 PDF(14537 KB)
PDF(14537 KB)


Research on the spatial correlation between forest carbon sequestration and low-carbon economy
ZHONG Yi, ZENG Weizhong, WANG Jie
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 276-284.
 PDF(14537 KB)
PDF(14537 KB)
 PDF(14537 KB)
PDF(14537 KB)
Research on the spatial correlation between forest carbon sequestration and low-carbon economy
【Objective】Strengthen the research on the interactive mechanisms and spatial correlation between forest carbon sinks and low-carbon economic development, aiming to provide a scientific foundation for regional forest resource management.【Method】This study leveraged forest carbon sink and low-carbon economy system indicator data from 31 provinces (municipalities and autonomous regions) in China, spanning the years 2008 to 2018. Utilizing a comprehensive evaluation model, kernel density estimation, and bivariated spatial autocorrelation, we analyzed the spatiotemporal dynamics of forest carbon sinks and low-carbon economies, as well as their spatial correlation characteristics.【Result】The spatial distribution of forest carbon sinks in China is transitioning from a “dual-core dominance” model to a more balanced “dual-core with a secondary core” pattern. Concurrently, the level of low-carbon economic development continues to rise, with its spatial pattern evolving from a “strip-cluster-area” structure. At the macro level, the Moran’s I values for 2008, 2013, and 2018 are -0.24, -0.26, and -0.26, respectively. These values underscore the persistent presence of the “resource curse” phenomenon. At the micro level, the spatial patterns of forest carbon sinks and low-carbon economies exhibit distinct aggregation characteristics: low-low and high-low aggregations are observed in contiguous distributions, while high-high and low-high aggregations appear in dispersed distributions.【Conclusion】It is imperative to seize the strategic opportunity of the dual-carbon goals (carbon peak and neutrality), leverage our forest resource advantages to facilitate a well-planned low-carbon economic transition, establish exemplary models of dual-driven development featuring both emission reduction and carbon sink enhancement, and explore regionally differentiated approaches to balance forest carbon sequestration with low-carbon economic development.
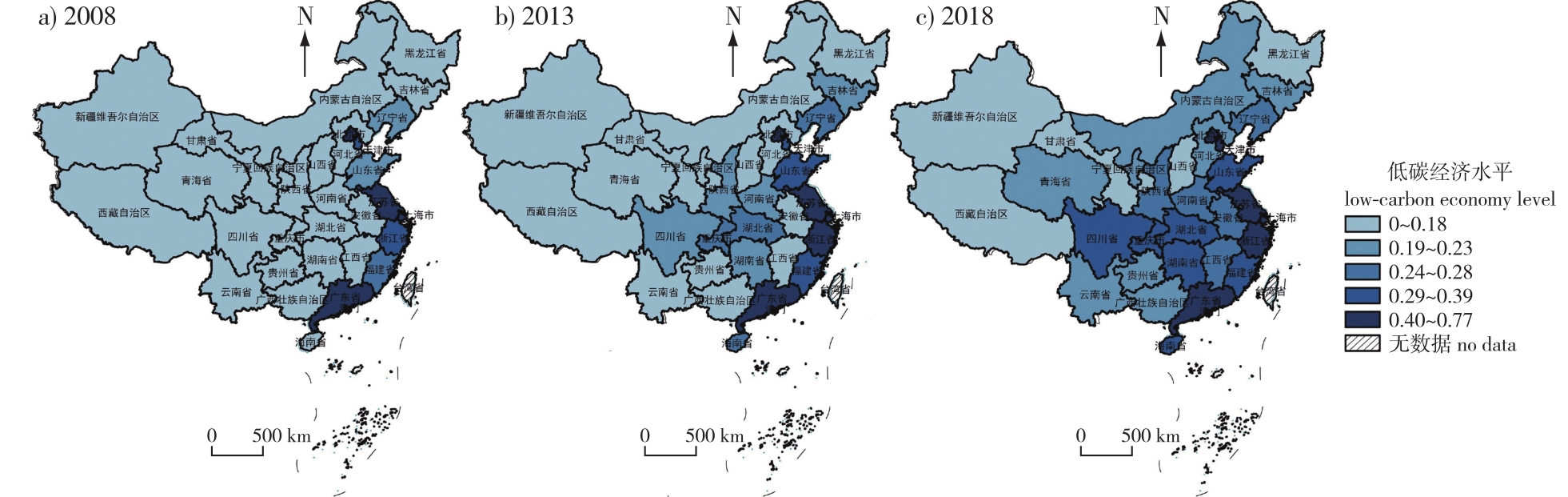
forest carbon sequestration / low-carbon economy / spatial correlation / Moran’s I index
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
丁骁. 生态环境部:党的十八大以来我国碳排放强度下降34.4%[EB/OL]. (2022-09-15) [2024-07-30]. https://news.cnr.cn/native/gd/20220915/t20220915_526010081.shtml.
|
| [3] |
郭文强, 史瑞雪, 雷明, 等. 中国省际碳排放空间关联网络结构特征及碳平衡分区[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(18): 1-18.
|
| [4] |
师玮, 赵思雪, 乔富伟, 等. 碳中和背景下的中国碳汇林业生产效率时空分异及影响因素研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(3):254-264.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
彭红军, 刘奕辰, 吴祎扬, 等. 林业碳汇市场化交易机制研究[J/OL]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版).
|
| [7] |
张娜, 孙芳城, 胡钰苓. 长江经济带碳排放效率的时空演变、区域差异及影响因素研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2024, 33(6): 1325-1339.
|
| [8] |
邝嫦娥, 李文意, 黄小丝. 长江中游城市群碳排放强度与经济高质量发展耦合协调的时空演变及驱动因素[J]. 经济地理, 2022, 42(8): 30-40.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
何金廖, 彭珏, 胡浩. 设计创意人才的空间集聚及其影响机理研究——基于城市舒适性视角[J]. 地理科学, 2021, 41(9): 1525-1535.
|
| [11] |
李卫兵, 邹萍. 空气污染与居民心理健康——基于断点回归的估计[J]. 北京理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2019, 21(6): 10-21.
|
| [12] |
李炳军, 曹斌, 周方. 创新生态系统共生、绿色技术创新与低碳经济高质量发展[J]. 统计与决策, 2023, 39(16): 48-53.
|
| [13] |
任保平. 新时代中国经济从高速增长转向高质量发展:理论阐释与实践取向[J]. 学术月刊, 2018, 50(3): 66-74,86.
|
| [14] |
陈建成, 程宝栋, 印中华. 生态文明与中国林业可持续发展研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2008, 19(4): 139-142.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
付伟, 李龙, 罗明灿, 等. 省域视角下中国森林碳汇空间外溢效应与影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(10): 4074-4085.
|
| [17] |
葛立宇, 莫龙炯, 黄念兵. 数字经济发展、产业结构升级与城市碳排放[J]. 现代财经(天津财经大学学报), 2022, 42(10): 20-37.
|
| [18] |
王雅莉, 侯林岐, 朱金鹤. 城市创新能否助力低碳经济发展——创新型城市试点政策对碳强度的影响评估及机制分析[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2022, 39(18): 39-49.
|
| [19] |
张伟, 朱启贵, 高辉. 产业结构升级、能源结构优化与产业体系低碳化发展[J]. 经济研究, 2016, 51(12): 62-75.
|
| [20] |
刘潭, 徐璋勇. 中国绿色金融与低碳经济耦合协调及时空特征[J]. 统计与决策, 2024, 40(8): 144-149.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |