 PDF(1603 KB)
PDF(1603 KB)


Growth variation and superior families early selection of Larix olgensis free-pollinated families
WANG Jiaxing, YAN Pingyu, SUN Baifei, LIU Jinhong, FENG Kele, ZHANG Hanguo
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 81-89.
 PDF(1603 KB)
PDF(1603 KB)
 PDF(1603 KB)
PDF(1603 KB)
Growth variation and superior families early selection of Larix olgensis free-pollinated families
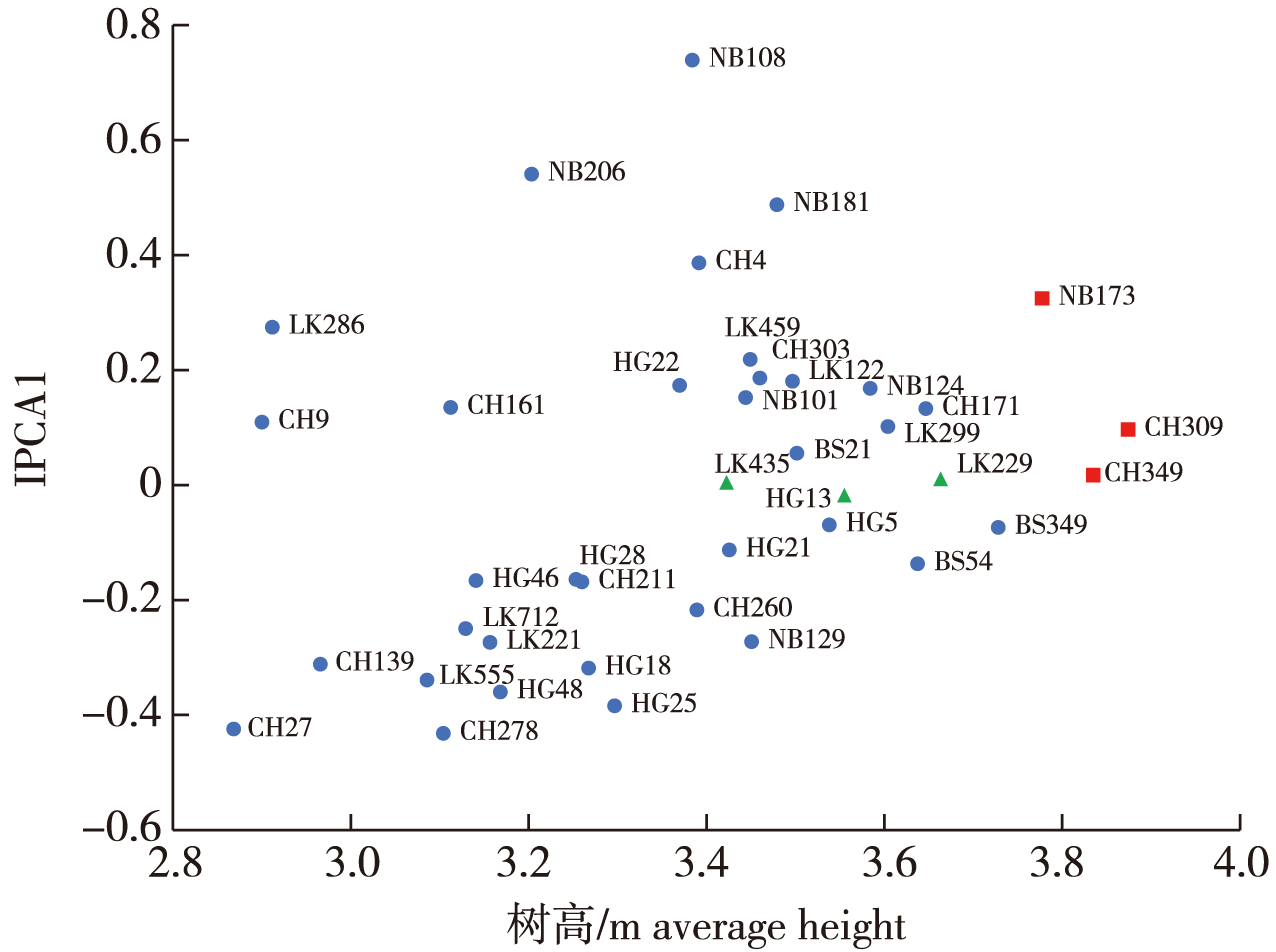
【Objective】 We investigated genetic variation and stability in growth characteristics across 40 free-pollinated families from four Larix olgensis seed orchards located in different regions, aiming to identify superior families. 【Method】 We analyzed progenies from four L. olgensis locations namely Hegang, Linkou, Yongji and Dagujia. The study involved single-point analysis of variance (ANOVA), multi-point multi-year ANOVA, genetic parameter analysis, stability analysis, and breeding value estimation on tree height and diameter at breast height (DBH) for trees aged 6-8 years to identify superior families. 【Result】 Single-point ANOVA results indicated significant differences in growth traits among families. Multi-point multi-year ANOVA revealed significant variations in the height of L. olgensis among families, locations, years, and their interactions. Genetic parameter analysis demonstrated that family heritability of height, ranging from 0.611 to 0.852 across sites, was greater than individual heritability, indicating strong genetic control. The phenotypic and genetic coefficients of variation at each site were 41.36% and 3.87%, respectively. Genetic gain in eight year height ranged from 23.35% to 38.89% at a 20% selection rate. Breeding value estimation identified high-yielding and stable families (CH309, CH349, HG5, BS349, and HG13) with an average breeding value of 0.528, an average height of 4.00 m (25.78% higher than that of the control), and an average stability parameter of 0.085, making them suitable for promotion in four locations. 【Conclusion】 L. olgensis exhibits rich genetic diversity in growth traits among families across different years and locations. The identified superior families are well-suited for cultivation in the three northeastern provinces and similar environments.
Larix olgensis / growth trait / genetic variation / stability analysis / superior family / early selection
| [1] |
苑海静, 成向荣, 虞木奎, 等. 麻栎优树自由授粉家系生长性状3地点间动态变异及优良家系选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2022, 35(2):9-18.
|
| [2] |
贾庆彬, 刘庚, 赵佳丽, 等. 红松半同胞家系生长性状变异分析与优良家系选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(4):109-116.
|
| [3] |
徐贵友, 张义飞, 薛明旭, 等. 落叶松遗传改良研究进展[J]. 林业科技情报, 2019, 51(4):65-68.
|
| [4] |
潘艳艳, 许贵友, 董利虎, 等. 日本落叶松全同胞家系苗期生长性状遗传变异[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(2):14-22.
|
| [5] |
高扬, 王有菊, 杨世桢, 等. 杂种落叶松优良家系的选择[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2013, 33(10):57-60.
|
| [6] |
中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志:第七卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978.
|
| [7] |
张敏, 袁辉. 拉依达(PauTa)准则与异常值剔除[J]. 郑州工业大学学报, 1997(1):84-88.
|
| [8] |
孙英豪, 张含国, 郝俊飞, 等. 3年生长白落叶松高生长遗传变异与多点稳定性[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, 46(8):1-7.
|
| [9] |
唐启义. DPS数据处理系统:专业统计及其他[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.
|
| [10] |
蒋开彬, 杜澄举, 李赛楠, 等. 4年生火炬松半同胞家系生长和分枝性状遗传评估[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(9):1-10.
|
| [11] |
王云鹏, 张蕊, 周志春, 等. 10年生木荷生长和材性性状家系变异及选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(5):85-92.
|
| [12] |
莫家兴, 华慧, 翁怀峰, 等. 柳杉全同胞家系生长和材性的遗传变异及优良家系选择[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(10):40-47.
|
| [13] |
解懿妮, 刘青华, 蔡燕灵, 等. 5年生马尾松生长性状3地点家系变异及评价[J]. 林业科学研究, 2020, 33(5):1-12.
|
| [14] |
吴世雄, 刘艳红, 张利民, 等. 不同产地东北红豆杉幼苗迁地保护的生长稳定性分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(12):27-37.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
刘宇, 徐焕文, 张广波, 等. 白桦半同胞子代多点生长性状测定及优良家系选择[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(3):7-15.
|
| [19] |
金国庆, 张振, 余启新, 等. 马尾松2个世代种子园6年生家系生长的遗传变异与增益比较[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(7):57-67.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
李光友, 徐建民, 李昌荣, 等. 杂交桉家系在桂北生长及优良性评价[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(2):8-15.
|
| [22] |
孙晓梅, 张守攻, 侯义梅, 等. 短轮伐期日本落叶松家系生长性状遗传参数的变化[J]. 林业科学, 2004, 40(6):68-74.
|
| [23] |
张谦, 曾令海, 蔡燕灵, 等. 樟树自由授粉家系生长与形质性状的遗传分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2014, 34(1):1-6.
|
| [24] |
梁德洋, 金允哲, 赵光浩, 等. 50个红松无性系生长与木材性状变异研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(6):51-59.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
李安琪, 严春晓, 连勇机, 等. 黑木相思半同胞子代家系苗期性状的遗传分析[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2023, 43(2):9-16.
|
| [27] |
唐良民, 周衍斌. 马尾松主要生长性状遗传参数和选择效果分析[J]. 南方林业科学, 2020, 48(6):29-34.
|
| [28] |
刘宇, 徐焕文, 李志新, 等. 白桦杂交子代家系生长变异及稳定性分析[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(6):937-944.
|
| [29] |
张磊. 杂种落叶松家系稳定性及优良家系初步选择研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2011.
|
| [30] |
李火根, 黄敏仁, 潘惠新, 等. 美洲黑杨新无性系生长遗传稳定性分析[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 1997, 25(6):1-5.
|
| [31] |
孙英豪. 5年生长白落叶松高生长遗传变异与多点稳定性分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2018.
|
| [32] |
刘宇, 徐焕文, 尚福强, 等. 3个地点白桦种源试验生长稳定性分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(5):50-57.
|
| [33] |
李红盛, 汪阳东, 徐刚标, 等. 山苍子家系幼林生长性状遗传变异及稳定性分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2018, 31(5):168-175.
|
| [34] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |