 PDF(2807 KB)
PDF(2807 KB)


Analysis of SSR locus based on the whole genome sequences of Cyclocarya paliurus and the development of polymorphic primers
LIU Li, QU Yinquan, YU Yanhao, WANG Qian, FU Xiangxiang
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 67-75.
 PDF(2807 KB)
PDF(2807 KB)
 PDF(2807 KB)
PDF(2807 KB)
Analysis of SSR locus based on the whole genome sequences of Cyclocarya paliurus and the development of polymorphic primers
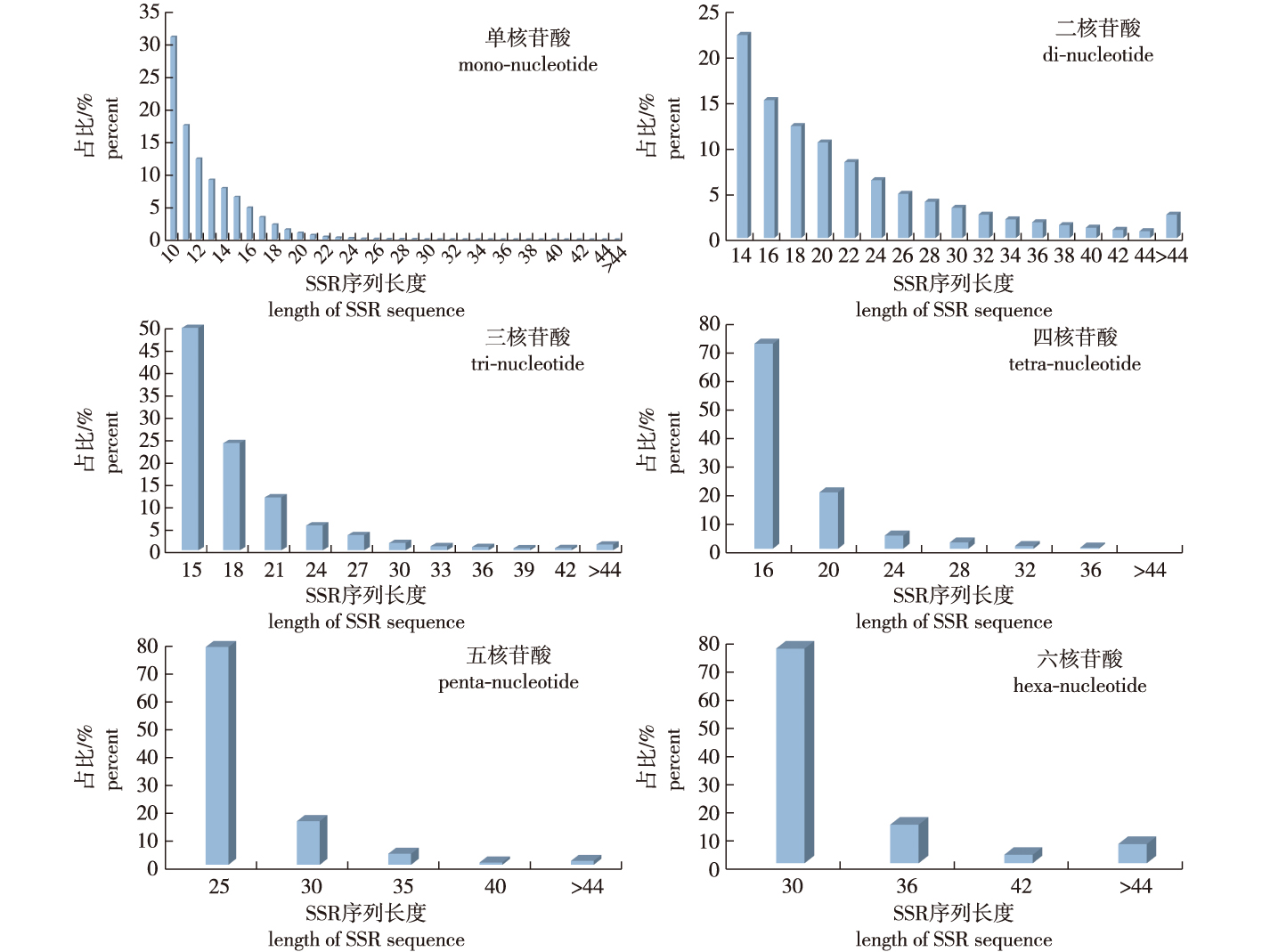
【Objective】Genomic simple repeat sequence (SSR) loci were analyzed by screening the whole genome of Cyclocarya paliurus. DNA molecular ID cards of 19 excellent medicinal clones of C. paliurus were constructed based on the newly-developed SSR primers. These genomic SSR markers could support further research, such as the evaluation of the germplasm resource, analysis of genetic diversity, and identification of cultivars/clones.【Method】The SSR loci were screened along with the whole genome of C. paliurus and were enriched and analyzed using MISA software. Subsequently, SSR primers were designed using Primer 3.0. Furthermore, a system for identifying clones of C. paliurus was constructed based on selected SSR markers with high reproducibility and stability.【Result】(1) We detected 89 741 SSR loci from the whole genome, with an occurrence frequency of 62.07%. (2) Among all SSR loci, the proportion of SSRs with a mononucleotide motif was the highest (62.67%) and a hexa-nucleotide repeat was the lowest (0.15%). Most of the repeated motifs in the SSR loci were dominated by (A/T)n. (3) The repeat number of mono-nucleotide and di-nucleotide motifs ranged from 6 to 16. With the increase in the repeat number, the frequencies of various SSR repetition types displayed a downward trend. (4) The length of the SSR sequences varied from 10 to 476 bp, and this length variation existed in different repetitive motifs. Additionally, the frequency of SSR occurrence tended to decrease as the repeat number increased. (5) We successfully designed 78 285 pairs of SSR primers using Primer 3.0. A total of 377 primer pairs were randomly synthesized for amplifying polymorphic SSR fragments, among which 75 pairs primers were successful. Moreover, quick response code DNA molecular ID cards for 19 medical-use clones of C. paliurus were constructed by five pairs of polymorphic SSR primers with a mono-nucleotide motif.【Conclusion】The frequency of genomic SSR loci was high, and there was variability in the type of SSR loci. Simple repeat sequences developed from the whole genome of C. paliurus could be effective candidate molecular markers with further applications in germplasm resource evaluation and fingerprint construction for multi-use clones of C. paliurus.
Cyclocarya paliurus / simple sequence repeat (SSR) / whole genome / DNA molecular ID card
| [1] |
方升佐, 洑香香. 青钱柳资源培育与开发利用的研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(1):95-100.
|
| [2] |
孙戴妍, 尚旭岚, 洑香香, 等. 青钱柳胸径生长和木材密度的地理变异规律[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(4):1-5.
|
| [3] |
侯小利, 刘晓霞, 王硕, 等. 青钱柳叶总黄酮对自发性高血压大鼠的影响[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2014, 30(2):62-69.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
郑观涛, 殷志琦. 药用植物青钱柳的开发研究进展[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019, 19(43):123-124.
|
| [7] |
林源, 陈培, 周明明, 等. 天然居群青钱柳叶主要生物活性物质及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(2):10-16.
|
| [8] |
周永晟, 徐子恒, 袁发银, 等. 亚热带3个地点青钱柳群落特征比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1):29-35.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
田力, 徐骋炜, 尚旭岚, 等. 青钱柳药用优良单株评价与选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1):21-28.
|
| [13] |
王久利, 朱明星, 徐明行, 等. 基于RAD-seq技术的异型花SSR信息分析[J]. 植物研究, 2017, 37(3):447-452,460.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
王希, 陈丽, 赵春雷. 利用MISA工具对不同类型序列进行SSR标记位点挖掘的探讨[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(10):150-156.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
乔舒婷, 董文其, 胡齐赞, 等. 基于丝瓜全基因组序列SSR分子标记开发[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(6):1937-1947.
|
| [23] |
郭艳春, 张力岚, 陈思远, 等. 黄麻应用核心种质的DNA分子身份证构建[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(1):80-93.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
宋立肖, 李国旗, 靳长青, 等. 大麻状罗布麻的全基因组分析和SSR标记开发[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(5):1309-1316.
|
| [26] |
崔哲, 左力辉, 韩坤瑾, 等. 毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa)全基因组SSR位点分布规律[J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(11):3683-3692.
|
| [27] |
蒋向辉, 苑静, 王翔. 青钱柳叶片转录组数据组装及基因功能注释[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 52(6):822-831.
|
| [28] |
陈秀娟, 柏明娥, 王丽玲, 等. 青钱柳种质资源亲缘关系的ISSR分析评价[J]. 中国林副特产, 2016(4):6-10.
|
| [29] |
周一旸, 洑香香, 尚旭岚, 等. 青钱柳种质资源多样性SRAP初步分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2011, 30(1):40-46.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
林恩文, 林榕榕, 陈钦常, 等. 龙眼全基因组和转录本序列SSR位点的鉴定[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 51(4):493-501.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
刘松卫, 卢迎春, 宋婉玲, 等. 基于灯盏花全基因组SSR位点分析及多态性引物开发[J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(12):4003-4009.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
王玉龙, 黄冰艳, 王思雨, 等. 四倍体野生种花生(A.monticola)全基因组SSR的开发与特征分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(15):2567-2585.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
宋莎, 冯建文, 吴亚维, 等. 基于RAD-seq技术的花红SSR信息分析[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2019, 47(11):103-106.
|
| [41] |
周晓君, 王海亮, 李方玲, 等. 基于RAD-seq技术开发灵宝杜鹃多态性SSR标记[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2019, 27(1):55-62.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |