 PDF(1626 KB)
PDF(1626 KB)


Effects of drought on nitrogen uptake and distribution in Camellia oleifera root under nitrogen addition
JIANG Xiaozeng, ZHU Yan, ZHOU Hengwei, HUANG Xingzhao, FU Longlong, WAN Fangfang
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1) : 95-102.
 PDF(1626 KB)
PDF(1626 KB)
 PDF(1626 KB)
PDF(1626 KB)
Effects of drought on nitrogen uptake and distribution in Camellia oleifera root under nitrogen addition
【Objective】This study investigates the growth response and nutrient utilization of the Camellia oleifera root system across different root orders under drought and nitrogen application. It aims to analyze how water and nitrogen affect root growth, nitrogen uptake, distribution and utilization, and to provide theoretical support for understanding the relationship between plant root architecture and nutrient strategies under climate warming. 【Method】 Two-year-old C. oleifera ‘Changlin 53’ trees were used. A pot experiment with 15N isotope tracing technology was conducted, setting two drought levels: normal irrigation (soil moisture content 75% ± 5%) and drought (soil moisture content 30%±5%). Two nitrogen application levels were used: no nitrogen and 15N-labeled ammonium nitrate (2.88 g/plant). After 75 days of drought treatment, the biomass, total nitrogen content, percentage of nitrogen from fertilizer (Ndff), and nitrogen use efficiency of roots of different diameter classes of C. oleifolia seedlings were measured. 【Result】 Under drought stress, there was a negative correlation between biomass and nitrogen content in grade 1-3, grade 5, and grade 6 roots, while a positive correlation was observed in grade 4 roots. Drought significantly affected 15N content and Ndff in all root diameter classes (P < 0.05). Drought inhibited 15N accumulation in all root diameter classes, with Ndff in grades 1-3 being most affected. Drought increased nitrogen distribution in roots, especially in grade 5 roots, which saw a 93.10% increase. However, the nitrogen use efficiency was inhibited to varying degrees across different root diameter classes. 【Conclusion】Nitrogen application increased root biomass and nitrogen allocation to coarse roots under drought but reduced fine root biomass and nitrogen accumulation. Drought significantly impacted the absorption, utilization, and distribution of fertilizer nitrogen in roots of all levels, enhancing nitrogen distribution, particularly in roots above grade 5, but inhibiting 15N absorption and utilization in roots of grades 1-4.
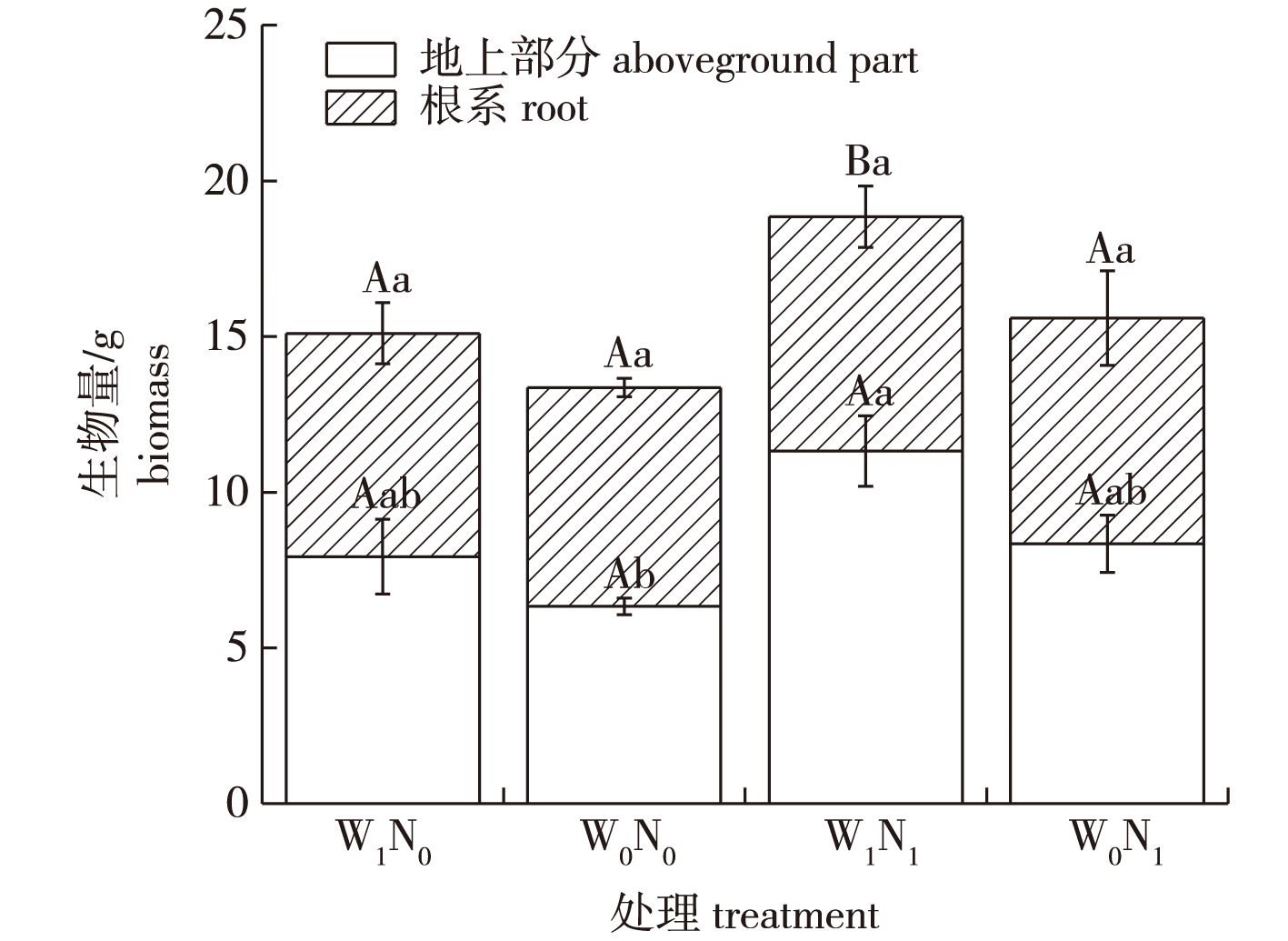
Camellia oleifera / nitrogenous addition / drought stress / root order / nitrogen fertilizer utilization
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
IPCC. Climate change 2022:mitigation of climate change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022.
|
| [3] |
董斌, 洪文泓, 黄永芳, 等. 广西4个油茶品种苗期对干旱胁迫的生理响应[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(2):1-8.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
田丽华. 氮对作物生长发育的影响及其施肥方法[J]. 河北农业科技, 2008(15):40.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
黄小辉, 吴焦焦, 王玉书, 等. 不同供氮水平的核桃幼苗生长及叶绿素荧光特性[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2):119-126.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
温伦敏. 江西省油茶林土壤肥力现状及养分优化管理建议[J]. 现代农业科技, 2016(9):197,200.
|
| [21] |
杨婷婷, 王雪梅, 陈波浪, 等. 施氮对库尔勒香梨树体氮素吸收和积累的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(4):103-107.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
杨安, 李燕青, 李壮, 等. 氮磷钾肥不同滴灌撒施组合对富士苹果15N吸收分配及利用率的影响[J]. 果树学报, 2022, 39(4):564-573.
|
| [26] |
黄海霞, 杨琦琦, 崔鹏, 等. 裸果木幼苗根系形态和生理特征对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1):197-207.
|
| [27] |
冰德叶. 氮添加与凋落物覆盖对油松和华山松幼苗生长的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021.
|
| [28] |
李敏, 赵熙州, 王好运, 等. 干旱胁迫及外生菌根菌对马尾松幼苗根系形态及分泌物的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2022, 58(7):63-72.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
张国娟, 濮晓珍, 张鹏鹏, 等. 干旱区棉花秸秆还田和施肥对土壤氮素有效性及根系生物量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(13):2624-2634.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
陶晨悦, 邵珊璐, 史文辉, 等. 氮沉降对干旱胁迫下毛竹实生苗生物量和保护酶活性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(9):31-40.
|
| [33] |
曲秋玲, 王国梁, 刘国彬, 等. 施氮对白羊草细根形态和生长的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(2):74-79.
|
| [34] |
王瑞, 陈隆升, 王湘南, 等. 氮素形态对油茶苗木生长及生理指标的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(4):26-32.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
陈丽楠, 韩晓日, 孙占祥, 等. 局部根区交替灌溉与氮素耦合对葡萄生长及15N-尿素利用的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(2):447-453.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
马晓东, 钟小莉, 桑钰. 干旱胁迫下胡杨实生幼苗氮素吸收分配与利用[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(20):7508-7519.
|
| [40] |
李树斌, 周丽丽, 伍思攀, 等. 不同氮素形态对干旱胁迫杉木幼苗养分吸收及分配的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(1):152-162.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |