 PDF(1905 KB)
PDF(1905 KB)


Effects of biochar types and their addition doses on soil chemical properties and Cyclocarya paliurus growth
WANG Shanshan, LAN Ziyu, DENG Rui, FANG Shengzuo
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 137-144.
 PDF(1905 KB)
PDF(1905 KB)
 PDF(1905 KB)
PDF(1905 KB)
Effects of biochar types and their addition doses on soil chemical properties and Cyclocarya paliurus growth
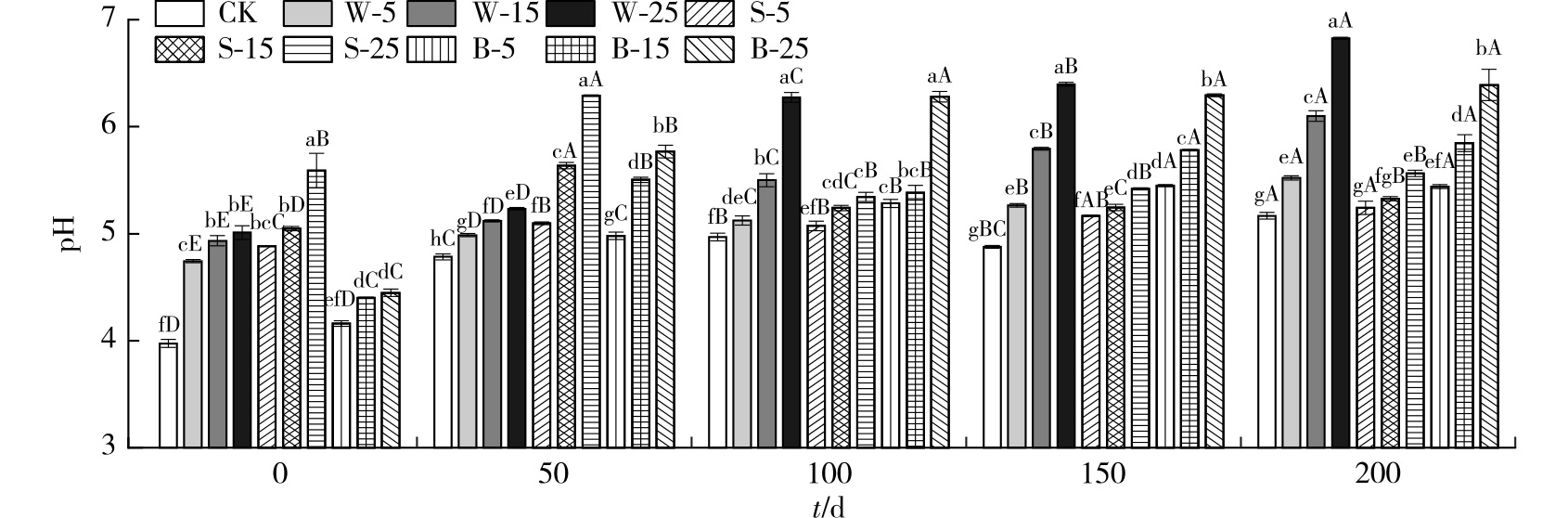
【Objective】Cyclocarya paliurus is a multifunctional tree species. This study investigated the impacts of biochar types and their addition doses on soil chemical properties, leaf photosynthetic pigment content, and growth of C. paliurus seedlings, aiming to provide a scientific basis for biochar application in future C. paliurus plantations.【Method】A two-factor randomized block experimental design was employed to investigate the effects of three biochar types (C. paliurus biochar, straw biochar, and bamboo biochar) and three application rates (5%, 15% and 25% V/V, equivalent to 1.0%, 3.5%, and 6.5% m/m) on soil chemical properties, seedling growth, and leaf photosynthetic pigment content through a pot experiment.【Result】After 200 days of treatment, biochar application significantly increased soil pH, ammonium nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium levels, while also enhancing chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoid contents in C. paliurus leaves. Application rate had a more pronounced effect on soil chemical indices than biochar type (P<0.05). Notably, adding 25% C. paliurus biochar increased soil pH by 32.1%, and 25% straw biochar significantly elevated available phosphorus and potassium levels by 145.3% and 250.0%, respectively, compared to the control. Biochar application also significantly influenced seedling growth and biomass production (P<0.05), with the 5% C. paliurus biochar treatment showing the most notable promotion in biomass production. Compared to the control, biomass in leaves, stems, roots, and total increased by 55.6%, 47.6%, 43.0%, and 47.0%, respectively, in the 5% C. paliurus biochar treatment. Correlation analysis revealed that seedling height and diameter growth were significantly positively correlated with leaf photosynthetic pigment contents. Additionally, all photosynthetic pigments were significantly and positively correlated with soil nitrate nitrogen (P<0.01), while only soil available potassium showed a significant correlation with carotenoid content (P<0.05).【Conclusion】Appropriate biochar application effectively enhances soil fertility and promotes C. paliurus seedling growth. Among treatments, the 5% C. paliurus biochar application proved optimal for maximizing biomass production.
Cyclocarya paliurus / biochar / soil pH / soil nutrient / photosynthetic pigment / biomass production
| [1] |
方升佐, 洑香香. 青钱柳资源培育与开发利用的研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(1):95-100.
|
| [2] |
郑观涛, 殷志琦. 药用植物青钱柳的开发研究进展[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019, 19(43):123-124.
|
| [3] |
关于批准裸藻等8种新食品原料的公告(2013年第10号)[EB/OL]. (2013-11-16) http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/s7890/201311/533ed8492dd04ff3aa63c7e7dd40c256.shtml.
|
| [4] |
方升佐. 青钱柳产业发展历程及资源培育研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):115-126.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
姜灿烂, 赵汝东, 蔡天明, 等. 林业废弃物生物炭对红壤丘陵区瘠薄土壤碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(2):202-208.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
胡华英, 殷丹阳, 曹升, 等. 生物炭对杉木人工林土壤养分、酶活性及细菌性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(11):4138-4148.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2000.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
刘泽茂, 晏昕, 吴文, 等. 竹炭添加对大叶榉树容器苗生长和营养状况的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2):111-118.
|
| [20] |
张红雪, 吴凤英, 陈宇琳, 等. 烟秆生物炭对土壤不同形态钾含量及烟草光合特性的影响[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 51(4):468-477.
|
| [21] |
凡莉莉,
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |