 PDF(3241 KB)
PDF(3241 KB)


Estimation of habitat suitability and climatic distribution change of Pegaeophyton scapiflorum based on the MaxEnt model
LI Ruilan, FAN Jinya, ZHAO Qian, LI Tingju, WANG Chenghui, DING Rong, GU Rui, ZHONG Shihong
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 173-180.
 PDF(3241 KB)
PDF(3241 KB)
 PDF(3241 KB)
PDF(3241 KB)
Estimation of habitat suitability and climatic distribution change of Pegaeophyton scapiflorum based on the MaxEnt model
【Objective】 Pegaeophyton scapiflorum can be found mainly in the high altitudes of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in China, and the traditional surveys are difficult to implement. This study explored the dominant climatic factors that limit the distribution of P. scapiflorum in China and simulated its suitable distribution areas. The goal was to provide a theoretical basis for the investigation and protection of wild resources of P. scapiflorum. 【Method】 This study was based on 88 distribution sites and eight environmental factor variables of P. scapiflorum in China. The MaxEnt model was employed to predict the changes in its potential habitat. Additionally, the possible influence of climatic change under the extremely pessimistic representative concentration pathways scenarios RCP 2.6, RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 for the 2050s and 2070s were estimated. A comprehensive analysis of the main environmental factors affecting the distribution of P. scapiflorum was conducted. 【Result】 (1) The prediction accuracy of the MaxEnt model was high, and the AUC was 0.887. The prediction showed that P. scapiflorum is mainly located in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau currently. The highly suitable areas were mainly distributed in the Kailas Range, Himalayas, southern valley of Xizang, Qaidam Basin, Nyainqêntanglha Mountains, Tanggula Mountains, the southern section of the Aemye Ma-chhen Range, the northern part of the Songpan-Ganzi Plateau, and Hengduan Mountain. The total suitable area of the potential geographical distribution of P. scapiflorum was approximately 310 × 104 km2, including 80.81 × 104 km2 of highly suitable areas. (2) The main environmental factor variables affecting the potential geographical distribution of P. scapiflorum were geomorphology, temperature, and precipitation, among which dem, isothermality, and annual precipitation aere the key environmental factors. (3) Under different climate change models, the suitable habitat will be reduced by 24%-28% compared with the present situation by 2050s and 2070s. The highly suitable area would be downgraded to the medium or low suitable area to significantly reduce or even disappear, and the distribution center of P. scapiflorum tended to migrate to the westward and higher altitudes. 【Conclusion】 Study results are an important reference for the conservation, sustainable development, and utilization of wild resources and artificial cultivation of P. scapiflorum.
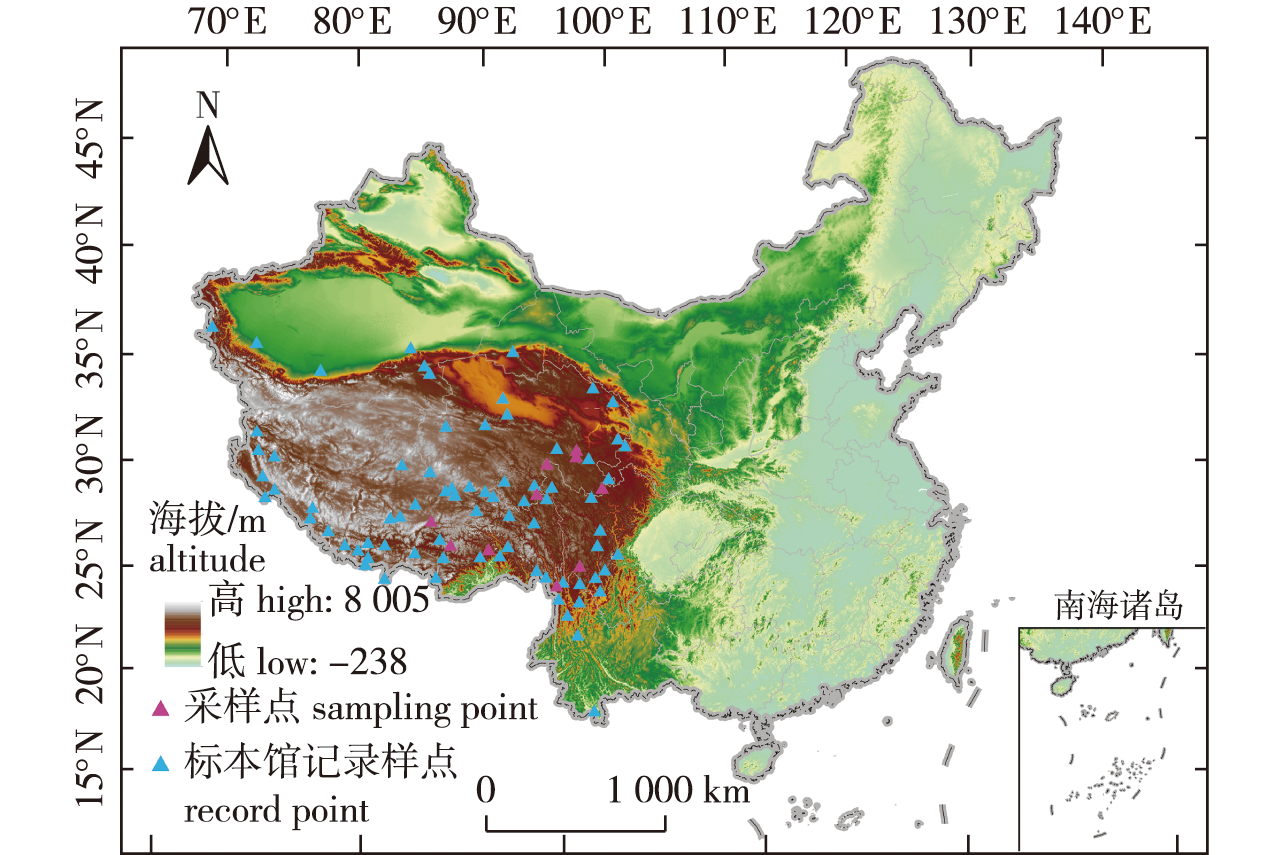
wild plant resources / Pegaeophyton scapiflorum / maximum entropy (MaxEnt) model / the potential distribution / Qihai-Xizang Plateau
| [1] |
蒂玛尔·丹增彭措. 晶珠本草[M].毛继祖,译. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2012:149.
|
| [2] |
杨耀先, 胡泽勇, 路富全, 等. 青藏高原近60年来气候变化及其环境影响研究进展[J]. 高原气象, 2022, 41(1):1-10.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
姚檀栋, 姚治君. 青藏高原冰川退缩对河水径流的影响[J]. 自然杂志, 2010, 32(1):4-8.
|
| [9] |
汤秋鸿, 兰措, 苏凤阁, 等. 青藏高原河川径流变化及其影响研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(27):2807-2821.
|
| [10] |
邢宇. 青藏高原32年湿地对气候变化的空间响应[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2015, 27(3):99-107.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
IPCC. Climate change 2014-impacts, adaptation and vulnerability, part A: global and sectoral aspects[C]// Working Group II Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, Volume 1:Global and Sectoral Aspects. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014.
|
| [13] |
张亮. 青藏高原濒危植物潜在地理分布及保护区建设研究[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2020.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
李巧媛. 不同气候变化情景下青藏高原冰川的变化[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2011.
|
| [17] |
马松梅, 聂迎彬, 段霞, 等. 蒙古扁桃植物的潜在地理分布及居群保护优先性[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(9):2960-2966.
|
| [18] |
乔慧捷, 胡军华, 黄继红. 生态位模型的理论基础、发展方向与挑战[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2013, 43(11):915-927.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
王运生, 谢丙炎, 万方浩, 等. ROC曲线分析在评价入侵物种分布模型中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(4):365-372.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
张海娟, 陈勇, 黄烈健, 等. 基于生态位模型的薇甘菊在中国适生区的预测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(S1):413-418,420.
|
| [27] |
张琴, 张东方, 吴明丽, 等. 基于生态位模型预测天麻全球潜在适生区[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(7):770-778.
|
| [28] |
塔旗, 李言阔, 范文青, 等. 基于最大熵生态位模型的中华穿山甲潜在适宜生境预测[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(24):9941-9952.
|
| [29] |
王鑫, 任亦钊, 黄琴, 等. 基于GIS和MaxEnt模型的赤水河地区濒危植物桫椤生境适宜性评价[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(15):6123-6133.
|
| [30] |
柳晓燕, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 等. 气候变化情景下中国外来入侵植物黄顶菊潜在分布区模拟与早期预警[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(12):2768-2776.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
秦媛媛, 鲁客, 杜忠毓, 等. 气候变化情景下孑遗植物绵刺在中国的潜在地理分布[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(11):4473-4484.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
陈冰瑞, 邹慧, 王臣, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的防风生境适宜区预测及生态特征研究[J]. 中药材, 2022, 45(5):1063-1069.
|
| [38] |
桑满杰. 环境变量对物种分布模型的影响与评价:以山茱萸潜在地理分布预测为例[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2015.
|
| [39] |
张宇欣, 李育, 朱耿睿. 青藏高原海拔要素对温度、降水和气候型分布格局的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 2019, 41(3):505-515.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
余迪, 段丽君, 温婷婷, 等. 青藏高原雨季特征及其对气候增暖的响应[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37(2):12-18.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
王继永, 郑司浩, 曾燕, 等. 中药材种质资源收集保存与评价利用现状[J]. 中国现代中药, 2020, 22(3):311-321.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |