 PDF(1847 KB)
PDF(1847 KB)


Comparative chloroplast genomics of the important resource plant Kadsura coccinea
ZHAI Xuechang, PENG Li, YAN Haifei, ZHU Kefan, ZHANG Shuyan, ZHANG Caiyun, LU Xiankai
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6) : 71-78.
 PDF(1847 KB)
PDF(1847 KB)
 PDF(1847 KB)
PDF(1847 KB)
Comparative chloroplast genomics of the important resource plant Kadsura coccinea
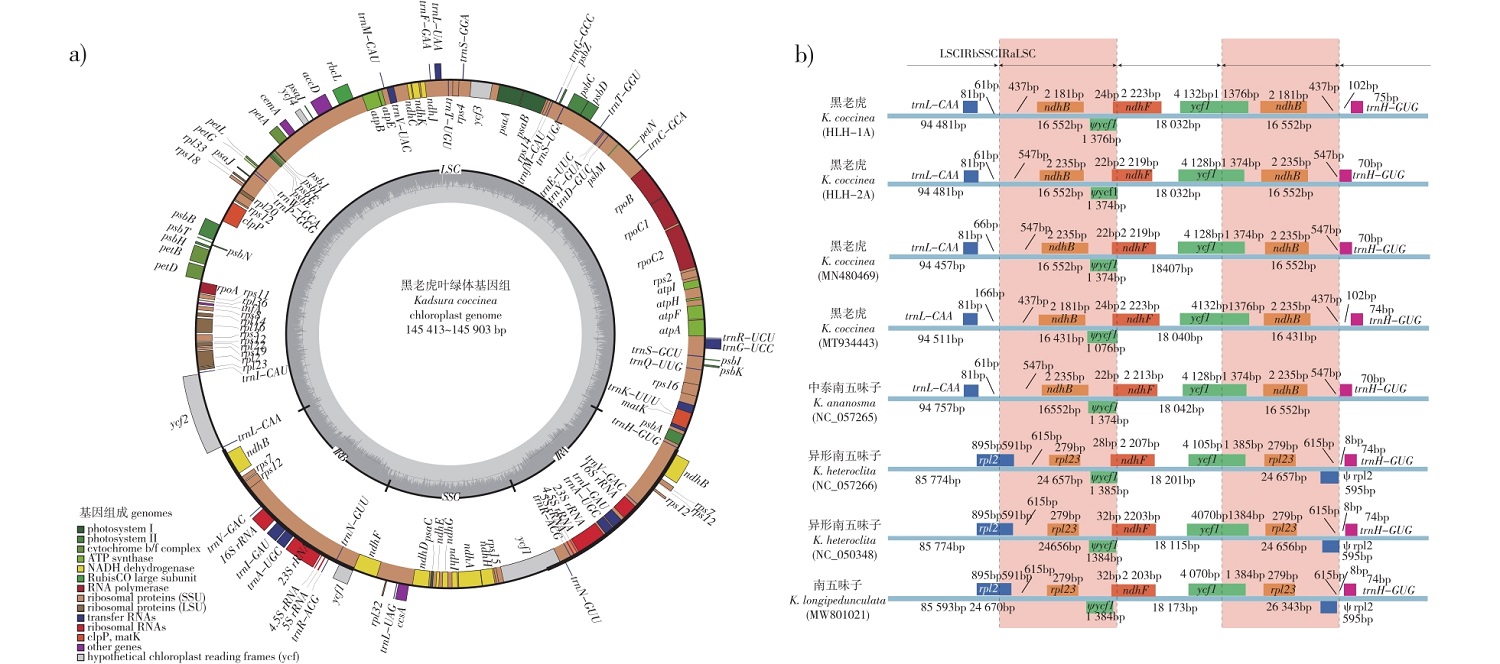
【Objective】This study aims to investigate the chloroplast genomes and SSR loci of Kadsura coccinea, an important plant resource in China, to establish a basis for assessing its genetic diversity and germplasm resources.【Method】The study obtained and analyzed the chloroplast genomes of five individuals of K. coccinea through genetical annotation, nucleotide polymorphism analysis, and SSR analysis using bioinformatics methods. Additionally, the phylogenetic analysis of Kadsura were reconstructed using two Schisandra spp. as outgroups.【Result】The chloroplast genome of K. coccinea showed a typical quadripartite structure, with genome lengths ranging from 145 413 to 145 903 base pairs (bp). The large single-copy region (LSC) spaned from 94 457 to 94 757 bp, while the small single-copy region (SSC) encompassed 18 032 to 18 047 bp. It encodes a total of 125 genes, including 82 protein-coding genes, 35 tRNA genes, and 8 rRNA genes. The genome had a total GC content of 39.7% and demonstrated substantial nucleotide polymorphisms (Pi > 0.03) in the intergenic regions of petN-psbM and trnS-GCU-trnG-UCC. A total of 212 single sequence repeat (SSR) loci were identified across the chloroplast genomes of this species. Mononucleotide repeats were the most prevalent, followed by trinucleotide repeats, and pentanucleotide repeats were the least frequent. Among these loci, 24 polymorphic SSR loci were found among five individuals of K. coccinea, indicating their potential utility in future. Phylogenetic analysis robustly clusters K. coccinea individuals into a distinct group, revealing no close relationship with other congeneric species.【Conclusion】This study presents the first systematic comparison of chloroplast genomes among multiple K. coccinea individuals. Our findings identified highly variable regions and SSR loci that can be valuable for evaluating the genetic diversity and germplasm resource of this species.
Kadsura coccinea / plastid genome / genetic diversity / SSR loci / phylogeny
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
林祁, 段林东, 姚炳矾. 南五味子属(五味子科)三种植物之补记[J]. 植物分类学报, 2005, 43(6):567-570.
|
| [3] |
黄珊珊, 黄晓玲, 宋卉, 等. 中药黑老虎的研究进展[J]. 海峡药学, 2021, 33(11):38-40.
|
| [4] |
苏维, 王欣悦, 付港, 等. 南五味子属植物的化学成分、药理作用及临床应用研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2024, 49(1):26-38.
|
| [5] |
杨赛男, 戴斌, 潘清平, 等. 黑老虎植物资源利用研究进展[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 2022, 9(3):112-120.
|
| [6] |
杨芝干. 地标奇果:通道“黑老虎”[J]. 生命世界, 2019(9):66-69.
|
| [7] |
林旭俊, 陆文, 李善志, 等. 药用植物黑老虎的资源调查[J]. 热带林业, 2019, 47(2):34-36.
|
| [8] |
韦霄, 梁惠凌, 唐辉, 等. 广西南五味子属植物的分布与利用[J]. 广西农业科学, 2006, 37(2):117-119.
|
| [9] |
邹建文, 罗先权, 饶红欣, 等. 常绿木质藤本植物黑老虎基因组SSR特征分析及引物开发[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(4):130-138.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
赵儒楠, 褚晓洁, 刘维, 等. 鹅耳枥属树种叶绿体基因组结构及变异分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(2):25-34.
|
| [13] |
袁钰晨, 谢旭强, 徐立清, 等. 不同年龄阶段胡桃楸天然更新幼树的光合生理特性[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39(4):29-37.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
邓叶, 李翔, 李平, 等. 黑老虎种质资源与分子生物学研究进展[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 2024, 11(1):96-104.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
杨圆圆, 于世河, 卜鹏图, 等. 不同培育模式下日本落叶松林灌草和土壤养分特征研究[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39(6):12-25.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
刘玉壶. 木兰科[C]//中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
毕海燕, 林祁, 刘长江, 等. 南五味子属(五味子科)的种子形态及其分类学意义[J]. 植物分类学报, 2002, 40(6):501-510.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |