 PDF(2345 KB)
PDF(2345 KB)


Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of nutrient components in bamboo shoots of different clones of Chimonobambusa utilis
BIAN Lili, LIANG Dahong, FAN Meiling, WU Hongyu, ZHOU Binao, YAO Wenjing, WANG Fusheng, DING Yulong, LIN Shuyan
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 159-167.
 PDF(2345 KB)
PDF(2345 KB)
 PDF(2345 KB)
PDF(2345 KB)
Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of nutrient components in bamboo shoots of different clones of Chimonobambusa utilis
【Objective】Differences in nutrient composition and mineral and amino acid contents between the original species (FY) and six clones (F1-F6) of bamboo shoots of Chimonobambusa utilis were compared to provide an important reference for further breeding and planting of C. utilis.【Method】The nutritional composition of bamboo shoots of C. utilis were analyzed by liquid chromatography, and their quality were evaluated by principal component analysis and cluster analysis.【Result】The water content of the seven kinds of bamboo shoots were greater than 90%. The crude protein content ranged from 1.86% to 5.96%, with clone F4 having the highest content. The fat content ranged from 0.38% to 0.68%, with clone F5 having the lowest content. The dietary fiber content ranged from 22.12% to 29.52%, and clone F6 had the highest content. Vc content ranged from 0.170 5 mg/g to 0.396 1 mg/g, with clone F1 having the highest content. The highest content of total sugar was found in FY, whereas the highest contents of fructose and glucose were in clone F3 and F6, respectively. The highest flavonoid content was found in FY (1.39 mg/g). The total acid content was 13.68-21.04 mg/g, and tannin content was 4.55-9.71 mg/g. In mineral elements, clone F4 had a high content of each element, whereas F2 had the opposite. For selenium content, FY,clone F4 and F6 ranked as the top three among the seven kinds of bamboo shoots. Seventeen amino acids were found in all seven kinds of bamboo shoots. The highest total content of amino acids was in clone F1 (14.93 mg/g), and the lowest content was in clone F3 (8.72 mg/g). The highest essential amino acid content was found in clone F2 (34.25%) and the lowest was in clone F1 (30.38%). The total amount of flavor amino acids was highest in clone F1 (14.64 mg/g) and lowest in F3 (8.08 mg/g). Five key indicators (total acid, calcium, dietary fiber, flavonoids, Vc) were extracted by principal component analysis, with a cumulative variance contribution rate of 96.797%. The overall quality ranking was clone F1, FY, clone F5, F4, F6, F2 and F3. Cluster analysis showed that the seven kinds of C. utilis bamboo shoots were clustered into two groups.【Conclusion】Compared with other bamboo species, the quality of bamboo shoots of the original species and clones of C. utilis is excellent. clone F1, FY and clone F5 showed the best performance in the comprehensive nutritional indexes of nutrient composition, followed by clone F4, F6, F2 and F3.
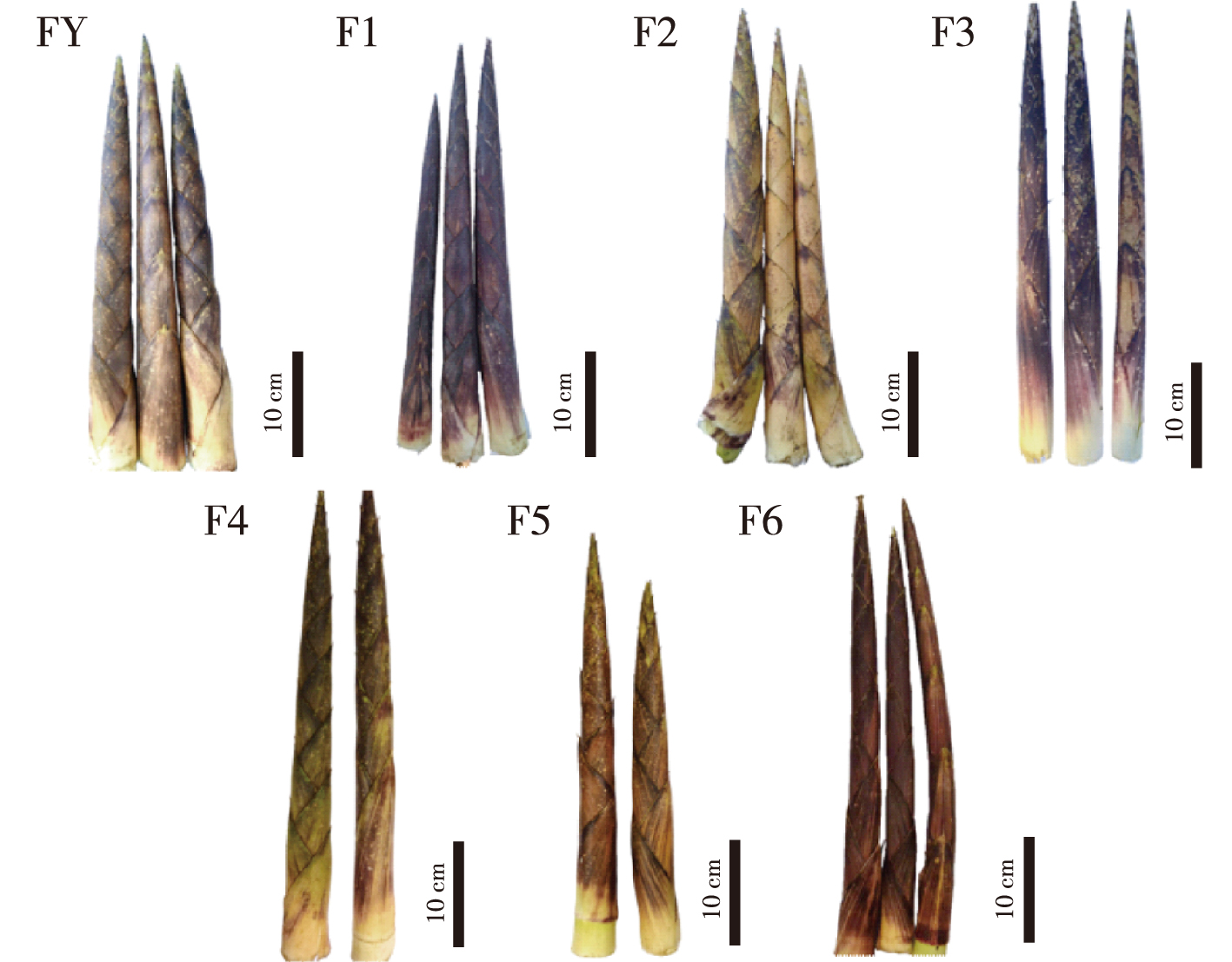
Chimonobambusa utilis / bamboo shoots / nutrient content / principal component analysis / cluster analysis
| [1] |
陈莉华, 高文昱, 王晓静, 等. 竹笋总多糖的提取及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2014, 34(5):157-161.
|
| [2] |
胡春水, 佘祥威, 骆琴娅, 等. 竹的药膳史及竹食品开发[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 1999, 18(1):27-31.
|
| [3] |
史军义, 周德群, 姚俊, 等. 中国药用竹类多样性及其价值[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2021, 19(3):72-78.
|
| [4] |
全国饮料工业标准化技术委员会. 饲料中单宁的测定分光光度法:GB/T 27985-2011[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.
|
| [5] |
湖南省食品标准化技术委员会. 植物源性食品中总黄酮的测定:DB 43/T 476—2009[S]. 长沙: 湖南省质量技术监督局. 2009.
DB 43/T 476—2009. Determination of flavone in vegetal food[S]. Hunan Provincial Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. 2009.
|
| [6] |
王学奎. 植物生理生化试验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006,190-192.
|
| [7] |
中华人民共和国卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准食品中脂肪的测定:GB 5009.6—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [8] |
中国卫生和计划委员会. 食品安全国家标准食品中膳食纤维的测定:GB 5009.88—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.
|
| [9] |
中华人民共和国农业部. 食用菌中总糖含量的测定:GB/T 15672—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.
|
| [10] |
国家技术监督局. 水果、蔬菜制品可滴定酸度的测定:GB 12293-90[S]. 北京: 国家技术监督局, 1990.
|
| [11] |
中华人民共和国卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准食品中灰分的测定:GB 5009.4—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Ash in Food[S]. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. 2017.
|
| [12] |
中华人民共和国农业部种植业管理司. 植物中氮、磷、钾的测定:NY/T 2017—2011[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国农业部. 2011.
|
| [13] |
中华人民共和国卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准食品中多元素的测定:GB 5009.268—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [14] |
王文平. 植物样品中游离氨基酸总量测定方法的改进[J]. 北京农学院学报, 1998, 3(13):9-13.
|
| [15] |
皮培尧, 顾李俭, 陈昂, 等. 13种中小径散生笋用竹出笋规律及营养分析[J]. 福建林业科技, 2018, 45(1):58-63.
|
| [16] |
李睿, 吴良如, 周昌平. 方竹笋矿质元素营养成分的研究[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 2007, 26(4):37-39.
|
| [17] |
任春春, 贾玉龙, 娄义龙, 等. 贵州金佛山方竹笋营养及功能成分剖析[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(10):214-221.
|
| [18] |
苟光前, 丁雨龙, 杨柳, 等. 寒竹属3个种竹笋营养成分的分析[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2010(16):79-81.
|
| [19] |
荆瑞勇, 卫佳琪, 王丽艳, 等. 基于主成分分析的不同水稻品种品质综合评价[J]. 食品科学, 2020, 41(24):179-184.
|
| [20] |
蔡如胜, 苏昌群, 徐才荣. 安徽霍山毛竹笋品质分析与评价[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2018, 16(1):42-44.
|
| [21] |
朱勇, 罗朝光. 绿竹笋营养成分的测定与分析[J]. 经济林研究, 2012, 30(3):103-105.
|
| [22] |
陈松河, 马丽娟, 丁振华, 等. 5种牡竹属笋用竹竹笋营养成分之比较[J]. 竹子学报, 2018, 37(4):4-8,19.
|
| [23] |
仲召鹏, 胡小松, 郑浩, 等. 膳食脂肪、肠道微生物与宿主健康的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(11):3836-3852.
|
| [24] |
甘小洪, 唐翠彬, 温中斌, 等. 寿竹笋的营养成分研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2013, 25(4):494-499.
|
| [25] |
王曙光, 普晓兰, 丁雨龙, 等. 云南箭竹不同地理种源竹笋营养成分之比较[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 2009, 28(1):35-38.
|
| [26] |
杨丽婷, 陈双林, 郭子武, 等. 增施氯肥对雷竹笋感观、营养和食味品质的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2020, 33(4):102-107.
|
| [27] |
王彩虹. 竹笋膳食纤维的提取、理化性质及降血脂效果研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2018.
|
| [28] |
王海霞, 曾庆南, 程平, 等. 7个雷竹类型(种源)竹笋营养及矿质元素含量分析[J]. 南方林业科学, 2019, 47(5):36-39.
|
| [29] |
张晗, 李全, 郭子武, 等. 施氮对毛竹笋营养成分的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(1):112-119.
|
| [30] |
于增金, 殷彪, 赵婷, 等. 不同地类对麻竹竹笋品质的影响[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2020, 47(1):76-81.
|
| [31] |
张佳佳, 白瑞华, 丁兴萃. 两种主要食用竹笋的营养及安全品质比较[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2021, 42(8):18-23.
|
| [32] |
董春凤, 赵一鹤. 储藏时间和温度对甜龙竹笋采后品质的影响[J]. 竹子学报, 2021, 40(4):80-86.
|
| [33] |
郑郁善, 高培军, 吴擢溪, 等. 绿竹笋营养成分及笋期叶养分的施肥效应[J]. 林业科学, 2004, 40(6):79-84.
|
| [34] |
朱玉燕, 邬波龙, 赵宇瑛, 等. 绿竹笋苦味物质成分分析[J]. 食品科技, 2015, 40(8):77-80.
|
| [35] |
邱永华, 金爱武, 张四海, 等. 不同施肥方式对竹笋品质的影响[J]. 竹子学报, 2017, 36(1):41-48.
|
| [36] |
李露双. 避光对麻竹笋苦涩味物质含量及其关键基因表达的影响[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2018.
|
| [37] |
郭子武, 杨丽婷, 林华, 等. 沙县苦竹笋外观、营养和食味品质变异的海拔效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(1):83-88.
|
| [38] |
孙小青, 王平, 孙吉康, 等. 雷竹笋中总黄酮和总甾醇的测定及比较[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 2014, 33(1):36-41.
|
| [39] |
裴佳龙, 李鹏程, 王茜, 等. 云南不同地理种源勃氏甜龙竹竹笋营养成分比较[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2018, 33(1):156-161.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
娄义龙. 金佛山方竹垂直分布及低海拔异地引种后笋产量和品质[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2021, 19(1):24-33.
|
| [42] |
王进, 戴晓勇, 殷建强, 等. 金佛山方竹原产地与异地种植地竹笋营养成分研究[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2015, 43(3):19-21.
|
| [43] |
林开文, 苏光荣, 郭永杰, 等. 锡金龙竹竹笋的营养成分分析与评价[J]. 西部林业科学, 2009, 38(1):48-54.
|
| [44] |
袁金玲, 熊登高, 胡炳堂, 等. 珍稀保护竹种筇竹笋营养成分的研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2008, 21(6):773-777.
|
| [45] |
贾维嘉, 王澍. 筇竹种子发芽条件及筇竹笋矿质元素分析[J]. 种子, 2021, 40(1):79-83.
|
| [46] |
李伟成, 王树东, 钟哲科, 等. 覆膜对酒竹笋营养元素与成分的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2009, 22(5):732-735.
|
| [47] |
刘小阳, 苏博, 栾锐锐. 宿州本地芹菜、菠菜和萝卜中锌和硒含量测定[J]. 宿州学院学报, 2019, 34(12):73-76.
|
| [48] |
张邦喜, 张勇, 付文军, 等. 贵阳市两个乡叶菜类蔬菜中硒含量的特征分析[J]. 现代食品科技, 2011, 27(7):867-869.
|
| [49] |
徐森, 杨丽婷, 陈双林, 等. 竹笋适口性形成及其主要影响因素研究综述[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(2):403-411.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |