 PDF(1692 KB)
PDF(1692 KB)


Steam explosion impact on the active ingredients, antioxidant activity and aroma components of the aqueous extract from Eucommia ulmoides leaves
ZHOU Yunfei, DU Qingxin, WANG Zhiyong, WANG Lu, WANG Yan, LIU Panfeng, SUN Zhiqiang
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 245-256.
 PDF(1692 KB)
PDF(1692 KB)
 PDF(1692 KB)
PDF(1692 KB)
Steam explosion impact on the active ingredients, antioxidant activity and aroma components of the aqueous extract from Eucommia ulmoides leaves
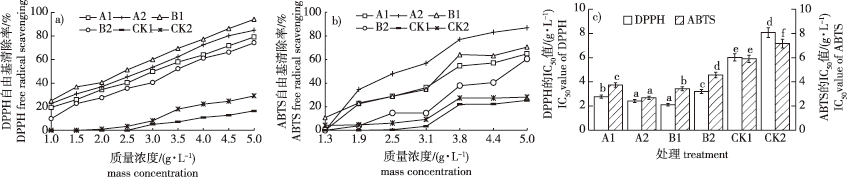
【Objective】 To evaluate the feasibility of manufacturing Eucommia ulmoides leaf tea via steam explosion (SE), the changes of active ingredients, antioxidant activity and aroma components were compared between tea produced using E. ulmoides mature leaves with and without an SE. 【Method】 Treatments based on physically rolling or not rolling the leaves were applied using E. ulmoides ‘Huazhong 8’ and ‘Huazhong 12’ mature leaves. A two-factor, three-level complete experimental design was used to determine the optimal SE parameters according to the contents of total flavonoids, polyphenols and polysaccharides, which were determined by UV spectroscopy. The active ingredients were detected by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The antioxidant activity of the samples was assessed using 1,1-diphenyl-2-trinitrophenylhydrazine (DPPH) and 2,2'-diazo-di(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diamine salt (ABTS) radical scavenging assays. Additionally, the correlation between the active ingredients of the samples and antioxidant activity was analyzed. The aroma components were determined by headspace solid-phase microextraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME/GC-MS). 【Result】 The optimal SE parameters were a pressure of 0.45 MPa and retention time of 300 s. Under these conditions, the total flavonoid and polyphenol contents of ‘Huazhong 8’ and ‘Huazhong 12’ were increased by 10.87 and 21.51, and 1.14 and 0.87-fold compared with the control, respectively. The contents of six active ingredients increased significantly (P < 0.01), with chlorogenic acid and gallic acid increased by 31.31% and 30.72%, respectively and methyl ester increased by 10.41 and 8.06-fold in non-twisted ‘Huazhong 8’ and twisted ‘Huazhong 12’ compared with the control, respectively. Overall, the antioxidant activity of mature E. ulmoides leaves was enhanced significantly with an SE, in which the antioxidant activity of non-twisted ‘Huazhong 8’ was greater than that of twisted ‘Huazhong 12’. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was negatively correlated with the contents of kynurenine, carnoside, and chlorogenic acid (P<0.05). Aromatic substances such as benzyl alcohol and β-cyclocitral were generated from the volatile compounds. 【Conclusion】 An SE treatment significantly improved the water solubility and antioxidant activity of the active ingredients of the aqueous extract of mature E. ulmoides leaves, with an increase in the type and content of aromatic substances. Because the resource availability of green-leaved E. ulmoides is much greater than that of red-leaved E. ulmoides at present, our results suggest that mature E. ulmoides leaves without a physical twisting treatment prior to an SE would result in a simplified tea-making process and effectively reduce the production cost of E. ulmoides green leaf tea, providing novel ideas for the large-scale processing and utilization of E. ulmoides leaves.
Eucommia ulmoides / active ingredients / antioxidant / aroma components / steam explosion
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
吴红艳, 彭呈军, 邓后勤. 杜仲叶化学成分研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(17): 360-364.
|
| [3] |
龚频, 韩业雯, 翟鹏涛, 等. 杜仲叶的活性成分、药理作用及其在食品加工中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(10): 395-404.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
王亮亮, 唐小兰, 王凯, 等. 杜仲的活性成分和保健功效及杜仲在食品加工中的应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2020, 11(10):3074-3080.
|
| [7] |
王亚洁, 何玉珏. 近年杜仲茶成分及工艺探究[J]. 科学大众(科学教育), 2017(7): 192.
|
| [8] |
刘雯. 杜仲复合功能茶杀青工艺研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2013.
|
| [9] |
刘梦培, 铁珊珊, 王璐, 等. 发酵条件对杜仲茶组分及抗氧化性的影响[J]. 食品科技, 2018, 43(2):105-108.
|
| [10] |
张丽华, 李珍珠, 赵光远, 等. 冠突散囊菌发酵杜仲茶的工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(21): 118-123.
|
| [11] |
黄友谊, 杨晓萍, 袁芳亭, 等. 杀青条件对杜仲茶主成分的影响[J]. 食品工业, 2003, 2: 17-19.
|
| [12] |
董尚胜, 翁蔚, 查森俊, 等. 复火对杜仲茶品质成份的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2000(5): 110-111.
|
| [13] |
杨延, 陆多林, 查银娟. 红茶品质影响因素研究进展[J]. 农业技术与装备, 2021(2): 12-13.
|
| [14] |
童启庆, 董尚胜, 翁蔚, 等. 杜仲茶风味化学的研究Ⅰ 杜仲绿茶初制工艺对品质成份的影响[J]. 茶叶, 2000, 26(1): 32-34.
|
| [15] |
张厅, 刘晓, 熊元元, 等. 四川黑茶渥堆过程中主要品质成分和茶汤色差变化及其相关性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 48(9): 154-162.
|
| [16] |
何永杰. 不同加工工艺对天津产杜仲茶品质的影响[D]. 天津: 天津农学院, 2018.
|
| [17] |
柯文林, 杨韧强. 复合酶辅助提取杜仲叶多酚及其应用[J]. 食品工业, 2021, 42(12): 224-228.
|
| [18] |
梁兆昌, 褚洪标, 肖琳, 等. 杜仲超微粉体理化特性及体外溶出性能研究[J]. 中草药, 2015, 46(11):1609-1614.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
魏锦锦, 辛东林, 陈翔, 等. 蒸汽爆破预处理对杜仲皮活性成分和杜仲胶提取的影响[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2019, 39(1): 88-94.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
丁欢欢, 张宁, 王璐, 等. 蒸汽爆破预处理提高杜仲总黄酮产量的效果[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(6): 147-156.
|
| [25] |
俞锐, 杜红岩, 胡文臻. 杜仲产业绿皮书:中国杜仲橡胶资源与产业发展报告[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2013.
|
| [26] |
李洪果, 许基煌, 杜红岩, 等. 基于等位基因最大化法初步构建杜仲核心种质[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(2): 42-51.
|
| [27] |
肖作为, 谢梦洲, 甘龙, 等. 山银花、金银花中绿原酸和总黄酮含量及抗氧化活性测定[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(1): 210-216.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
王黎明, 夏文水. 蒽酮-硫酸法测定茶多糖含量的研究[J]. 食品科学, 2005, 26(7): 185-188.
|
| [30] |
孟益德, 王琦, 刘攀峰, 等. 短周期叶用林模式下不同杜仲无性系枝皮化学成分分析[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2022, 34(11): 1871-1882.
|
| [31] |
唐思颉, 涂传海, 胡文秀, 等. 红茶菌发酵黄浆水的体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(17): 1-6.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
李慧, 张婉, 李静, 等. ‘华仲12号’杜仲叶片黄酮类物质组成鉴定及含量分析[J]. 经济林研究, 2022, 40 (3): 133-141.
|
| [35] |
朱景乐. ‘红叶’杜仲叶片呈色生理特性及关键基因筛选[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2017.
|
| [36] |
施树云, 郭柯柯, 彭胜, 等. DPPH-HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS快速筛选和鉴定杜仲黑茶中抗氧化活性成分[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2018, 30(11):1913-1917.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
崔潇文, 袁茂翼, 叶发银, 等. 蒸汽爆破预处理对番茄皮渣膳食纤维组成及理化特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(21): 170-177.
|
| [40] |
韩士群, 杨莹, 周庆, 等. 蒸汽爆破对芦苇纤维及其木塑复合材料性能的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(1): 136-142.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
杨晶, 黄星球, 杨文. 桑叶红茶的加工技术[J]. 食品工业, 2022, 43(12):8-11.
|
| [44] |
宋娟娟, 谢婷, 刘文涵, 等. 丙二醛对豆粕蛋白质氧化的影响及茶多酚的缓解作用[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2023, 46(2):324-332.
|
| [45] |
康育鑫, 陈永快, 肖两德, 等. 安溪铁观音加工过程中影响色、香、味的成分变化[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(12): 291-298.
|
| [46] |
路买林, 陈梦娇, 张嘉嘉, 等. ‘红叶’杜仲叶色转变过程中叶片生理指标变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1): 86-92.
|
| [47] |
屠万倩, 张留记, 夏曼玉, 等. 杜仲叶清除DPPH自由基动力学特性及抗氧化活性成分筛选[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2022, 57(4): 264-268.
|
| [48] |
刘梦培, 李佳, 靳学远, 等. 不同乳酸菌发酵杜仲叶水提液的香气成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(9): 36-43.
|
| [49] |
曾桥, 唐文洁, 温谨瑞, 等. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱法分析杜仲叶茯砖茶加工过程中挥发性成分[J]. 食品工业科技, 2023, 44(1): 96-108.
|
| [50] |
王娟, 赵江, 陈见容, 等. 红枣杜仲复合饮料的配方优化及其风味物质分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(2): 215-222.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |