 PDF(1758 KB)
PDF(1758 KB)


Effects of wild release of Elaphurus davidianus on soil ecological stoichiometric characteristics of Yancheng coastal wetlands
CHEN Li, LUAN Zhaoqing, LI Min, LI Jingtai, LIU Yao, ZHANG Chenyan, HE Xiaorou, WU Xiaowei, WU Cuiling
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 38-44.
 PDF(1758 KB)
PDF(1758 KB)
 PDF(1758 KB)
PDF(1758 KB)
Effects of wild release of Elaphurus davidianus on soil ecological stoichiometric characteristics of Yancheng coastal wetlands
【Objective】This study aimed to investigate the impacts of Elaphurus davidianus disturbance on soil ecological stoichiometry in Yancheng coastal wetlands, assess the current state of soil degradation, and provide a scientific foundation for the sustainable management of the reserve.【Method】The third core area of Yancheng Dafeng Milu National Nature Reserve was selected as the study site. Based on field surveys, the area was stratified into five disturbance intensity levels: weak (Ⅰ), mild (Ⅱ), moderate (Ⅲ), secondary heavy (IV), and severe (V). Soil physicochemical properties, including bulk density (BD), soil water content (WC), pH, the content of soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP), were measured through laboratory analyses. The effects of varying disturbance intensities on soil properties and ecological stoichiometric ratios were systematically evaluated. 【Result】(1) With the increase of E. davidianus disturbance intensity, soil BD frist decreased, and then increased, soil pH increased, while soil TN, TP content and soil WC first increased and then decreased, and SOC content showed a fluctuating trend. (2) With the increase of E. davidianus disturbance intensity, the soil C/N (mass ratio) increased, the soil N/P (mass ratio) decreased, and the soil C/P (mass ratio) fluctuated. (3) The correlations between soil C/P and SOC, and between soil N/P and TN were extremely high, and the correlation between C/N and SOC gradually decreased with the increase of E. davidianus disturbance intensity. SOC content was the main limiting factor of soil C/N and C/P, and soil TN content was the main limiting factor of soil N/P. 【Conclusion】E. davidianus disturbance not only changes the basic soil properties and ecological stoichiometric characteristics, but also changes the intensity of soil stoichiometric ratios. Moderate and mild disturbance of E. davidianus is more conducive to soil mineralization and nutrient cycling. These findings suggest that maintaining E. davidianus populations within a reasonable threshold is critical for preserving soil nutrient equilibrium in Yancheng coastal wetlands.
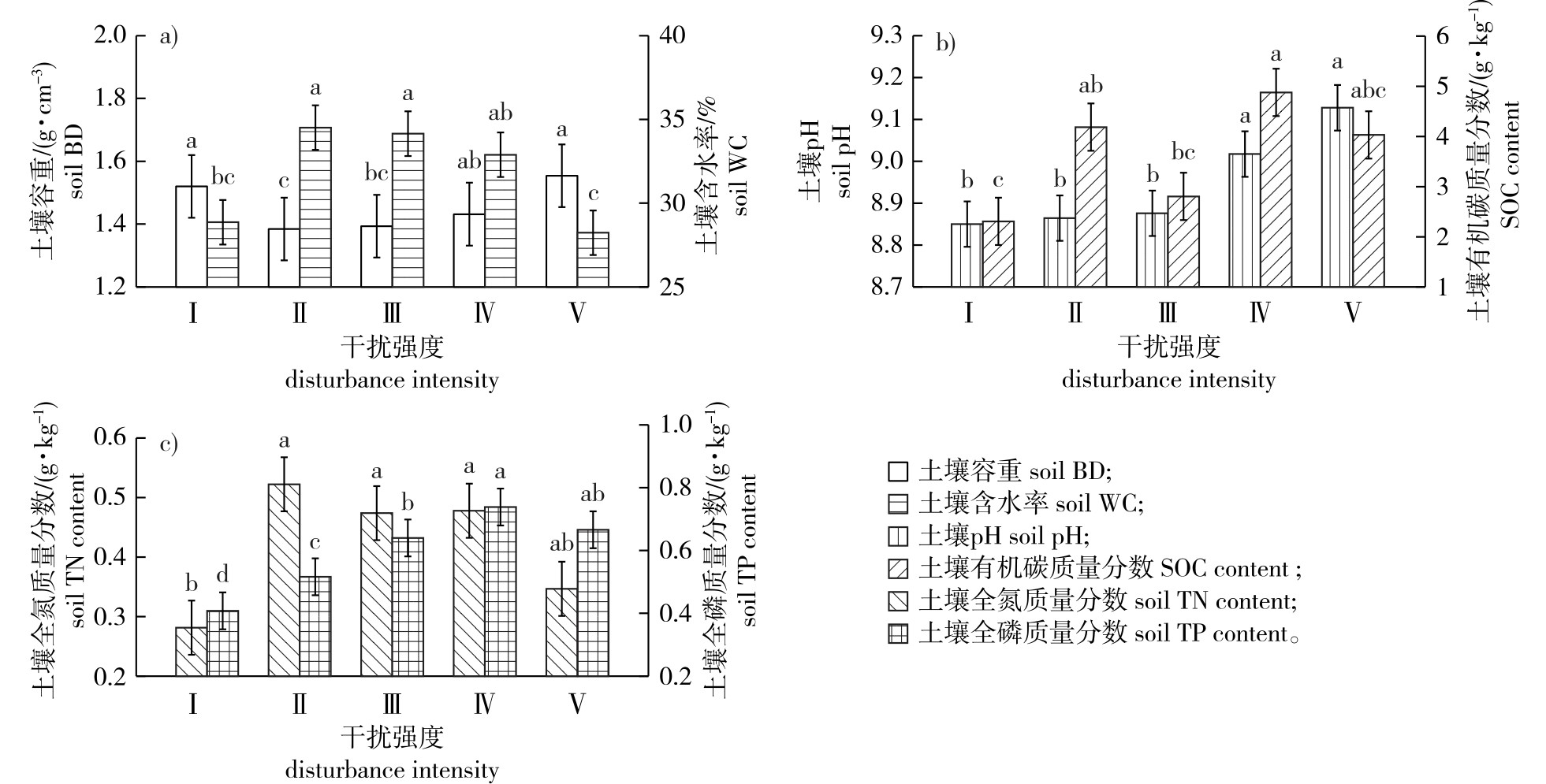
Yancheng coastal wetlands / Elaphurus davidianus(elk) / soil basic properties / ecological stoichiometric characteristics
| [1] |
王振, 王子煜, 韩清芳, 等. 黄土高原苜蓿草地土壤碳、氮变化特征研究[J]. 草地学报, 2013, 21(6): 1073-1079.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
盖杨菊, 刘爽, 张昆, 等. 围栏禁牧对纳帕海湿地土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(10): 2351-2358.
|
| [4] |
王军, 满秀玲. 去除凋落物和草毡层对寒温带典型森林土壤氮素的短期影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (4): 1-9.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
刘丝雨, 李晓兵, 李梦圆, 等. 内蒙古典型草原植被和土壤特性对放牧强度的响应[J]. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(9): 23-31.
|
| [8] |
刘忆轩, 李多才, 侯扶江. 甘肃马鹿春秋季放牧对高寒草原土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2019, 36(2): 273-283.
|
| [9] |
朱明淏, 刘艳菊, 张婷婷, 等. 不同栖息环境下麋鹿活动对土壤理化特性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(1): 208-217.
|
| [10] |
张亮, 沈潮, 邓杰, 等. 放牧干扰对草地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 防护林科技, 2016(12): 1-4, 17.
|
| [11] |
王东波, 陈丽. 放牧对草地生态系统土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 内蒙古科技与经济, 2006(10): 105-106.
|
| [12] |
刘玉祯, 刘文亭, 杨晓霞, 等. 放牧对全球草地生态系统碳氮磷化学计量特征影响的Meta分析[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(5): 1251-1259.
|
| [13] |
王立波, 姜慧, 安玉亭, 等. 中国麋鹿种群现状分析及保护对策探讨[J]. 野生动物学报, 2020, 41(3): 806-813.
|
| [14] |
安玉亭, 刘彬, 王立波, 等. 不同麋鹿干扰强度对栖息地土壤理化特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(11): 3571-3578.
|
| [15] |
张怀胜. 石首麋鹿栖息地生态环境评价研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2020.
|
| [16] |
周存宇, 费永俊, 吴雷, 等. 麋鹿放养对天鹅洲草地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(4): 115-121.
|
| [17] |
么秀颖, 闫丹丹, 李静泰, 等. 盐城大丰麋鹿自然保护区滨海湿地土壤有机碳分布特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2022, 44(3): 101-108.
|
| [18] |
徐安宏, 俞晓鹏. 大丰麋鹿保护现状与可持续发展策略探讨[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(5): 107-109.
|
| [19] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [20] |
丁小慧, 宫立, 王东波, 等. 放牧对呼伦贝尔草地植物和土壤生态化学计量学特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(15): 4722-4730.
|
| [21] |
戎郁萍, 韩建国, 王培, 等. 放牧强度对草地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2001, 23(4): 41-47.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
杨林, 马秀枝, 李依倩. 放牧对荒漠草原克氏针茅种群和土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(2): 328-334.
|
| [24] |
张旭冉, 张卫青, 王海茹, 等. 克氏针茅草原土壤生态化学计量特征对放牧强度的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(13): 5309-5316.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
张国斌, 薛建辉, 吴永波. 半圈养状态下麋鹿对生境的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23(7): 180-184.
|
| [27] |
李云龙, 许益伟, 郁洁, 等. 蚯蚓粪施用对滨海盐碱地土壤质量及玉米产量的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(11): 2053-2061.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
方昕, 郭雪莲, 郑荣波, 等. 不同放牧干扰对滇西北高原泥炭沼泽土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(2): 9-14.
|
| [30] |
郝建锋, 周润惠, 姚小兰, 等. 二代野猪放牧对夹金山针阔混交林物种多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(2): 197-207.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
安钰, 安慧, 李生兵. 放牧对荒漠草原土壤和优势植物生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 94-102.
|
| [33] |
高巧静, 朱文琰, 侯将将, 等. 放牧强度对高寒草甸植物叶片生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(3): 45-50.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
吴雨晴, 田赟, 周建琴, 等. 不同放牧制度草地土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2019, 25(4): 801-807.
|
| [36] |
李岚. 滩羊放牧对典型草原生态化学计量特征和多功能性的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021.
|
| [37] |
张建文, 徐长林, 杨海磊, 等. 高寒草甸冷季放牧对凋落物分解及C、N、P化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2017, 34(10): 2009-2016.
|
| [38] |
蓝芙宁, 李衍青, 赵一, 等. 放牧对峰丛洼地植物-土壤C、N、P化学计量特征的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(5): 742-751.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |