 PDF(4909 KB)
PDF(4909 KB)


The relationship between bamboo shoot quality and soil nutrients in severely degraded Phyllostachys violascens forests with mulching
FAN Lili, LI Yuxin, CHEN Shuanglin, WANG Sheping, ZHANG Jingrun, GUO Ziwu
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 188-195.
 PDF(4909 KB)
PDF(4909 KB)
 PDF(4909 KB)
PDF(4909 KB)
The relationship between bamboo shoot quality and soil nutrients in severely degraded Phyllostachys violascens forests with mulching
【Objective】 Forest degradation leads to adverse changes in soil characteristics in mulched Phyllostachys violascens forests, negatively impacting bamboo shoot quality. This study aims to investigate the key soil nutrients affecting bamboo shoot quality in degraded P. violascens forests, providing scientific insights for the restoration and sustainable management of these forests. 【Method】The research examined severely degraded P. violascens and normal bamboo forests, comparing differences in bamboo shoot appearance, nutritional quality, and taste quality. Additionally, the study analyzed the constraining relationship between these qualities and soil nutrients. 【Result】After forest degradation, the soil pH significantly decreased by 65.42% compared to the normal bamboo forest (P<0.05). However, the total and available nutrient content significantly increased (P < 0.05). In degraded forests, the fresh weight, base diameter, and edibility rate of bamboo shoots was decreased compared to those in normal bamboo forests. However, the height-diameter ratio and shoot sheath color factors increases. Notably, shoot sheath color significantly responded to forest degradation (P<0.05). Protein, fat, starch, and vitamin C contents of bamboo shoots in degraded bamboo forests significantly decreased compared to those in normal bamboo forests (P<0.05), while the lignin and cellulose contents significantly increased (P< 0.05). In degraded forests, the total acid, oxalic acid, and tannin contents of bamboo shoots significantly increased compared to normal bamboo forests (P<0.05), whereas the soluble sugar and sugar-acid ratio significantly decreased (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in the amino acid composition and proportion between both forest types. Correlation and principal component analysis indicate that soil pH significantly influenced the nutritional quality and formation of sugar-acid taste compounds in bamboo shoots, while nitrogen and phosphorus were crucial for influencing color, roughness, and the formation of acidic and astringent taste compounds in bamboo shoots. 【Conclusion】The severe degradation of P. violascens forests significantly deteriorates bamboo shoot appearance, nutritional quality, and palatability. This deterioration is closely associated with decreased soil pH and increased nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients.
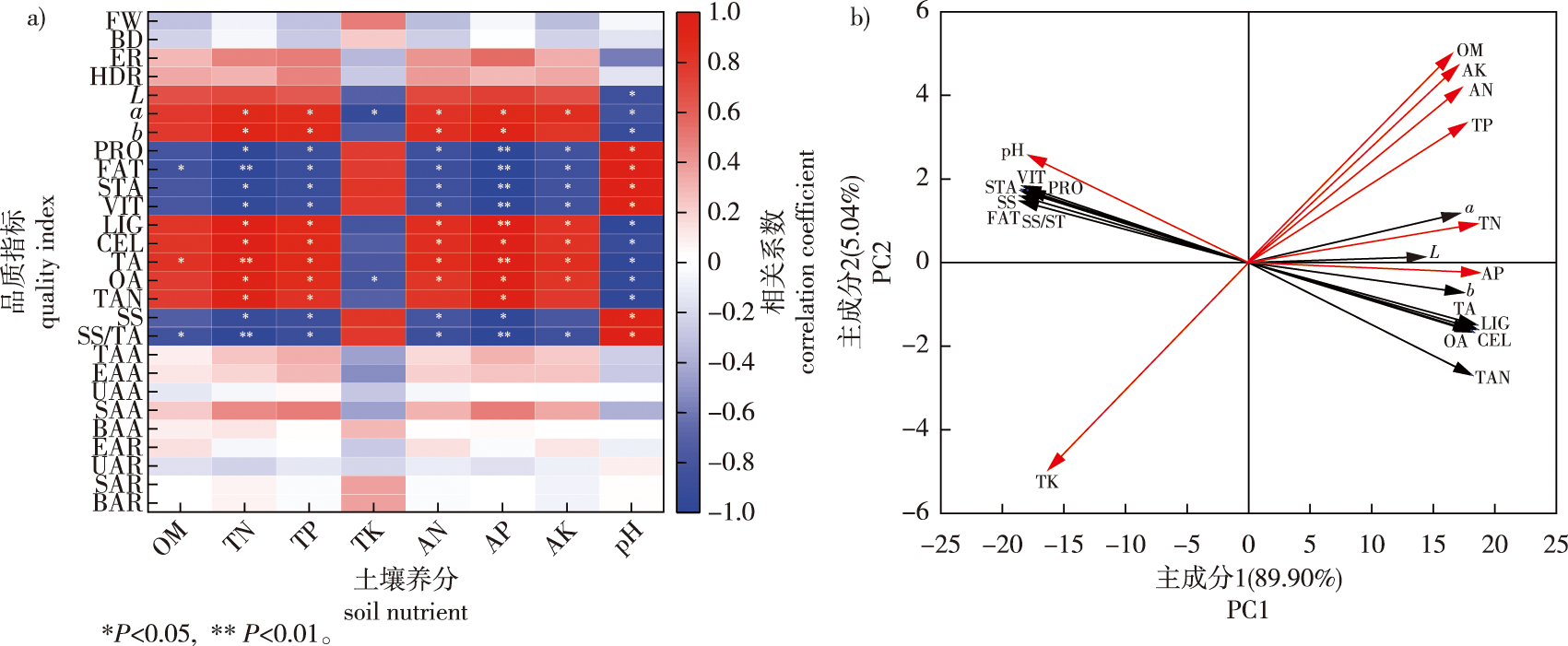
bamboo forest degradation / Phyllostachys violascens / bamboo shoots / nutritional quality / flavor compounds / soil nutrients
| [1] |
杨丽婷, 谢燕燕, 俞文仙, 等. 长期林地覆盖经营对雷竹林自然笋外观、营养和食味品质的影响[J]. 竹子学报, 2021, 40(3):7-12.
|
| [2] |
郭子武, 王为宇, 杨清平, 等. 林地覆盖对雷竹林土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 广西植物, 2013, 33(5):627-632.
|
| [3] |
郭子武, 俞文仙, 陈双林, 等. 林地覆盖对雷竹林土壤微生物特征及其与土壤养分制约性关系的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(18):5623-5630.
|
| [4] |
翟婉璐, 杨传宝, 张小平, 等. 林地覆盖经营对雷竹生物量及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(4):1147-1155.
|
| [5] |
翟婉璐, 钟哲科, 高贵宾, 等. 覆盖经营对雷竹林土壤细菌群落结构演变及多样性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(9):133-142.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
刘丽, 陈双林, 李艳红. 基于林分结构和竹笋产量的有机材料覆盖雷竹林退化程度评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2010, 27(1):15-21.
|
| [8] |
刘丽, 陈双林. 有机材料林地覆盖对雷竹林生态系统的负面影响研究综述[J]. 广西植物, 2009, 29(3):327-330.
|
| [9] |
李苑, 张令, 黎祖尧, 等. 不同产地厚竹笋的营养成分及其对土壤养分的响应特征[J]. 经济林研究, 2017, 35(4):147-154.
|
| [10] |
郑蓉. 产地绿竹笋品质及土壤养分的主成分与典型相关分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2012, 29(5):710-714.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
刘亚迪, 范少辉, 蔡春菊, 等. 地表覆盖栽培雷竹林植被退化特征分析[J]. 竹子学报, 2017, 36(3):29-38.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
郭子武, 杨丽婷, 林华, 等. 沙县苦竹笋外观、营养和食味品质变异的海拔效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(1):83-88.
|
| [19] |
环境保护部. 土壤有机碳的测定重铬酸钾氧化-分光光度法:HJ 615—2011[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2011.
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Soil-determination of organic carbon-potassium dichromate oxidation:HJ 615—2011[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2011.
|
| [20] |
国家林业局. 森林土壤磷的测定:LY/T 1232—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Phosphorus determination methods of forest soils:LY/T 1232—2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [21] |
国家林业局. 森林土壤氮的测定:LY/T 1228—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Nitrogen determination methods of forest soils:LY/T 1228—2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015.
|
| [22] |
国家林业局. 森林土壤钾的测定:LY/T 1234—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Potassium determination methods of forest soils:LY/T 1234—2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [23] |
国家林业局. 森林土壤pH值的测定:LY/T 1239—1999[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of pH value in forest soil:LY/T 1239—1999[S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 2015.
|
| [24] |
祝小祥, 谢国雄, 徐进, 等. 临安市雷竹林土壤肥力分析与培肥措施[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(28):72-76.
|
| [25] |
孙晓, 庄舜尧, 刘国群, 等. 集约经营下雷竹林土壤酸化的初步研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(6):1339-1343.
|
| [26] |
杨圆圆, 于世河, 卜鹏图, 等. 不同培育模式下日本落叶松林灌草和土壤养分特征研究[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (6): 12-25.
|
| [27] |
徐森, 杨丽婷, 陈双林, 等. 竹笋适口性形成及其主要影响因素研究综述[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(2):403-411.
|
| [28] |
何玉友, 陈双林, 郭子武, 等. 覆盖雷竹笋色泽与品质相关性分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(6):157-167.
|
| [29] |
徐森, 谷瑞, 陈双林, 等. 毛竹春笋营养、食味和基于重金属的安全品质的海拔效应[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2021, 43(1):144-152.
|
| [30] |
时俊帅, 章超, 陈双林, 等. 高节竹笋出土后外观、营养和食味品质的时序变化[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(6):137-143.
|
| [31] |
徐森, 董亚文, 陈双林, 等. 6属22竹种箨叶养分与竹笋食味品质的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(6):1373-1380.
|
| [32] |
郭子武, 江志标, 陈双林, 等. 覆土栽培对高节竹笋品质的影响[J]. 广西植物, 2015, 35(4):515-519.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
徐森, 谷瑞, 陈双林, 等. 覆盖下雷竹笋箨叶性状和食味品质的变化及其相关性[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(9):34-41.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
魏昊泰, 李怡雪, 赵嘉诺, 等. 水分条件对不同发育阶段番茄果实外观、营养及风味品质的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(9):1701-1710.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |