 PDF(1807 KB)
PDF(1807 KB)


Identification of a newly recorded species of Aphelenchoides paradanlianensis in China
WANG Lichao, CHEN Fengmao, DONG Xiaoyan, SHENG Ruocheng, LI Huan, WANG Mengyao
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 169-174.
 PDF(1807 KB)
PDF(1807 KB)
 PDF(1807 KB)
PDF(1807 KB)
Identification of a newly recorded species of Aphelenchoides paradanlianensis in China
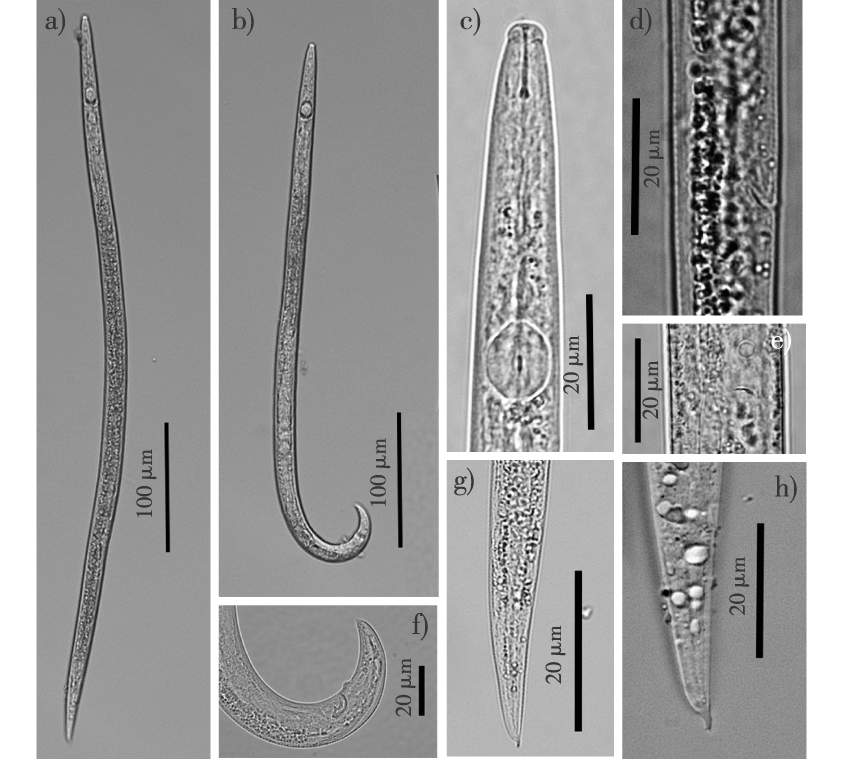
【Objective】Parasitic nematodes are invertebrates that infest pine trees, feeding on plant cells and potentially harming tree health. Some nematodes can even kill pines (Pinus spp.). In 2022, a new parasitic nematode was isolated from black pine (Pinus thunbergii) and tentatively named the Liaoning nematode. To clarify its taxonomic status, both morphological and molecular biological identifications were performed to determine its species and guide its prevention and control.【Method】The Baermann funnel method was employed to separate nematodes from dead wood samples. After three washes with sterile water, the nematodes were transferred to Botrytis cinerea for seven days. Morphological characteristics of female and male adult nematodes were observed and measured using light microscopy. For molecular identification, DNA was amplified and sequenced using 18S rDNA, 28S rDNA, and COI gene primers to construct an evolutionary tree and further assess the taxonomic status.【Result】The primary morphological features of the Liaoning nematode are as follows: The average body length of female adults is 580.6 μm, mean body width is 17.3 μm. Female adults are slightly ventrally curved when heat-relaxed, with fine annules between the lip and body and a stylet with small basal swellings. The median bulb is ovoid, with a height and width of 11.8 and 8.4 μm, respectively. The vulva, without a vulval flap, is inclined at 45° and located between 60%-70% of the body length, with a distance from the posterior vaginal sac of 25.6 μm. The average distance between the vagina and anus is 131.9 μm. The tail measures 33.1 μm in length and has terminal shapes resembling snail feelers. The male nematode’s anterior region is similar to the female’s but forms a “J” shape when heat-relaxed and has a shorter body length, approximately 479.2 μm. The stylet length is 10.1 μm, and the body width is about 19.0 μm wider than that of female adults. The spicule length is 14.8 μm, with well-developed condylus and rostrum positioned in the middle and upper part of the spicules. The tail length is 28.0 μm, with short protrusions at the terminal. These morphological features align with A. paradanlianensis. DNA cloning and sequencing of the 18S rDNA, 28S rDNA, and COI genes produced target fragments of 914, 769 and 687 bp, respectively. BLAST alignment on NCBI revealed the highest similarity to A. paradanlianensis. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that the Liaoning nematode and A. paradanlianensis are closely related, confirming the nematode’s taxonomic status.【Conclusion】 Combining morphological and molecular characteristics, the Liaoning nematode isolated from P. thunbergii has been identified as A. paradanlianensis, marking its first discovery on pine trees in China. While morphological measurements of the Chinese population are slightly higher than those of the Korean population, the characteristics are generally consistent, possibly due to geographic variations or intra-species differences.
pine(Pinus spp.) / parasitic nematodes / new record species / Aphelenchoides paradanlianensis
| [1] |
叶建仁, 吴小芹. 松材线虫病研究进展[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2022, 41(3):1-10.
|
| [2] |
王立超, 苏胜荣, 陈凤毛, 等. 黄山马尾松林天牛及携带线虫种类初步调查[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46 (4): 29-35.
|
| [3] |
叶建仁. 松材线虫病在中国的流行现状、防治技术与对策分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(9): 1-10.
|
| [4] |
于海英, 吴昊, 黄瑞芬, 等. 辽宁抚顺樟子松松材线虫分离与鉴定[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2020, 39(2):6-10.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
董瀛谦, 阎合, 潘佳亮, 等. 我国松材线虫病防控对策[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2022, 41(4):1-8.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
宋雅婷, 王立超, 孙守慧, 等. 滑刃属线虫1个中国新记录种[J]. 南京林业大学学报 (自然科学版), 2020, 44(3): 105-110.
|
| [13] |
宋雅婷, 刘仁军, 江奕, 等. 中国辽宁咽滑刃线虫的形态与分子系统学描述[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4):93-101.
|
| [14] |
姜生伟, 吴昊, 李德斌, 等. 我国东北地区松材线虫灾害特征分析[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2022, 41(4):9-15.
|
| [15] |
国家林业和草原局. 国家林草局 2023 年第 7 号公告[EB/OL]. (2023-02-17) [2023-06-20]. http://www.forestry.gov.cn/c/www/gkzfwj/380005.jhtml.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
史延梅, 陈凤毛, 叶建仁, 等. 我国松树寄生线虫分类检索[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(1): 137-141.
|
| [20] |
王磊, 叶建仁, 史丽娜. 利用腐生线虫加速替代疫木中松材线虫种群数量研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(4): 36-44.
|
| [21] |
国家林业和草原局森林和草原病虫害防治总站, 南京林业大学. 中国松材线虫病的发生规律与防治技术[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2019.
General Station of Forest and Grassland Pest Control of National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Nanjing Forestry University. The occurrence regulation and control techniques of pine wilt disease in China[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2019.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
盛若成, 李敏, 陈军, 等. 两株我国南北松材线虫虫株形态指标与致病力比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6): 18-24.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |