 PDF(2196 KB)
PDF(2196 KB)


The variation characteristics of tea leaf quality during the expansion of Pleioblastus amarus into tea plantations
JIANG Xiuqin, CHEN Shuanglin, FAN Lili, HU Ruicai, GUO Ziwu, WANG Zhonghua
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 152-160.
 PDF(2196 KB)
PDF(2196 KB)
 PDF(2196 KB)
PDF(2196 KB)
The variation characteristics of tea leaf quality during the expansion of Pleioblastus amarus into tea plantations
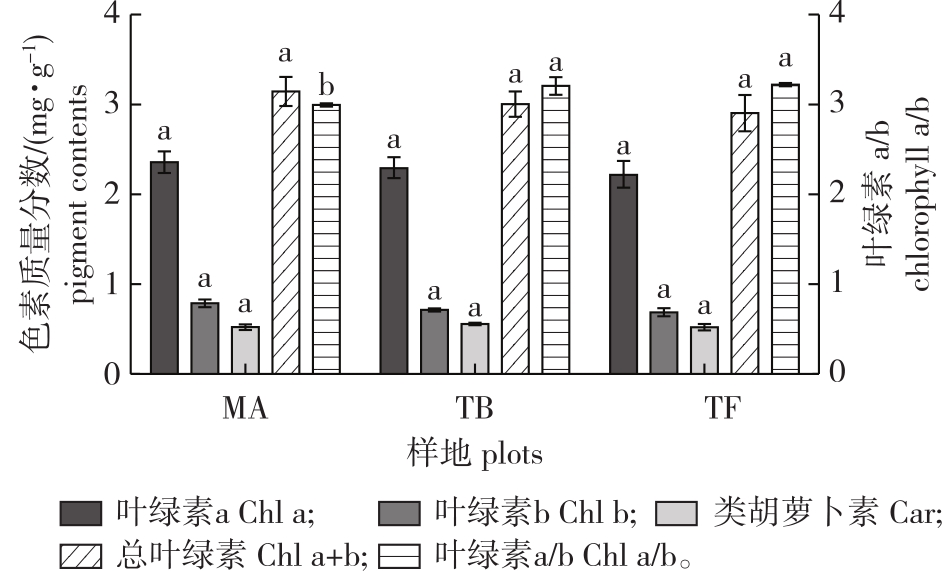
【Objective】The expansion of bamboo forests leads to environmental heterogeneity within the tea plantation ecosystem, exerting a significant impact on the growth of tea plants and the quality of tea leaves. Unveiling the potential effects of bamboo forest expansion on the growth of tea plants and the quality of tea leaves is paramount for the scientific management of tea plantations undergoing bamboo expansion.【Method】The study focused on the continuous patches of bitter bamboo (Pleioblastus amarus) and tea (Camellia sinensis) tree expansion forests in Longyou County, Zhejiang Province. Three types of plots were established, namely, the tea-bamboo mixed forest interface zone, the mixed forest center zone, and the pure tea plantation zone. Various parameters, including growth characteristics, tea pigments, tea polyphenols, caffeine, free amino acids, and mineral nutrients in tea leaves, were measured. The differences in the growth characteristics of tea trees and tea leaf quality after the expansion of P. amarus into tea plantation were analyzed using multivariate statistical methods, orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis, and variable projection importance methods.【Result】(1) The expansion of P. amarus significantly influences the growth and branching number of tea plants, with a notable impact on the average height (P< 0.05). (2) With the expansion of P. amarus into tea plantations, there was no significant impact on the pigment content of tea leaves. However, there was a significant effect on the chlorophyll a/b of tea leaves in the mixed forest interface zone (P<0.05). The impact of pigments did not significantly contribute to tea leaf quality. (3) Influenced by the expansion of P. amarus, the contents of tea polyphenols and caffeine in the interface zone were significantly lower than those in the mixed forest center and pure tea plantation zones (P<0.05). The change in ratio of phenol to ammonia was not obvious, and all three parameters contribute significantly to tea leaf quality. (4) With the expansion of P. amarus into tea plantations, there was an increasing trend in the content of the 14 free amino acid components in tea leaves. However, in the mixed forest interface and center zones, the contents of methionine and cysteine were significantly higher than in the pure tea plantation zone (P<0.05). The content of serine was highest in the mixed forest center zone, but the change was not obvious. All three amino acids contributed significantly to tea leaf quality. (5) With the expansion of P. amarus into tea plantations, there was a significant decrease (P<0.05) in the content of calcium, manganese, magnesium, iron, and copper elements in tea leaves. These elements were noticeably accumulated in the mixed forest interface zone, while the zinc content exhibited an opposite trend. The variations in these mineral nutritional elements contribute significantly to the differences in tea leaf quality.【Conclusion】The expansion of P. amarus induced changes in the growth strategy of tea trees, altered the composition of effective components and mineral nutrient elements in tea leaves, thereby influencing tea quality and hindering its improvement.
tea(Camellia sinensis) plantation / bamboo expansion / growth characteristics / tea quality / effective components / mineral nutrition elements / Pleioblastus amarus
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
黎健龙, 张曼, 唐颢, 等. 影响茶树生长和茶叶品质的主要环境因子及其适应机制[J]. 茶叶通讯, 2023, 50(4):437-445.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
郭春芳, 孙云, 张木清. 不同土壤水分对茶树光合作用与水分利用效率的影响[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2008, 28(4):333-337.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
刘俏, 林勇, 胡小飞, 等. 氮磷肥对茶树锌硒等中微量元素吸收与分配的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(2):637-644.
|
| [9] |
赵阳, 杨超伟, 冯延芝, 等. 亚热带低山丘陵区桐茶复合经营对茶叶品质的影响[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2023(5):46-51.
|
| [10] |
程建新, 何玉友, 郭子武, 等. 苦竹杉木混交林界面区竹子克隆分株抽枝展叶效率变化特征[J]. 竹子学报, 2022, 41(2):24-33.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
景雄, 蔡春菊, 范少辉, 等. 环境胁迫下竹类植物生态适应性研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2018, 31(4):36-41.
|
| [14] |
刘希珍, 范少辉, 刘广路, 等. 毛竹林扩展过程中主要群落结构指标的变化特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(12):3165-3171.
|
| [15] |
黄慧敏, 董蓉, 钱凤, 等. 紫耳箭竹克隆形态可塑性对典型冠层结构及光环境的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(19):6835-6845.
|
| [16] |
刘骏, 杨清培, 余定坤, 等. 细根对竹林-阔叶林界面两侧土壤养分异质性形成的贡献[J]. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(8):739-749.
|
| [17] |
刘美雅, 伊晓云, 石元值, 等. 茶园土壤性状及茶树营养元素吸收、转运机制研究进展[J]. 茶叶科学, 2015, 35(2):110-120.
|
| [18] |
尹晓雷, 刘旭阳, 金强, 等. 不同管理模式对茶树碳氮磷含量及其生态化学计量比的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(7):749-759.
|
| [19] |
巩雪峰, 余有本, 肖斌, 等. 不同栽培模式对茶园生态环境及茶叶品质的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2008, 28(12):2485-2491.
|
| [20] |
杨海滨, 盛忠雷, 谢堃, 等. 不同栽培模式对山地茶园生态环境和茶叶品质的季节调控[J]. 西南农业学报, 2015, 28(4):1559-1563.
|
| [21] |
杨丽冉, 蒋宾, 焦文文, 等. 茶李间作对茶树生长及秋季绿茶品质的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2023, 54(10):1-15.
|
| [22] |
高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
全国茶叶标准化技术委员会. 茶咖啡碱测定:GB/T8312—2013[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.
National Technical Committee 339 on Tea of Standardization Administration of China. Tea-determination of caffeine content:GB/T 8312-2013[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014.
|
| [25] |
全国饲料工业标准化技术委员会. 饲料中钙、铜、铁、镁、锰、钾、钠和锌含量的测定原子吸收光谱法:GB/T 13885—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
National Feed Industry Standardization Tedinical Committee. Determination of the contents of calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, sodium and zinc in feeds-method using atomic absorption spectrometry:GB/T 13885-2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
郭舒臣, 郑玉忠, 郭瑞, 等. 不同年份老香黄定量分析及其化学模式识别研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 2021, 40(1):10-18.
|
| [28] |
王茜, 尚丽丽, 晏婷婷, 等. 不同产地沉香的高效液相色谱指纹特征[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(2):150-159.
|
| [29] |
高贵宾, 钟浩, 潘雁红, 等. 生态因子对美丽箬竹盆栽苗生物量分配的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(5):35-41.
|
| [30] |
王叶, 张国林, 阳树英, 等. 生境对茶叶品质和产量影响的光合生理机制[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(11):3596-3606.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
石浥阳, 申晓林, 王佳, 等. 芳香族氨基酸解氨酶在生物制造中的应用[J]. 生物加工过程, 2024, 22(6):611-621.
|
| [34] |
方仕茂, 张拓, 杨婷, 等. 基于HPLC-FLD靶向分析古茶树游离氨基酸积累特征[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(4):1070-1077.
|
| [35] |
何相玉, 周冠军, 张新洁, 等. 氮磷添加对水曲柳人工林叶片、细根和土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (1): 73-81.
|
| [36] |
黄芳, 钱佳佳, 傅秀敏. 茶叶氨基酸合成代谢及转化研究进展[J]. 中国茶叶, 2023, 45(9):10-18.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
胡玉玲, 胡冬南, 周城师, 等. 施肥对赣无系列油茶叶片SPAD值及养分的影响[J]. 林业工程学报, 2011, 25(2):20-23.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |