 PDF(2378 KB)
PDF(2378 KB)


Effects of drought on soil particulate organic carbon and mineral-associated organic carbon in poplar plantation
XIAO Ruoyu, RUAN Honghua, LIU Huihui, FANG Yu, ZHA Quanzhi, XIE Youchao, XU Yaming, CAO Guohua, SHEN Caiqin
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 55-64.
 PDF(2378 KB)
PDF(2378 KB)
 PDF(2378 KB)
PDF(2378 KB)
Effects of drought on soil particulate organic carbon and mineral-associated organic carbon in poplar plantation
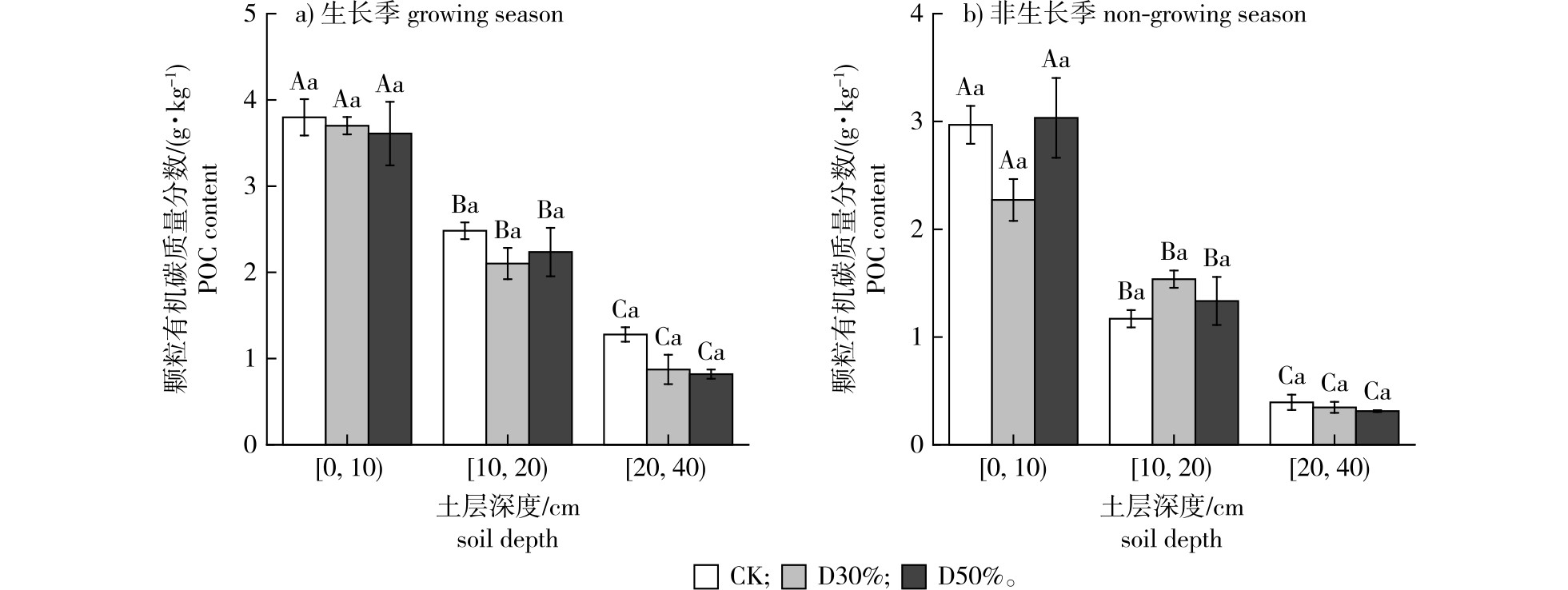
【Objective】The increasing frequency of global drought events has significantly affected the structure and function of forest ecosystems. This study aims to estimate the effects of drought on contents of particulate organic carbon (POC) and mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC) at different soil depths in poplar plantation, providing a theoretical basis for predicting the responses of forest soil organic carbon (SOC) and its stability to drought in the future.【Method】We took a 10-year-old poplar plantation in Dongtai Forest Farm, Jiangsu Province as the research object. In August 2018, three drought treatments for reducing throughfall were set up: i.e., a control treatment (CK), a moderate drought with reduced 30% throughfall (D30%), and a severe drought with reduced 50% throughfall (D50%). Three replicate sample plots were set up for each treatment with a total of nine sample plots. After four consecutive years of field controll experiments, soil samples were collected in July and November 2022, and February and April 2023 in each drought-treated sample plot to determine soil POC and MAOC contents in the growing (July 2022) and non-growing (February 2023) seasons, as well as soil physicochemical properties such as SOC, dissolved organic carbon, microbial biomass carbon, and readily oxidizable organic carbon in these four periods. Based on ANOVA, correlation analysis, and redundancy analysis, we quantified the characteristics of changes in soil POC and MAOC under drought stress and analyzed the key factors driving the variation in their contents.【Result】Drought had no significant effect on soil POC content, while its impact on soil MAOC content was constrained by season, drought degree and soil depth. Specifically, during the growing season, moderate drought (D30%) significantly increased the MAOC content in the surface soil [0,10)cm, while both drought treatments (D30% and D50%) significantly decreased the MAOC content in the middle soil layer ([10,20)cm) and lower soil layers ([20,40) cm). During the non-growing season, both drought treatments (D30% and D50%) significantly reduced the MAOC content in the surface soil, but had no significant effect on the middle and lower soil layers. Vertically, the soil POC and MAOC content decreased significantly with soil depth. The correlation results showed that POC and MAOC content were significantly and positively correlated with most soil physical and chemical properties, while were significantly and negatively correlated with bulk density and carbon to nitrogen ratio(C/N). Redundancy analysis indicated that soil microbial biomass carbon was the key factor driving the dynamic changes of soil POC and MAOC content under drought.【Conclusion】Drought had no significant effect on soil POC content in the poplar plantation; however, it significantly altered soil MAOC contents, and the effect was constrained by factors such as season, drought degree, and soil depth. This study suggests that when predicting the response of forest soil carbon pool stability to drought in the future, factors such as season, drought degree and soil depth should be fully considered.
soil organic carbon / microbial biomass carbon / season of growing / throughfall reduction / poplar plantation
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
习丹, 翁浩东, 胡亚林, 等. 林冠氮添加和林下植被去除对杉木林土壤有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(21):8525-8534.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
孙长山. 探索中国森林资源发展现状[J]. 林业勘查设计, 2020, 49(4):22-24,42.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
黄永梅, 杨智杰, 郭剑芬, 等. 隔离降雨对杉木林土壤可溶性有机碳和微生物生物量碳的影响[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2014, 9(1):38-45.
|
| [19] |
鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
柳敏, 宇万太, 姜子绍, 等. 土壤活性有机碳[J]. 生态学杂志, 2006, 25(11):1412-1417.
|
| [31] |
雷丽群, 卢立华, 农友, 等. 不同林龄马尾松人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 林业科学研究, 2017, 30(6):954-960.
|
| [32] |
汤靖文, 李晨晞, 彭政淋, 等. 氮磷钾肥对水曲柳雌雄株叶片光合生理及化学计量特征的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (2): 30-38, 46.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |