 PDF(2089 KB)
PDF(2089 KB)


The litter decomposition of fallen leaves and branches from sub-alpine Quercus aquifolioides of central Yunnan Plateau under simulated nitrogen deposition
XING Jinmei, WANG Keqin, SONG Yali, FU Hongwei
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 191-199.
 PDF(2089 KB)
PDF(2089 KB)
 PDF(2089 KB)
PDF(2089 KB)
The litter decomposition of fallen leaves and branches from sub-alpine Quercus aquifolioides of central Yunnan Plateau under simulated nitrogen deposition
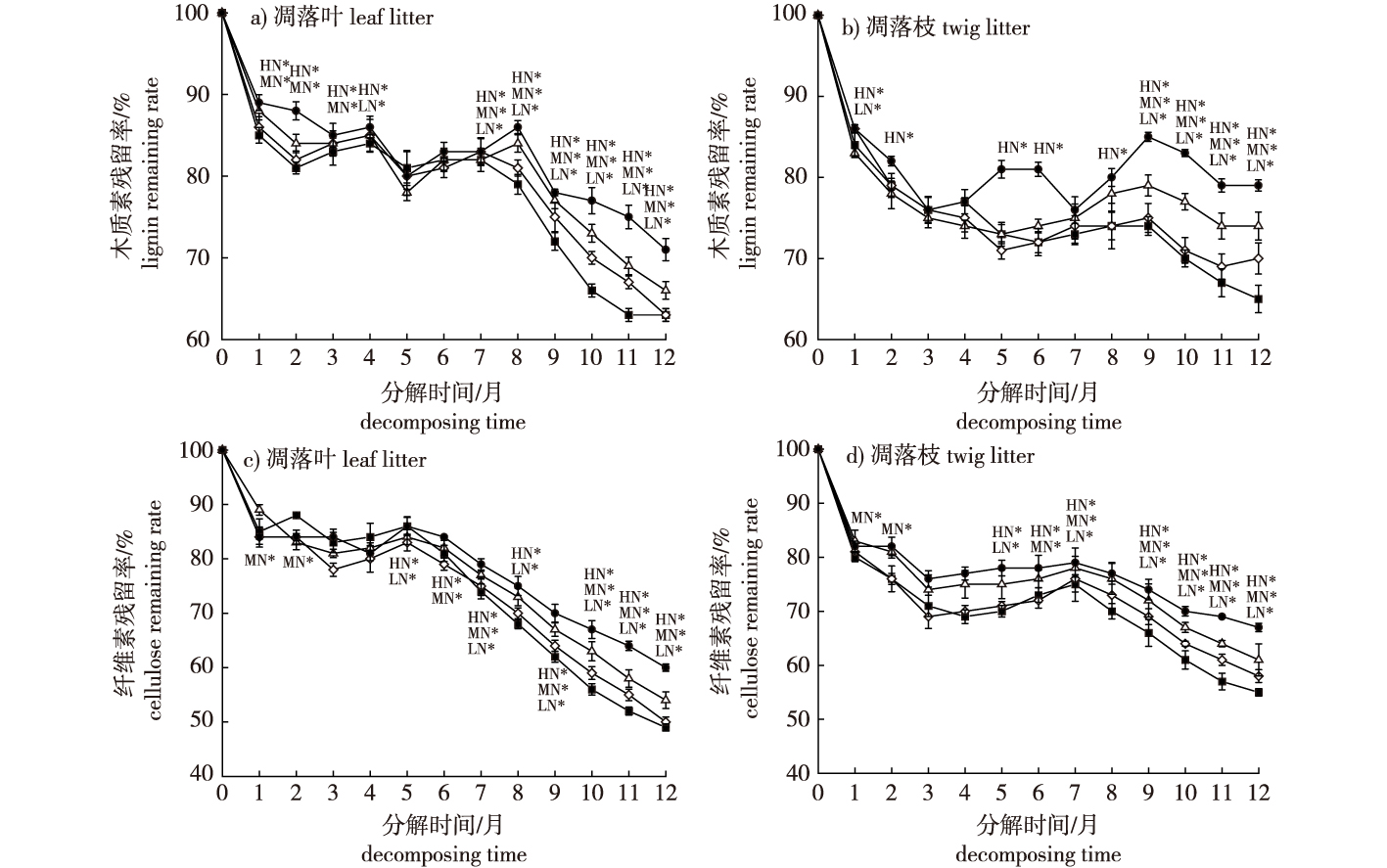
【Objective】Increased nitrogen (N) deposition affects carbon (C) and N availability by affecting the litter decomposition process, after which it affects the C-nutrient balance of the biogeochemical cycle. In this study, the nylon mesh bag method was used to study the decomposition rate and nutrient content changes of Quercus aquifolioides litter under simulated N deposition, providing a reference for an effective Q. aquifolioides forest ecosystem management.【Method】The in situ litter decomposition test was carried out in the Q. aquifolioides forest of Mopanshan in Xinping County, central Yunnan Province. Four N levels were applied using the nylon mesh bag method, with urea (CH4N2O) as the N source for in situ decomposition of litter and N deposition treatment. The four N deposition levels were: control [CK, 0 g/(m2·a)], low N [LN, 10 g/(m2·a)], medium N [MN, 20 g/(m2·a)] and high N [HN, 25 g/(m2·a)]. Leaf litter and twig mass remaining, lignin, cellulose, and C, N, P and K contents were then measured.【Result】① After one year of decomposition, the N deposition treatment significantly increased the mass remaining rate (P<0.05) of leaf litter (0.84%-3.87%) and twig (1.67%-3.30%). The litter decomposition was inhibited, and the inhibition intensity was proportional to N content application. ② Variation coefficients of leaf and twig litter decomposition were 0.271-0.368 and 0.167-0.218 kg/(kg·a), respectively. The lhe C/N (69.02) and lignin/N (54.65) of twig litter were significantly higher compared with leaf litter (52.09 and 44.42, respectively). Leaf decomposition rate was faster compared with that of twig. ③ The chemical composition of the litter affected its mass remaining rate, which was negatively correlated with N and P contents of leaf and twig litters, and positively correlated with C, cellulose, C/N, C/P, lignin/N and cellulose/N.【Conclusion】The N deposition inhibits litter decomposition, and this effect is significantly enhanced by increased nutrient content. Initial nutrient content effects nutrient retention and litter release processes, among which N level, C/N and lignin/N are important influencing factors.
leaf litter / twig litter / decomposition rate / lignin / cellulose / central Yunnan Plateau / Quercus aquifolioides / N deposition
| [1] |
岳可欣, 龚吉蕊, 于上媛, 等. 氮添加下典型草原凋落物质量和土壤酶活性对凋落物分解速率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6):71-82.
|
| [2] |
于美佳, 叶彦辉, 韩艳英, 等. 氮沉降对森林生态系统影响的研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(3):19-24,27.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
汪星星, 廖文海, 许祖元, 等. 森林凋落物分解影响因素的研究进展[J]. 北方园艺, 2022(4):126-132.
|
| [6] |
段娜, 李清河, 多普增, 等. 植物响应大气氮沉降研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2019, 32(4):6-11.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
莫江明, 薛璟花, 方运霆. 鼎湖山主要森林植物凋落物分解及其对N沉降的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(7):1413-1420.
|
| [14] |
胡宗达, 刘世荣, 史作民, 等. 川滇高山栎林土壤氮素和微生物量碳氮随海拔变化的特征[J]. 林业科学研究, 2012, 25(3):261-268.
|
| [15] |
曹丽花, 尹为玲, 刘合满, 等. 西藏东南部色季拉山主要类型森林叶片和枯落物养分含量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(11):4029-4038.
|
| [16] |
贾钧彦. 西藏高原大气氮湿沉降研究[D]. 拉萨: 西藏大学, 2008.
|
| [17] |
杨开军, 杨万勤, 庄丽燕, 等. 四川盆地西缘都江堰大气氮素湿沉降特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(1):107-111.
|
| [18] |
李仰征, 雷兴庆, 薛晓辉, 等. 纱帽山不同海拔大气氮湿沉降通量差异及递变规律的数学模拟[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(9):3180-3189.
|
| [19] |
余功友, 杨常亮, 刘楷, 等. 云南阳宗海大气氮、磷沉降特征[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(5):1134-1142.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 3版[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [22] |
张毓涛, 李吉玫, 李翔, 等. 模拟氮沉降对天山云杉凋落叶分解及其养分释放的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(5):966-973.
|
| [23] |
涂利华, 胡红玲, 胡庭兴, 等. 华西雨屏区亮叶桦凋落叶分解对模拟氮沉降的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(2):99-108.
|
| [24] |
李仁洪. 华西雨屏区慈竹林凋落物分解、养分释放及其对模拟氮沉降的响应[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2009.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
周世兴, 黄从德, 向元彬, 等. 模拟氮沉降对华西雨屏区天然常绿阔叶林凋落物木质素和纤维素降解的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(5):1368-1374.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
涂利华, 戴洪忠, 胡庭兴, 等. 模拟氮沉降对华西雨屏区撑绿杂交竹凋落物分解的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(5):1277-1284.
|
| [29] |
马慧君, 张雅坤, 许文欢, 等. 模拟氮沉降对杨树人工林土壤微生物群落碳源利用类型的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(5):1-6.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
铁烈华, 张仕斌, 熊梓岑, 等. 华西雨屏区常绿阔叶林凋落叶分解过程中木质素降解对模拟氮、硫沉降的响应[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(2):25-31.
|
| [33] |
铁烈华, 符饶, 张仕斌, 等. 华西雨屏区常绿阔叶林凋落叶分解过程中纤维素降解对模拟氮、硫沉降的响应[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2019, 25(1):16-22.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
林成芳, 彭建勤, 洪慧滨, 等. 氮、磷养分有效性对森林凋落物分解的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(1):54-62.
|
| [36] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |