 PDF(1893 KB)
PDF(1893 KB)


The vertical distribution patterns of soil exchangeable cations in typical southern subtropical forests of China
LIU Rongzhen, LIU Peiling, LU Xiankai
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 104-111.
 PDF(1893 KB)
PDF(1893 KB)
 PDF(1893 KB)
PDF(1893 KB)
The vertical distribution patterns of soil exchangeable cations in typical southern subtropical forests of China
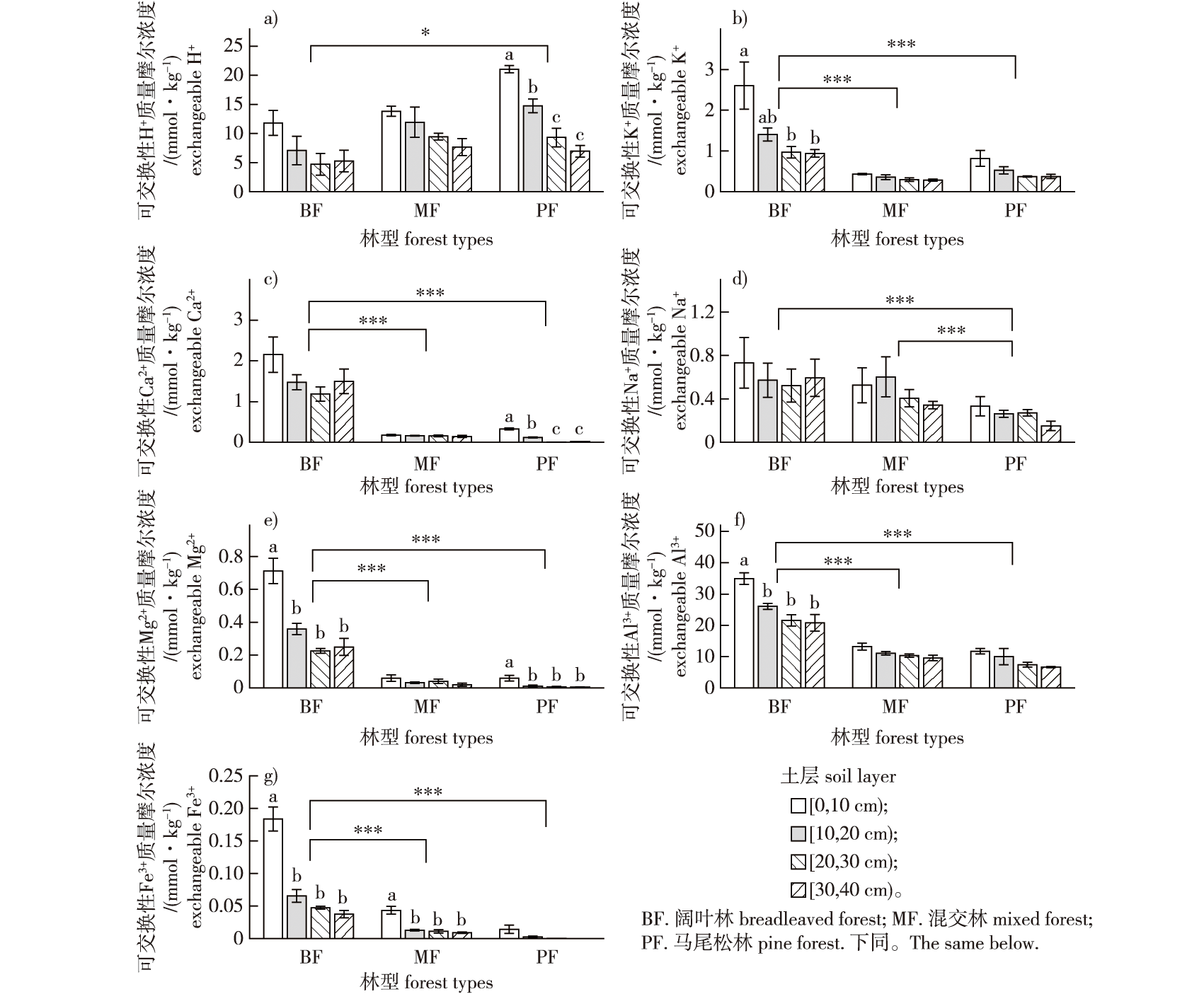
【Objective】 This study aims to explore the vertical distribution patterns of exchangeable cations in southern subtropical forest soils and identify their potential influencing factors, so as to provide theoretical support for the conservation and sustainable development of southern subtropical forest ecosystems.【Method】Three representative southern subtropical forests in the Dinghushan National Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province were selected for this study. These forests include the monsoon evergreen broadleaved forest (broadleaved forest/primary forest), mixed Pinus massoniana/broadleaved forest (mixed forest/secondary forest), and P. massoniana forest (pine forest/planted forest). The exchangeable cations (H+, Al3+, K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Fe3+), cation exchange capacity (CEC), aluminum saturation (Al-S), base saturation (BS), and pH in different soil layers [0, 10), [10, 20), [20, 30), and [30, 40) cm of three forests were analyzed.【Result】The results indicated that pH was generally lower than 4.2, BS was below 8%, and Al-S was typically higher than 60% across the three forests. Along the soil profile, the concentrations of exchangeable cations, CEC, BS, and exchangeable acidity generally decreased with increasing soil depth, while soil pH and Al-S showed an increasing trend. Overall, the broadleaved forest had significantly higher CEC, BS, Al-S, and exchangeable cation contents (except for H+) than the other two forests, but had lower soil pH. The mixed and coniferous forests exhibited similar patterns in exchangeable cation distribution. 【Conclusion】In conclusion, the southern subtropical forests of China are acid-sensitive ecosystems characterized by nutrient-poor soils within an aluminum buffering system. Exchangeable cations are predominantly concentrated in the upper soil layers. Land-use history and its legacy effects contribute to the varying soil acidification status among these three forests. Given the global change, it is essential to prioritize the replenishment of key cations like calcium and magnesium, rather than focusing solely on aluminum toxicity, in forest restoration and management efforts.
southern subtropical forest / soil acidification / cation exchange capacity (CEC) / base saturation (BS) / land use / Dinghushan, Guangdong Province
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
鲁显楷, 莫江明, 张炜, 等. 模拟大气氮沉降对中国森林生态系统影响的研究进展[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2019, 27(5): 500-522.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
刘菊秀, 周国逸, 温达志, 等. 酸沉降影响下广东陆地生态系统表层土壤特征[J]. 农业环境保护, 2001, 20(4): 231-234.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
李沁宇, 刘鑫, 张金池. 长三角区域酸雨类型转变趋势研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1): 168-174.
|
| [36] |
张智扬, 尹海魁, 李新旺, 等. 河北省县域土地利用碳排放空间格局及协调分区[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(2):281-292.
|
| [37] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |