 PDF(6192 KB)
PDF(6192 KB)


The identification and functional analysis of BZR1 genes in yellowhorn
XU Huihui, BAN Zhuo, WANG Chenxue, BI Quanxin, LIU Xiaojuan, WANG Libing
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 12-22.
 PDF(6192 KB)
PDF(6192 KB)
 PDF(6192 KB)
PDF(6192 KB)
The identification and functional analysis of BZR1 genes in yellowhorn
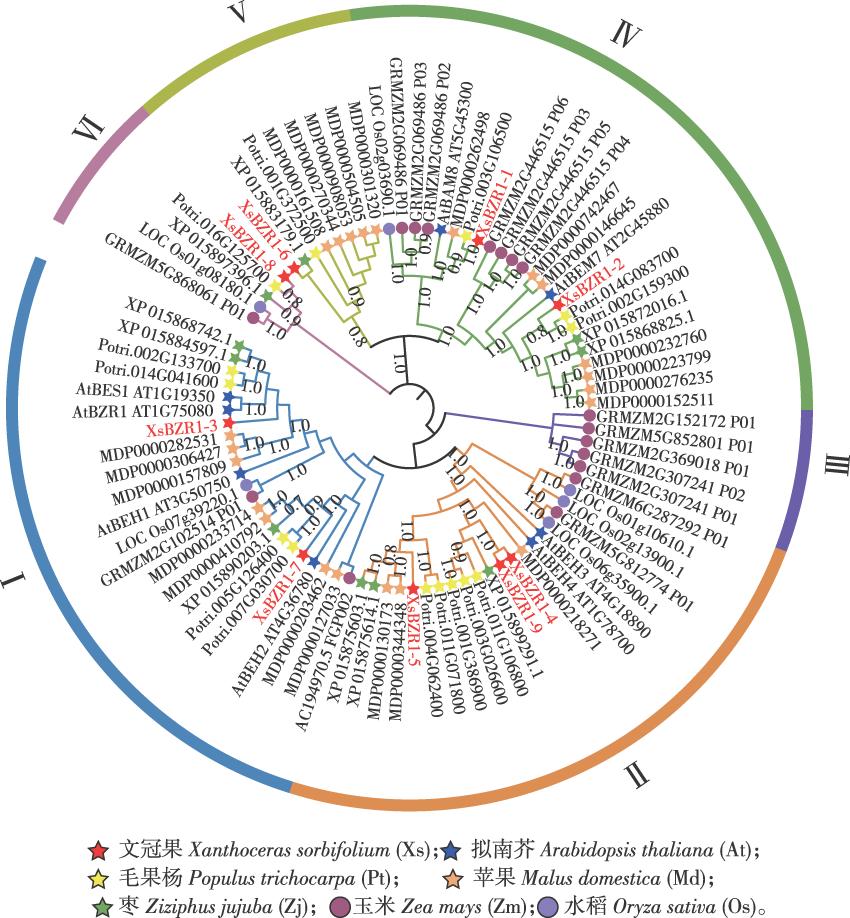
【Objective】This study aimed to systematically characterize the BZR1 transcription factor family in yellowhorn (Xanthoceras sorbifolium) and elucidate its functional roles in abiotic stress response, thereby providing insights for breeding stress-resistant cultivars.【Method】Genome-wide identification of XsBZR1 genes was performed using bioinformatics tools. Subcellular localization of XsBZR1 proteins was validated via 35S::XsBZR1-eYFP fusion constructs. Expression profiles under abiotic stresses (low temperature, salt, drought) and abscisic acid (ABA) treatment were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Functional validation was conducted by overexpressing XsBZR1- 9 in Arabidopsis thaliana and assessing salt tolerance phenotypes.【Result】Nine XsBZR1 genes (XsBZR1-1 to XsBZR1-9) were identified and distributed unevenly across six chromosomes. Phylogenetic and synteny analyses revealed close evolutionary relationships with dicotyledonous BZR1 orthologs. Promoter regions harbored abundant cis-regulatory elements associated with light responsiveness (48.9%), hormone signaling (35.0%) and stress adaptation (24.6%). The nuclear localization of all XsBZR1 proteins was experimentally confirmed. Differential expression patterns were observed under stress conditions: low temperature (4 ℃) rapidly induced eight XsBZR1 genes (1.3- to 6.0-fold upregulation at 3 h; P<0.05), except XsBZR1-7. Salt stress (150 mmol/L NaCl) suppressed XsBZR1-3/4/5/7 but strongly upregulated XsBZR1-1 (26.1-fold) and XsBZR1-9 (19.6-fold) at 9 h (P<0.001). Drought stress (mass fraction 25% PEG6000) elevated XsBZR1- 3/7/8/9 expression (>1.9-fold at 9 h), while others remained stable. ABA treatment (100 μmol/L) universally induced XsBZR1 genes, with XsBZR1-8 showing a 35.4-fold increase (P<0.001).Transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing XsBZR1-9 exhibited enhanced salt tolerance, with taproot lengths twice that of the wild-type under 100 mmol/L NaCl (P<0.01).【Conclusion】The XsBZR1 gene family plays pivotal roles in yellowhorn’s abiotic stress response, with XsBZR1-9 demonstrating significant potential for improving salt tolerance. These findings advance the molecular understanding of stress adaptation mechanisms in woody plants and provide targets for precision breeding.
yellowhorn(Xanthoceras sorbifolium) / BZR1 transcription factor / abiotic stress tolerance / gene overexpression / salt stress response / XsBZR1- 9
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
王孟珂, 杨晓明, 汪贵斌, 等. 外施24-表油菜素内酯(EBR)对银杏叶片发育和生理特征影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):81-87.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
沈春洋. 番茄BZR基因家族生物信息学分析及抗逆基因功能鉴定[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2022.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
麻云霞. 文冠果种子特性变异及优良砧用种源选择[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021.
|
| [21] |
刘志. 文冠果WRKY转录因子家族的鉴定及非生物胁迫响应模式分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020.
|
| [22] |
常巧颖. 文冠果bZIP转录因子家族鉴定和非生物胁迫应答模式分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020.
|
| [23] |
杨娟, 姜阳明, 周芳, 等. PEG模拟干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性玉米品种苗期形态与生理特性的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2021(1):82-89.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
周晔, 赵璇, 王璐, 等. 植物BZR家族基因调控非生物胁迫应答和生长发育的研究进展[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2020, 42(4):499-511.
|
| [27] |
王黎明, 杨瑞珍, 孙加强. 油菜素内酯调控作物农艺性状和非生物胁迫响应的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(1):34-49.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
尹魁林, 程莎莎, 艾长丰, 等. 枣BZR基因家族的鉴定及其在果实发育中的表达分析[J/OL]. 分子植物育种:1-13[2024-03-26].
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
明川. 玉米BES1/BZR1转录因子基因鉴定[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
杜巧丽, 刘均霞, 陈美晴, 等. 高粱BR信号转录因子BZR1基因家族的鉴定及激素应答分析[J]. 植物保护学报, 2022, 49(3):848-856.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
陈旭, 沈春洋, 莫福磊, 等. 番茄BZR基因家族鉴定及非生物胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52(11):9-17.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |