 PDF(3079 KB)
PDF(3079 KB)


The spatio-temporal characteristics of soil erosion in orchards of Dalian City based on the CSLE model
JI Xinyu, YU Yue, ZHANG Sifan, LIU Yuanyuan
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 117-124.
 PDF(3079 KB)
PDF(3079 KB)
 PDF(3079 KB)
PDF(3079 KB)
The spatio-temporal characteristics of soil erosion in orchards of Dalian City based on the CSLE model
【Objective】 The orchards in Dalian City suffer from soil erosion due to vigorous developmental activities. This study aimed to quantitatively analyze the status of soil erosion, determine the spatio-temporal characteristics of soil erosion in orchards in Dalian City, and explore the key factors that influence soil erosion. The results can provide significant insights for the healthy development and ecological protection of the orchard industry in Dalian City. 【Method】 The characteristics of soil erosion in orchards in Dalian City were assessed by using the Chinese soil loss equation (CSLE) model, based on geographic big data available online. The results were visually interpreted, and the dynamic changes and factors influencing soil erosion in the study area were subsequently analyzed. 【Result】 The area of soil erosion constituted approximately 40% of the total area of Dalian City, and the erosion was serious in the northern and southern mountainous and hilly regions. The average soil erosion modulus of the orchards in Dalian City was 1 230.29, 1 150.95, 2 311.36, 6 384.55, 3 399.60 and 3 484.24 t/(km2·a) in 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019 and 2020, respectively. Analysis of the intensity of soil erosion primarily revealed micro and slight erosion. Strong and above grade erosion was primarily observed in Ganjingzi, Jinzhou, and Lüshunkou District. Soil erosion was primarily observed in slope grades below 25° and in regions with rainfall grades ranging between 500 and 900 mm. The finding revealed that greenhouse coverage could reduce soil erosion in greenhouse orchards and open field/facility orchards, and vegetation coverage could effectively reduce soil erosion in open field orchards. 【Conclusion】 Soil erosion in the orchards in Dalian City exhibits obvious spatial distribution characteristics in that the intensity of erosion is high in the south and low in the north area. The successful control of soil erosion in orchards and the efficient promotion and sustainable development of the orchard industry can be achieved in future by increasing the area of greenhouse coverage, increasing the vegetation coverage of outdoor greenhouses, and selecting the location of orchards reasonably.
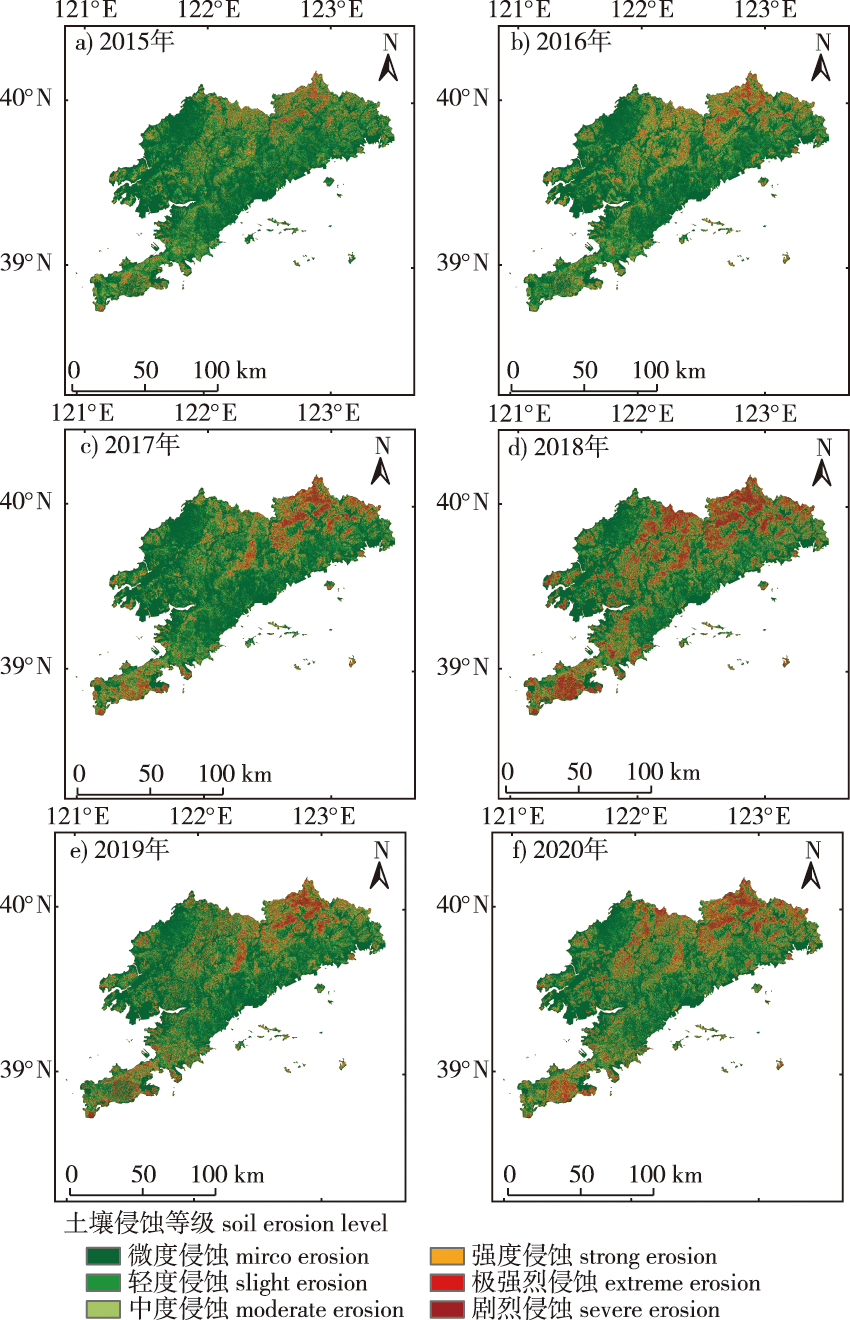
soil erosion / soil erosion modulus / CSLE model / facility greenhouse / orchard of Dalian City
| [1] |
怡凯, 王诗阳, 王雪, 等. 基于RUSLE模型的土壤侵蚀时空分异特征分析: 以辽宁省朝阳市为例[J]. 地理科学, 2015, 35(3): 365-372.
|
| [2] |
张燕, 彭补拙, 高翔, 等. 人类干扰对土壤侵蚀及土壤质量的影响: 以苏南宜兴低山丘陵区为例[J]. 地理科学, 2002, 22(3): 336-341.
|
| [3] |
王坚桦, 邱凡, 谢福倩, 等. 清耕对赤红壤果园坡面土壤侵蚀特征的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(3): 12-17.
|
| [4] |
大连市统计局. 大连统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021.
Dalian Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Dalian statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House, 2021.
|
| [5] |
王耕, 韩冬雪. 1964—2014年大连市降雨侵蚀力时空演变分析[J]. 中国水土保持, 2017(11): 54-56, 67.
|
| [6] |
陈茁新, 张金池. 近10年全球水土保持研究热点问题述评[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(3): 167-174.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
陈锐银, 严冬春, 文安邦, 等. 基于GIS/CSLE的四川省水土流失重点防治区土壤侵蚀研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(1): 17-26.
|
| [11] |
董丽霞, 蒋光毅, 张志兰, 等. 重庆市中国土壤流失方程因子研究进展[J]. 中国水土保持, 2021(2): 40-44,69.
|
| [12] |
陈羽璇, 杨勤科, 刘宝元, 等. 基于CSLE模型的珠江流域土壤侵蚀强度评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学(中英文), 2021, 19(6): 86-93.
|
| [13] |
李嘉麟, 陈家慧, 华丽, 等. 基于CSLE的湖北省土壤侵蚀时空变化特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(4): 43-52,62.
|
| [14] |
游浩妍, 黄曦涛, 陈瑞. 基于CSLE模型的神木市土壤侵蚀模数计算[J]. 中国水土保持, 2021(4): 47-49,68,9.
|
| [15] |
沈子雅, 杨志, 李建国, 等. 基于CSLE模型的宁夏黄土地区水土保持措施因子研究[J]. 中国水土保持, 2021(7): 53-55,5.
|
| [16] |
马亚亚, 王杰, 张超, 等. 基于CSLE模型的陕北纸坊沟流域土壤侵蚀评价[J]. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(6): 95-102.
|
| [17] |
顾治家, 谢云, 李骜, 等. 利用CSLE模型的东北漫川漫岗区土壤侵蚀评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(11): 49-56.
|
| [18] |
苏新宇, 吴镇宇, 刘霞, 等. 基于CSLE模型的区域水土流失风险分析[J]. 中国水土保持科学(中英文), 2021, 19(5): 27-36.
|
| [19] |
黄艳玲, 栾其琛. 大连市绿色有机及地理标志农产品发展现状与对策建议[J]. 农产品质量与安全, 2021(6): 63-66.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
崔云燕. 大连市土壤侵蚀评价[D]. 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2010.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
张科利, 彭文英, 杨红丽. 中国土壤可蚀性值及其估算[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(1): 7-13.
|
| [27] |
符素华, 刘宝元, 周贵云, 等. 坡长坡度因子计算工具[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2015, 13(5): 105-110.
|
| [28] |
蔡崇法, 丁树文, 史志华, 等. 应用USLE模型与地理信息系统IDRISI预测小流域土壤侵蚀量的研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2000, 14(2): 19-24.
|
| [29] |
中华人民共和国水利部. 土壤侵蚀分级分类标准[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2008.
Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Standards for classification and gradation of soil erosion[S]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2008.
|
| [30] |
刘思艺, 黄凤荣. 基于GIS的大连市土壤侵蚀强度估测[J]. 科学技术创新, 2021(22): 173-175.
|
| [31] |
汤紫霞. 福建省农业大棚遥感信息提取[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2021.
|
| [32] |
周璟, 张旭东, 何丹, 等. 基于GIS与RUSLE的武陵山区小流域土壤侵蚀评价研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2011, 20(4): 468-474.
|
| [33] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |