23):8383-8391.
|
| [47] |
朱弘, 朱淑霞, 李涌福, 等. 尾叶樱桃天然种群叶表型性状变异研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(12):1168-1178.
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |