 PDF(2174 KB)
PDF(2174 KB)


The tailwater purification effectiveness of three aquatic plants and their subsequent physiological changes aquatic
XIA Tongtong, WU Yongbo, PU Keyi, WANG Mingli
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 221-227.
 PDF(2174 KB)
PDF(2174 KB)
 PDF(2174 KB)
PDF(2174 KB)
The tailwater purification effectiveness of three aquatic plants and their subsequent physiological changes aquatic
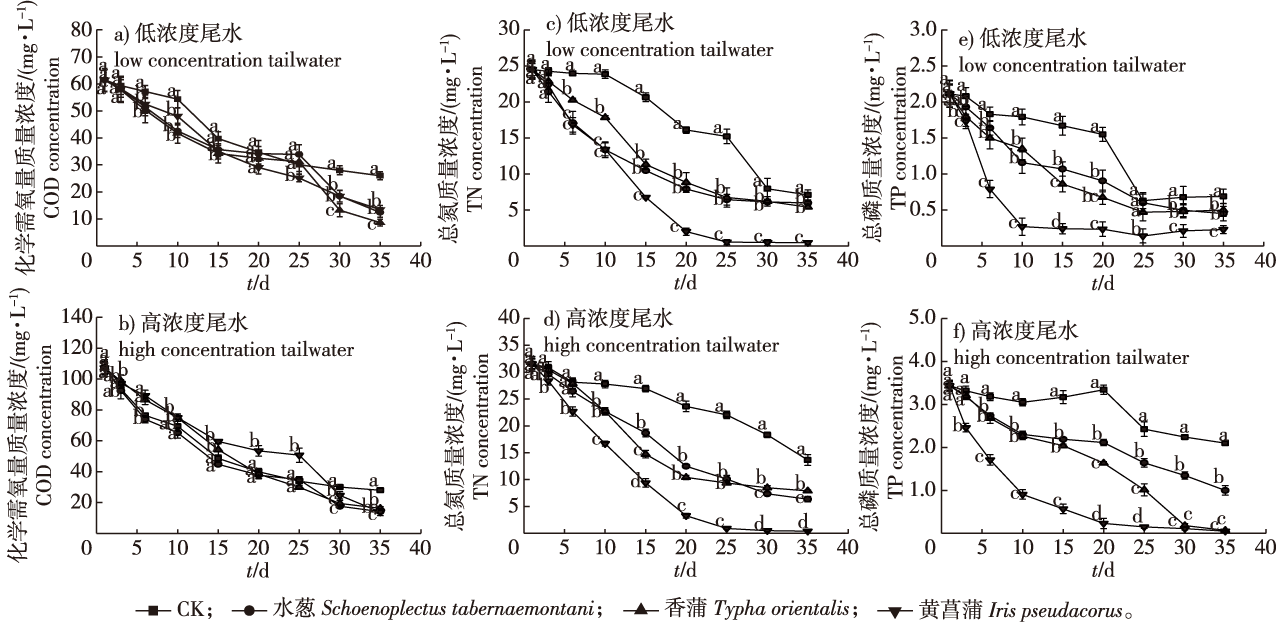
【Objective】 This study aims to explore the effectiveness of hydrophytes in purifying tailwater from a sewage plant and the subsequent changes in their physiological characteristics. The results will provide a reference for the effective purification of tailwater and the selection of suitable hydrophytes for this task. 【Method】 Taking Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani, Typha orientalis and Iris pseudocorus as research objects, pot-control experiments were conducted to simulate the preparation of two different tailwaters, each characterized by different concentrations of contaminants. The removal effects on chemical oxygen demand (COD), total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP), and the subsequent physiological characteristics of the three hydrophytes in the two different tailwaters were analyzed. 【Result】 The three types of hydrophytes all had strong removal effects for COD, TN and TP in tailwater. The COD concentration in tailwater decreased from 61.42-107.28 to 8.63-16.20 mg/L, the TN concentration decreased from 24.49-31.54 to 0.40-7.90 mg/L, and the TP concentration decreased from 2.11-3.43 to 0.05-1.00 mg/L. The antioxidant enzyme activity and relative conductivity of S. tabernaemontani and I. pseudocorus increased in the tailwater, while the peroxidase activity and relative conductivity of T. orientalis decreased significantly (P <0.05), and the catalase activity increased significantly (P <0.05). The chlorophyll content of all three hydrophytes in the tailwater decreased significantly (P <0.05), while the photosynthesis of S. tabernaemontani decreased in the tailwater with the higher concentration of contaminants. 【Conclusion】 Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani, T. orientalis and I. pseudocorus had significant removal effects on COD, TN and TP in the tailwater. The physiological metabolism of hydrophytes was affected following the exposure to the tailwater. It was concluded that S. tabernaemontani and T. orientalis can be planted together for purifying tailwater with low concentrations of contaminants, while I. pseudocorus can be used for the purification of severely contaminated tailwater.
aquatic plant / tailwater purification / physiological characteristics / Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani / Typha orientalis / Iris pseudacorus
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
国家环境保护总局. GB 3838—2002 地表水环境质量标准[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
何强, 胡书山, 向泽毅, 等. 垂直流人工湿地系统净化污水厂尾水脱氮效果[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(8) :3956-3965.
|
| [6] |
丁仁伟. 曝气强化人工湿地深度处理污水厂尾水试验研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021.
|
| [7] |
管策, 郁达伟, 郑祥, 等. 我国人工湿地在城市污水处理厂尾水脱氮除磷中的研究与应用进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(12):2309-2320.
|
| [8] |
李青, 张琼华, 周卫东, 等. 人工湿地净化污水处理厂低浓度尾水的效果[J]. 水生生物学报, 2022, 46(10):1456-1465.
|
| [9] |
张倩妮, 陈永华, 杨皓然, 等. 29种水生植物对农村生活污水净化能力研究[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2019, 36(3):392-402.
|
| [10] |
康彩霞, 戴星照, 刘艳. 高浓度氨氮或磷胁迫对亚洲苦草生理特性的影响[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2018, 25(3):72-77.
|
| [11] |
程丽芬, 张欣. 5种水生植物对煤矿废水的适应性及净化效果[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(4):801-809.
|
| [12] |
谢东升, 朱文逸, 陈劲鹏, 等. 5种华南地区水生植物对城市生活污水的净化效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(8):1903-1908.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
耿兵, 张燕荣, 王妮珊, 等. 不同水生植物净化污染水源水的试验研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(3):548-553.
|
| [15] |
国家环境保护总局. 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准:GB 18918—2002[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2002.
|
| [16] |
中华人民共和国环境保护部. 水质化学需氧量的测定重铬酸盐法:HJ 828—2017[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2017.
|
| [17] |
中华人民共和国环境保护部. 水质总氮的测定碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法:HJ 636—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012.
|
| [18] |
国家环境保护总局. 水质总磷的测定钼酸铵分光光度法:GB 11893—89[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1989.
|
| [19] |
陈建勋, 王晓峰. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 2版. 广州: 华南理工大学出版社, 2006:64-65.
|
| [20] |
李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000:130,164-165.
|
| [21] |
周晓红, 王国祥, 冯冰冰, 等. 3种景观植物对城市河道污染水体的净化效果[J]. 环境科学研究, 2009, 22(1):108-113.
|
| [22] |
李美玉, 李婉, 魏佳明, 等. 人工湿地在污水处理厂尾水水质净化中的应用[J]. 环境生态学, 2022, 4(6):54-58.
|
| [23] |
汤显强, 李金中, 李学菊, 等. 7种水生植物对富营养化水体中氮磷去除效果的比较研究[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2007, 2(2):8-14.
|
| [24] |
李龙山, 倪细炉, 李志刚, 等. 5种湿地植物生理生长特性变化及其对污水净化效果的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(8):1625-1632.
|
| [25] |
褚润, 陈年来, 王小娟, 等. 人工湿地挺水植物脱氮效果研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2017, 39(8):884-889.
|
| [26] |
伏彩中, 肖瑜, 高士祥. 模拟水生生态系统中沉水植物对水体营养物质消减的影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2006, 28(10):753-756.
|
| [27] |
吴湘, 王友慧, 郭建林, 等. 3类水生植物对池塘养殖废水氮磷去除效果的研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(9):1876-1881.
|
| [28] |
孙瑞莲, 刘健. 3种挺水植物对污水的净化效果及生理响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(5):926-932.
|
| [29] |
张波, 师生波, 李和平, 等. 青藏高原不同海拔地区唐古特山莨菪叶片光合色素含量和抗氧化酶活性的比较研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2008, 28(9):1778-1786.
|
| [30] |
黄雪方, 李冬林, 金雅琴, 等. 5种挺水植物对污水浸淹的生理反应及净水效果[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 55(5):66-70.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
赵湘江, 杨兰. 水质恶化影响下香蒲、水葱叶片的光合响应[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(20):77-80.
|
| [35] |
高冠龙, 冯起, 张小由, 等. 植物叶片光合作用的气孔与非气孔限制研究综述[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(4):929-937.
|
| [36] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |