 PDF(3859 KB)
PDF(3859 KB)


Influences of mountains and water on the distribution of traditional villages in Jinting Town, Taihu Lake scenic area
LIU Lan, QIU Bing, CAI Runhui, XIONG Xing, TANG Peng
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 165-171.
 PDF(3859 KB)
PDF(3859 KB)
 PDF(3859 KB)
PDF(3859 KB)
Influences of mountains and water on the distribution of traditional villages in Jinting Town, Taihu Lake scenic area
【Objective】 This study explored the rules governing the spatial relationships among mountains, water and the locations of traditional villages to shed light on their reasonable protection and construction. 【Method】 Jinting Town, a scenic location near Taihu Lake with well-protected traditional villages and towns, was selected as the research subject. Based on extracted digital topography, satellite maps and the general planning CAD base map data for Jinting Town, we analyzed the spatial relationships among the mountains, water and villages using ArcGIS (ver. 10.0). We also analyzed the correlations between the distributions of mountains and water with the distribution of villages. We used spatial logistic regression modeling to analyze the factors affecting the distribution of traditional villages. 【Result】 The spatial distribution of traditional villages in Jinting Town exhibited a cluster mode, with circular spatial density characteristics. The impacts of mountain elevation and distance from a river were negatively correlated with the spatial distribution of traditional villages. Owing to the terrain, which is surrounded by lakes on all sides, the circular distribution of traditional villages in Jinting Town has a special research value. The elevation of the mountains affected the direction of the water system and roads in Jinting Town and was the main driving force for constructing villages in the region. The proximity to the water also affected the distribution of villages. 【Conclusion】 Using ArcGIS and logistic regression modeling, the spatial relationships among villages, mountains, and water can be analyzed and widely used in the pre-planning stages of protecting and constructing traditional villages and towns.
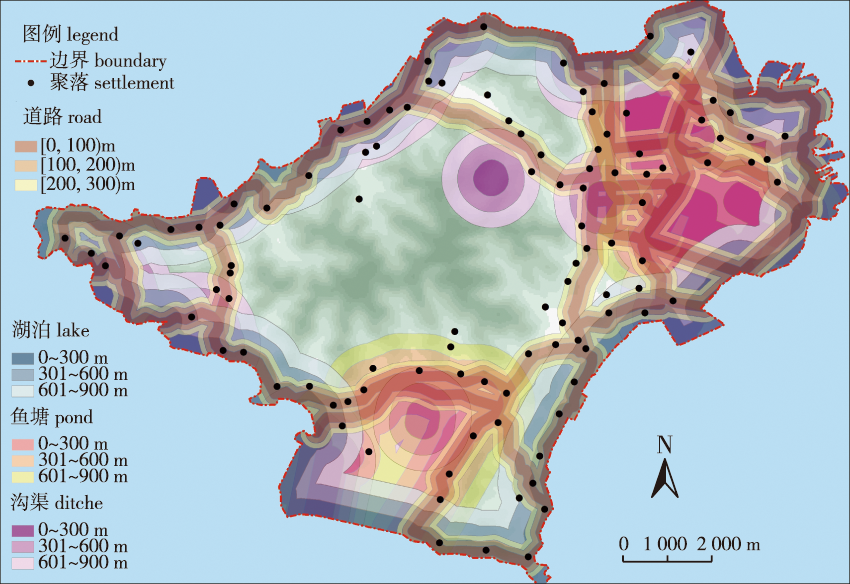
mountain and water distributions / traditional village / settlements distribution / spatial relationship / Taihu Lake scenic area
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
冯文兰, 周万村, 李爱农, 等. 基于G1S的岷江上游乡村聚落空间聚集特征分析:以茂县为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2008, 17(1):57-61.
|
| [8] |
吴江国, 张小林, 冀亚哲. 不同尺度乡村聚落景观的空间集聚性分形特征及影响因素分析:以江苏省镇江市为例[J]. 人文地理, 2014, 29(1):99-107.
|
| [9] |
杨忍. 基于自然主控因子和道路可达性的广东省乡村聚落空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(10):1859-1871.
|
| [10] |
胡航箫, 戴文远, 徐乙文, 等. 福州山区乡村聚落空间格局及其与水土资源的耦合态势[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(2):164-171.
|
| [11] |
代婷婷, 许铭, 徐雁南. 乡村聚落时空分布特征及驱动因素分析:以安徽黟县为例[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(5): 155-162.
|
| [12] |
魏佳轩, 程武学, 王永祥, 等. 巴中市乡村聚落空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(4):285-291.
|
| [13] |
李琛, 吴映梅, 高彬嫔, 等. 高原湖泊乡村聚落空间分异及驱动力探测:以环洱海地区为例[J]. 经济地理, 2022, 42(4):220-229.
|
| [14] |
许建和, 柳肃, 熊鹰, 等. 南方山地乡村聚落空间分布及其格局优化调整:以临武县西山瑶族乡为例[J]. 经济地理, 2017, 37(10):221-227.
|
| [15] |
胡震, 赵翠薇, 李朝仙, 等. 喀斯特高原峡谷区少数民族村寨空间分布格局及影响因素研究:以贵州省威宁县为例[J]. 山地学报, 2019, 37(4):575-588.
|
| [16] |
马晓蓉, 查小春. 陕南秦巴山区乡村聚落空间分布特征及影响因素:以陕西省汉中市为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(1):307-314.
|
| [17] |
海贝贝, 李小建, 许家伟. 巩义市农村居民点空间格局演变及其影响因素[J]. 地理研究, 2013, 32(12):2257-2269.
|
| [18] |
宋晓英, 李仁杰, 傅学庆, 等. 基于GIS的蔚县乡村聚落空间格局演化与驱动机制分析[J]. 人文地理, 2015, 30(3):79-84.
|
| [19] |
马晓蓉, 查小春. 秦巴山区乡村聚落空间格局演变及影响因子:以陕西宁强县为例[J]. 山地学报, 2020, 38(5):726-739.
|
| [20] |
邵楠. 南阳市乡村聚落空间分布特征及驱动力分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2020, 41(2):220-225.
|
| [21] |
李全林, 马晓冬, 沈一. 苏北地区乡村聚落的空间格局[J]. 地理研究, 2012, 31(1):144-154.
|
| [22] |
毛琦红. 美丽乡村背景下浙江省乡村聚落空间特征及格局优化研究:以浙江省为例[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2021, 42(2):150-157.
|
| [23] |
张荣天, 张小林, 李传武. 镇江市丘陵区乡村聚落空间格局特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2013, 22(3):272-278.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |