 PDF(2663 KB)
PDF(2663 KB)


Analysis of ornamental fruit characteristics in crabapple cultivars
XU Tianwei, ZHANG Wangxiang, FENG Lan, LU Xiaoji, YU Pengfei
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 183-190.
 PDF(2663 KB)
PDF(2663 KB)
 PDF(2663 KB)
PDF(2663 KB)
Analysis of ornamental fruit characteristics in crabapple cultivars
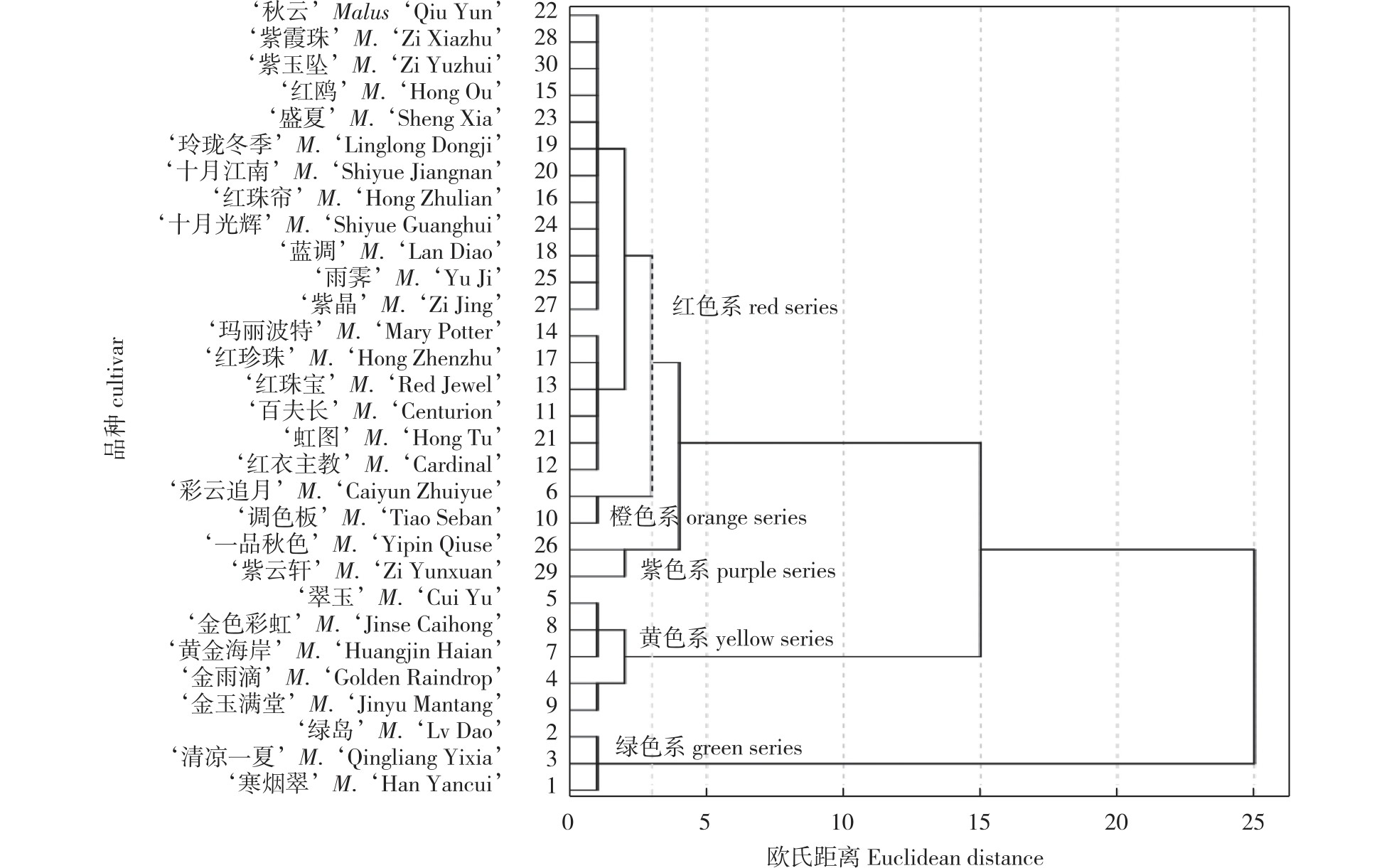
【Objective】This study investigated the ornamental characteristics of fruit color in 30 ornamental crabapple cultivars, aiming to provide references for breeding and landscape applications. 【Method】Seasonal variations in fruit color were observed to classify cultivars into color groups and determine optimal viewing periods. The diversity and temporal complementarity of fruit color within the cultivar group were systematically analyzed.【Result】The results showed that:cluster analysis of fruit color parameters (Euclidean distance = 3) categorized the cultivars into five color series: green (10.0%), yellow (16.6%), orange (6.7%), red (60.0%), and purple (6.7%).Brightness values followed the hierarchy: green series (67.7) > yellow series (64.9) > orange series (46.5) > red series (32.6) > purple series (20.5). The optimal fruit viewing period was at the same tinie frame in autumn (September-November), with cultivar diversity index showing a normal distribution pattern: early-autumn (50.0%), mid-autumn (60.0%), and late-autumn (63.3%). The average optimal viewing duration was 1.5 months, with the shortest being 1 month and the longest neaching 3 months. Based on color vividness, surface gloss, and spot presence, the ornamental value of the 30 cultivars was classified into three tiers (A-C). Top-tier (A) cultivars included Malus ‘Han Yancui’, M. ‘Red Jewel’, M. ‘Hong Ou’, M. ‘Hong Zhenzhu’, M. ‘Hong Tu’, M. ‘Sheng Xia’, M. ‘Shiyue Guanghui’, and M. ‘Yu Ji’. 【Conclusion】The crabapple cultivars exhibit high fruit color diversity, extended group viewing seasons and individual viewing periods. These multi-colored, multi-seasonal cultivars provide significant support for autumn tourism and ornamental applications, demonstrating substantial value for promoting the crabapple tourism industry.
ornamental crabapple / fruit color / optimal viewing period / cultivar diversity
| [1] |
葛红娟, 黄粤, 万述伟, 等. 观赏海棠新品种‘大棠婷靓’[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5):247-248.
|
| [2] |
李育农. 世界苹果和苹果属植物基因中心的研究初报[J]. 园艺学报, 1989, 16(2):101-108.
|
| [3] |
李育农. 苹果属植物种质资源研究[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2001.
|
| [4] |
沈红香, 张杰, 晋恺娜, 等. 观赏海棠新品种‘紫美人’[J]. 园艺学报, 2011, 38 (3):607-608.
|
| [5] |
刘胜男, 彭洁, 王瑞博, 等. 30种北美海棠表型多样性分析与观赏性综合评价[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2022:1-11. (2022-01-27). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD&filename=FZZW20220125009.
|
| [6] |
鲍嵚, 许涛, 史锋厚, 等. 观赏海棠新品种‘赞春’[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(3): 234-236.
|
| [7] |
储吴樾, 范俊俊, 张往祥. 观赏海棠花期物候稳定性及其对温度变化的响应[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5):247-248.
|
| [8] |
张往祥, 张龙, 江皓, 等. 观赏海棠新品种‘洛可可女士’[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(4):203-204.
|
| [9] |
李欣, 沈向, 张鲜鲜, 等. 观赏海棠叶、果、花色彩的数字化描述[J]. 园艺学报, 2010, 37(11): 1811-1817.
|
| [10] |
吴晓星, 刘凤栾, 房义福, 等. 36个欧美观赏海棠品种(种)应用价值的综合评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(1): 93-98.
|
| [11] |
闫淑芳, 冯树香, 李义红, 等. 基于北美海棠果实颜色特征的品种分类及呈色研究[J]. 经济林研究, 2016, 34(1):19-25,32.
|
| [12] |
张丹丹, 范俊俊, 王欢, 等. 不同观赏海棠种质果色动态变化规律研究[J]. 经济林研究, 2017, 35(3):161-167.
|
| [13] |
吴再兴, 陈玉和, 马灵飞, 等. 紫外辐照下染色竹材的色彩稳定性[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2014, 34(2):127-132.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
张往祥, 魏宏亮, 江志华, 等. 观赏海棠品种群的花期物候特征研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(4):713-725.
|
| [17] |
李扬森, 张国君, 冯树香, 等. 基于AHP观赏海棠切枝观果品种评价与筛选[J]. 河北科技师范学院学报, 2022, 36(3):16-21.
|
| [18] |
刘胜男. 观赏海棠表型多样性分析与评价[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2022.
|
| [19] |
马策, 肖长城, 胡红菊, 等. 不同颜色果袋对‘云红梨2号’果皮色泽形成的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(3):813-818.
|
| [20] |
郑暄昂, 王佳洋, 卢素文, 等. 葡萄果粉积累规律及结构分析[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2021(4):50-53.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
杜立, 段玮, 肖正, 等. 苹果斑点落叶病的发生规律与防治技术[J]. 西北园艺(果树), 2012. (6):26-27.
|
| [24] |
闫文涛, 岳强, 冀志蕊, 等. 苹果斑点落叶病的诊断与防治实用技术[J]. 果树实用技术与信息, 2019,(10):29-30.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |