 PDF(1515 KB)
PDF(1515 KB)


Relationship between aboveground biomass and environmental factors of subtropical typical evergreen broad-leaved forest in east China
DONG Yujie, MAO Lingfeng, ZHANG Min, LU Xudong, WU Xiuping
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 74-80.
 PDF(1515 KB)
PDF(1515 KB)
 PDF(1515 KB)
PDF(1515 KB)
Relationship between aboveground biomass and environmental factors of subtropical typical evergreen broad-leaved forest in east China
【Objective】Taking the Castanopsis spp. and Schima superba forests in subtropical typical evergreen broad-leaved forests in east China as the research subjects, the effects of environmental factors on aboveground biomass of the tree layer were studied.【Method】The aboveground biomass of the community was calculated based on the allometric growth equation of various plant species, and the Pearson correlation test was used to analyze the relationship between aboveground biomass and environmental factors in different types of evergreen broad-leaved forests. The mechanism of action between environmental factors and aboveground biomass was constructed by the partial least squares structural equation model (PLS-SEM), which was employed to analyze the relationship between multiple sets of variables.【Result】(1) The aboveground biomass of subtropical typical evergreen broad-leaved forests in east China showed a extremely significant increasing trend with forest age. (2) The aboveground biomass of Castanopsis and S. superba natural forests positively correlated with soil pH in the study area, and for the S. superba natural forest, air temperature and total solar radiation intensity factors significantly affected the aboveground biomass. (3) In the structural equation model constructed using environmental factors and the aboveground biomass of Castanopsis natural forests, the direct effect coefficient of climate factors on aboveground biomass was significantly greater than that of soil factors.【Conclusion】The total solar radiation intensity, soil pH, and soil bulk density significantly affected the aboveground biomass of subtropical typical evergreen broad-leaved forests in east China. Among them, in the Castanopsis natural forest, aboveground biomass positively correlated with air the soil pH factor. In the S. superba natural forest, aboveground biomass negatively correlated with air temperature factor and total solar radiation intensity factor and positively correlated with soil pH factor.
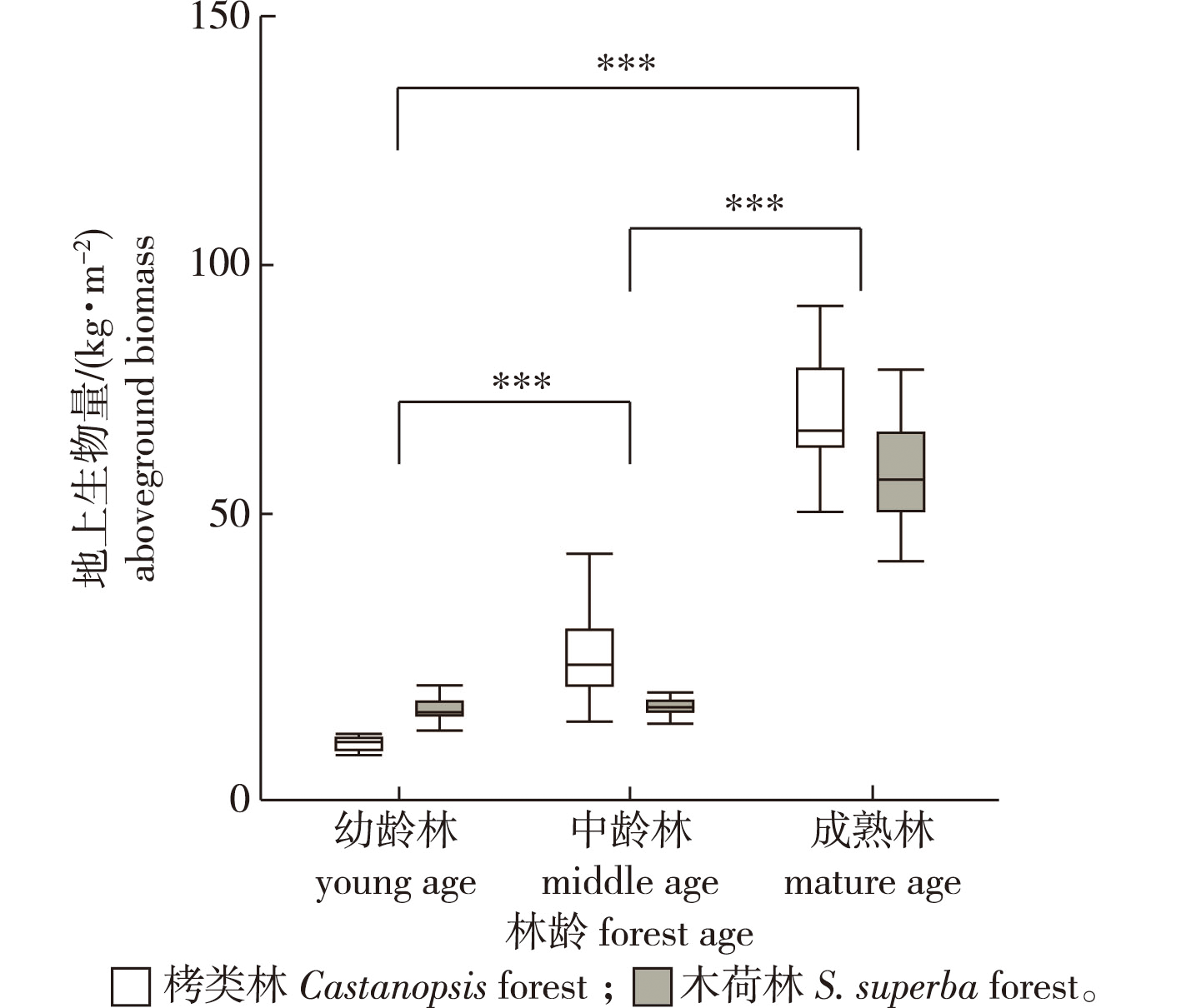
subtropical / evergreen broad-leaved forest / aboveground biomass / solar radiation intensity / soil pH / soil bulk
| [1] |
芦伟, 余建平, 任海保, 等. 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落物种多样性的空间变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9):1023-1028.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
杨远盛, 张晓霞, 于海艳, 等. 中国森林生物量的空间分布及其影响因素[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2015, 35(6):45-52.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
孔祥海. 福建梅花山国家级自然保护区常绿阔叶林生态学研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2008.
|
| [16] |
樊海东, 陈海燕, 吴雁南, 等. 金华北山南坡主要植被类型的群落特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(10):921-928.
|
| [17] |
温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 等. 桉树生态营林的理论探索与实践[J]. 广西科学, 2019, 26(2):159-175+252.
|
| [18] |
赖江山, 张谧, 谢宗强. 三峡库区常绿阔叶林优势种群的结构和格局动态[J]. 生态学报, 2006(4):1073-1079.
|
| [19] |
胡喜生, 洪伟, 吴承祯, 等. 木荷天然种群生命表分析[J]. 广西植物, 2007, 7(3):469-474.
|
| [20] |
李川, 张廷军, 陈静. 近40年青藏高原地区的气候变化——NCEP和ECMWF地面气温及降水再分析和实测资料对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 2004(S1):97-103.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
王晓濛, 侯继华, 何念鹏. 中国植物群落生产力由东向西分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(6):2488-2500.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
孙丽娜. 山西省森林生物量碳密度空间格局和影响因素研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2020.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
钱春花, 李明阳, 郑超. 苏南丘陵山区森林生物量时空变化驱动因素分析[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2021, 37(2):382-388.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
文国卫, 黄秋良, 吕增伟, 等. 气候变化情境下木荷潜在地理分布及生态适宜性分析[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(16): 1-10.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |