 PDF(2463 KB)
PDF(2463 KB)


Simulation of beam radiation of understory solar radiation based on easy measurable tree factors
DU Xin, DONG Xue, GU Huiyan, LI Yubo, CHEN Xiangwei
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 205-213.
 PDF(2463 KB)
PDF(2463 KB)
 PDF(2463 KB)
PDF(2463 KB)
Simulation of beam radiation of understory solar radiation based on easy measurable tree factors
【Objective】 This study aims to assess the simulation accuracy of two measures of understory beam radiation: the scaled weighted beam shading degree and the weighted inside-boundary neighbor beam shading degree. These measures are part of a forest understory radiation simulation system based on easy measurable tree factors. The study also seeks to identify model structural characteristics using these simple, measurable tree factors to provide a reasonable and accurate estimate of beam radiation at any understory location. 【Method】A stand pixel model was established using broadleaf Pinus koraiensis (Korean pine) forest stand survey information and it simulated the understory beam transmittance. This transmittance served as a benchmark to evaluate the scaled weighted beam shading degree and the weighted inside-boundary neighbor beam shading degree. Various parameters for these degrees were optimized using a hill-climbing algorithm. The simulation performance of these measures was assessed by comparing the proportions of beam radiation transmitted through gaps, using Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients and linear regression determination coefficients between understory beam transmittance and the two degrees under the optimized parameters.【Result】The results indicate that the scaled weighted beam shading degree provided the best linear regression fit for understory beam transmittance in the broadleaf Korean pine forest, with a neighbor tree selection minimum scale (rmin) of 6.332 m and a maximum scale (rmax) of 13.609 m. The Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients, as well as the linear regression determination coefficient between this measure and understory beam transmittance, were -0.581, -0.645 and 0.338, respectively. By contrast, the weighted inside-boundary neighbor beam shading degree showed a linear regression fit for understory beam transmittance, with a neighbor tree selection maximum threshold (Tmax) of 1.965 and a minimum threshold (Tmin) of 0.502. The Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients, as well as the linear regression determination coefficient for this measure, were -0.738, -0.695, and 0.545, respectively. 【Conclusion】(1) Both the scaled weighted beam shading degree and the weighted inside-boundary neighbor beam shading degree effectively reflect the understory beam radiation, with the latter performing better. (2) When constructing a simulation model of beam radiation in forests based on tree factors, it is crucial to select neighboring trees that influence beam radiation and to seek a straightforward method to accurately represent beam radiation at various times.
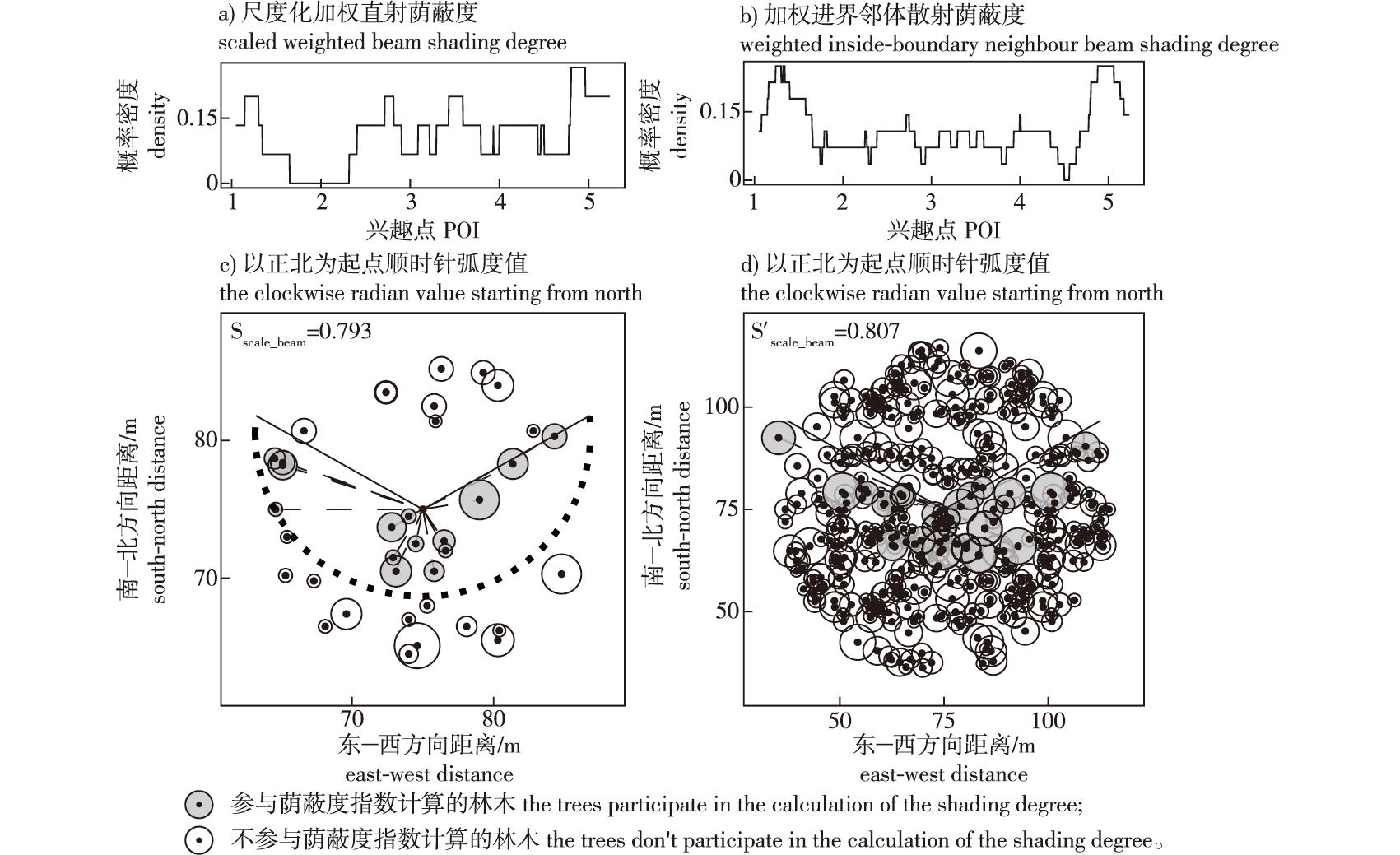
solar radiation / beam transmittance / scaled weighted beam shading degree / weighted inside-boundary neighbor beam shading degree / broadleaf Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis)
| [1] |
王德利. 植物生态场导论[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社, 1994.
|
| [2] |
徐化成. 中国红松天然林[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2001.
|
| [3] |
帖利民. 林下入射辐射对冻土的影响[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2021.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
邹小伟, 孙维君, 杨堤益, 等. 云量对祁连山老虎沟12号冰川表面能量平衡的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 2021, 43(2):342-356.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
李树人, 赵勇, 阎志平. 日本落叶松林冠层光生态场研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 1997, 8(2):123-126.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
杜昕, 董雪, 谷会岩, 等. 基于易测林木因子的林下太阳辐射模拟(Ⅰ):林下散射辐射模拟[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 49(6):26-36.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
李爱贞, 刘厚凤. 气象学与气候学基础[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2001.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
方斌, 朱清科, 李文华, 等. 林木个体影响林下太阳辐射分布的动态仿真[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 36(6):113-118,125.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
陈梅, 朱教君, 闫巧玲, 等. 辽东山区次生林不同大小林窗光照特征比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(12):2555-2560.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |