 PDF(2526 KB)
PDF(2526 KB)


A glutathione-stabilized fluorescent copper nanoclusters-based rapid detection method for environmental residue ofloxacin
DAI Jing, JIANG Wenping, WANG Anqi, YANG Jin, XU Erman, YANG Yihe, LI Wei, LI Taihua
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6) : 225-230.
 PDF(2526 KB)
PDF(2526 KB)
 PDF(2526 KB)
PDF(2526 KB)
A glutathione-stabilized fluorescent copper nanoclusters-based rapid detection method for environmental residue ofloxacin
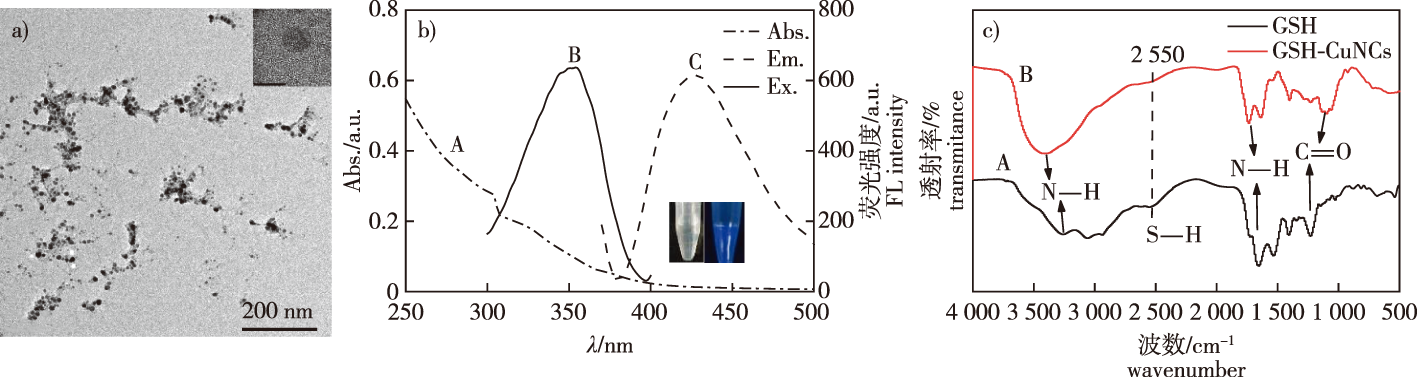
【Objective】This study aims to develop a simple, rapid and sensitive fluorescence detection method for residual ofloxacin (OFL) in liquid samples, broaden the applications of copper nanoclusters and providing a theoretical foundation for portable diagnostic devices.【Method】A one-pot synthesis method was employed to prepare glutathione-stabilized copper nanoclusters (GSH-CuNCs) with excellent water solubility and optical properties. In an acidic condition, GSH-CuNCs and OFL have maximum emission peaks at 425 nm and 510 nm respectively upon excitation wavelength at 340 nm. With OFL, the green fluorescence intensity of the system at 510 nm was significantly enhanced compared to GSH-CuNCs, meanwhile the blue fluorescence intensity at 425 nm was slightly decreased. Thus, a GSH-CuNCs-based ratiometric fluorescent probe was constructed for the simple rapid, sensitive and selective detection of residual OFL in the enviroment.【Result】After optimization of the experimental conditions, the ratiometric fluorescent probe exhibited a linear response to OFL concentrations in the range of 0.005-10.000 μmol/L, with a detection limit (LOD) of 1.5 nmol/L. This ratiometric probe has been applied to detect OFL in the actual spiked water and milk samples. Applying with spiked real sample, the recovery rate of OFL was 93.6%-103.3%, and relative standard deviations (RSD) were all less than 10%.【Conclusion】The developed ratiometric fluorescent probe offers the advantages of simplicity, low cost, high sensitivity, and excellent selectivity, enabling rapid and accurate detection of residual ofloxacin in real-world applications.
ofloxacin(OFL) residues / copper nanoclusters(CuNCs) / ratiometric fluorescent probe / fluoroquinolones(FQs) / one-pot synthesis method / rapid detection
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
徐健恒, 黄锦楼, 杨晓进, 等. 华北典型地区农村生活污水中药品和个人护理产品(PPCPs)污染特征与生态风险评价[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2025, 41(8):1002-1012.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
李威, 李佳熙, 李吉平, 等. 我国不同环境介质中的抗生素污染特征研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(1):205-214.
抗生素在人类医疗和畜禽水产养殖中发挥了重要作用,但由于其大量使用带来的环境残留和生态风险也引起了广泛关注。笔者分析总结了近10年我国地表水、土壤和动植物体内等环境介质中的抗生素污染特征发现:① 地表水和沉积物中不同程度地检出了磺胺类(SAs)、喹诺酮类(QNs)、大环内酯类(MLs)和四环素类(TCs)抗生素,其中海河、辽河和珠江的抗生素污染较为严重;② 耕地土壤也受到不同程度的抗生素污染,主要污染因子为QNs和TCs,北方和珠江三角洲区域的耕地土壤中抗生素污染较为严重;③ 鱼类和蔬菜植物中也检出了抗生素残留,主要的污染物为QNs。笔者认为,在今后的研究中,应进一步加强对水体沉积物、畜禽粪便、土壤和蔬菜中抗生素的污染特征的监控,特别是要深入研究抗生素在水-沉积物体系、畜禽粪便-土壤体系、土壤-植物体系中的迁移转化,以期准确了解抗生素的环境行为,为其生态风险评估提供依据。
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
王雪, 王安琪, 钱美汝, 等. 基于比率型荧光探针和增敏剂快速高灵敏检测美他环素[J]. 分析化学, 2023, 51(4):531-538.
|
| [11] |
韩冰雁, 侯绪芬, 相荣超, 等. 基于铜纳米簇的聚集诱导发光检测铅离子[J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(1):23-27.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |