 PDF(2123 KB)
PDF(2123 KB)


Differential proteomic analysis on dormant and dormancy releasing seeds of Cercis chinensis
SUN Yonglian, GAO Yunpeng, HOU Jing, WANG Wenwu, WU Xuelian, LI Shuxian
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 137-143.
 PDF(2123 KB)
PDF(2123 KB)
 PDF(2123 KB)
PDF(2123 KB)
Differential proteomic analysis on dormant and dormancy releasing seeds of Cercis chinensis
【Objective】This study investigated proteom-level changes between dormant and broken dormancy seeds of Cercis chinensis to get a better understanding of the intrinsic mechanisms underlying seed dormancy and germination.【Method】The mature seeds were soaked in hot water until they reached a constant weight, and then subjected to stratification treatment mixed with moisture sand in a 4 ℃ environment until dormancy was released and germination occurred. Label-free quantitative proteomics and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) were used to perform proteome quantitative and qualitative analysis on dormant and dormancy-broken seeds after 45 days of cold stratification were performed based on, respectively. Bioinformatics analysis was also conducted to explore the expression and function mechanism of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) between dormant and dormancy-broken seeds, and to discuss the proteins and its mechanisms related to the dormancy release.【Result】A total of 3 928 proteins were identified in this study, with 3 122 proteins were detected in dormant samples and 3 758 proteins were detected in dormancy-broken samples. After screening the proteins based on the standard of fold changes greater than 2.0 and P<0.05, we filtered 1 031 DEPs. Among these, 779 proteins were up-regulated and 252 proteins were down-regulated. The DEPs were annotated using GO annotation into three categories and 49 subcategories of biological processes, cellular components and molecular functions. The annotated DEPs were closely related to metabolic processes, enzyme catalytic activity, synthesis of cellular components, and stress response. In addition, the KEGG metabolic pathway annotation results showed that 1 012 DEPs were annotated, involving 264 pathways. The DEGs were mainly associated with carbon metabolism, polysaccharide decomposition, and protein processing. The significant enrichment results revealed seven pathways, mainly involving the hormone synthesis, secondary metabolite synthesis, and lipid metabolism. The highly abundant DEPs that may be linked to dormancy breaking are proteins related to β-glucosidase activity, ubiquinone, terpene quinone organisms related proteins, and glyoxylic acid cycle-related proteins. 【Conclusion】This study demonstrates that the dormancy release of C. chinensis seeds is a complex biological process that involves cell morphological changes, enzyme catalysis, polysaccharide decomposition and hormone signal transduction. The release of dormancy is regulated by the interaction of multiple metabolic pathways. Further research is needed to study the molecular mechanism of dormancy release using molecular biological methods such as transcriptomics and metabonomics.
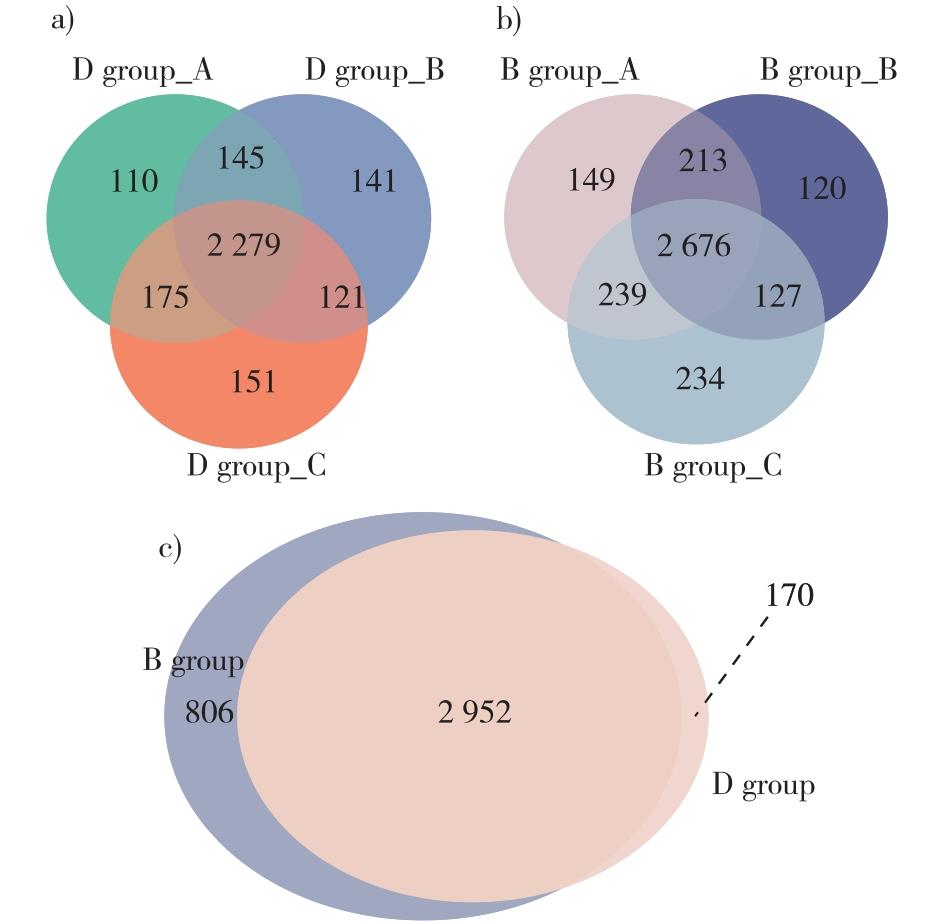
Cercis chinensis / seed dormancy / proteome / metabolic pathway
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
兰海, 冷亦峰, 周树峰, 等. 强休眠玉米种子休眠前后的蛋白差异表达[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(1):23-28.
|
| [3] |
李佳, 陆秀君, 梅梅, 等. 种子发育和萌发过程的蛋白质组学研究[J]. 种子, 2016, 35(5):59-64.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
米建华, 孙雪霞, 娄秋莲, 等. 打破紫荆种子休眠方法研究[J]. 河南农业科学, 2016, 45(11):100-104.
|
| [14] |
王浩宇, 高云鹏, 朱铭玮, 等. 内源抑制物对加拿大紫荆种子萌发的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5):104-112.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
曹晓林, 巩佳第, 陈铭学, 等. 新型亲和去垢小柱净化-液相色谱-串联质谱法分析水稻叶片蛋白质组[J]. 色谱, 2014, 32(11):1181-1186.
|
| [17] |
曹运梅, 张建, 向云, 等. 铜钱树种子休眠特性及破眠技术研究[J]. 种子, 2019, 38(8):73-76.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
董艳, 张正海, 王宁, 等. 基于Label-free技术的汉麻籽不同发芽时期蛋白质组学分析[J]. 食品科学, 2020, 41(14):190-194.
|
| [20] |
苏小霞. 基于转录组和miRNA测序的细叶百合鳞茎休眠解除的分子机理[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2018.
|
| [21] |
郑蕊, 徐晓燕, 李春梅, 等. 大豆种子发育过程中差异表达蛋白的蛋白质组分析[J]. 大豆科学, 2008, 27(4):556-563.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |