 PDF(7720 KB)
PDF(7720 KB)


Simulation and multi-scenario prediction of land use change in the urban belt of Wanjiang River based on the PLUS model
GAO Chang, GUO Weiling, XU Liuyang, JIA Ji’ang
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 93-103.
 PDF(7720 KB)
PDF(7720 KB)
 PDF(7720 KB)
PDF(7720 KB)
Simulation and multi-scenario prediction of land use change in the urban belt of Wanjiang River based on the PLUS model
【Objective】 As a critical strategic area for promoting integrated economic development in the Yangtze River Delta and the rise of the central region, it is of great significance to explore the rational deployment of land use resources and achieve coordinated development of regional ecology and economic growth in the Wanjiang urban belt.【Method】Four scenarios, natural development, arable land protection, ecological protection, and rapid development, were established to simulate land use in the Wanjiang urban belt by 2030 and analyzed land use changes under various development goals. These scenarios utilized the patch-generating land use simulation model, intensity map model, and land use transfer matrix. Eighteen driving factors were selected based on these models to analyze spatial and temporal patterns of land use changes and driving forces in the Wanjiang urban belt from 2000 to 2020, considering natural and socio-economic factors.【Result】The findings indicated that: (1) cropland and forest land, constituting nearly 90% of the total area, were the predominant land use types in the Wanjiang urban belt. Construction land area expanded rapidly while cropland and grassland areas steadily declined, resulting in stable land use changes from 2000 to 2020. The single-movement rate of construction land was high, at 14.30%, with its greatest comprehensive dynamic degree observed between 2000 and 2005, at 0.36%. (2) The PLUS model accurately simulated land use in 2020 during the five year interval from 2010 to 2015, achieving 94.84% total accuracy with the highest Kappa coefficient of 91.24%. (3) From 2000 to 2020, factors such as night lighting, proximity to major roads, and distance from rural areas predominantly drove construction land expansion, while natural and socio-economic factors drove expansion of other land use types. (4) Significant differences in land use changes were observed among the scenarios. The ecological protection scenario balanced ecological development and economic construction by expanding construction land while preserving ecological land. It presented innovative concepts for advancing sustainable development in the Wanjiang urban belt. 【Conclusion】Land use changes in the Wanjiang urban belt remained stable over 20 years, with the ecological protection scenario emerging as the preferred approach for guiding future land use decisions and management in the region.
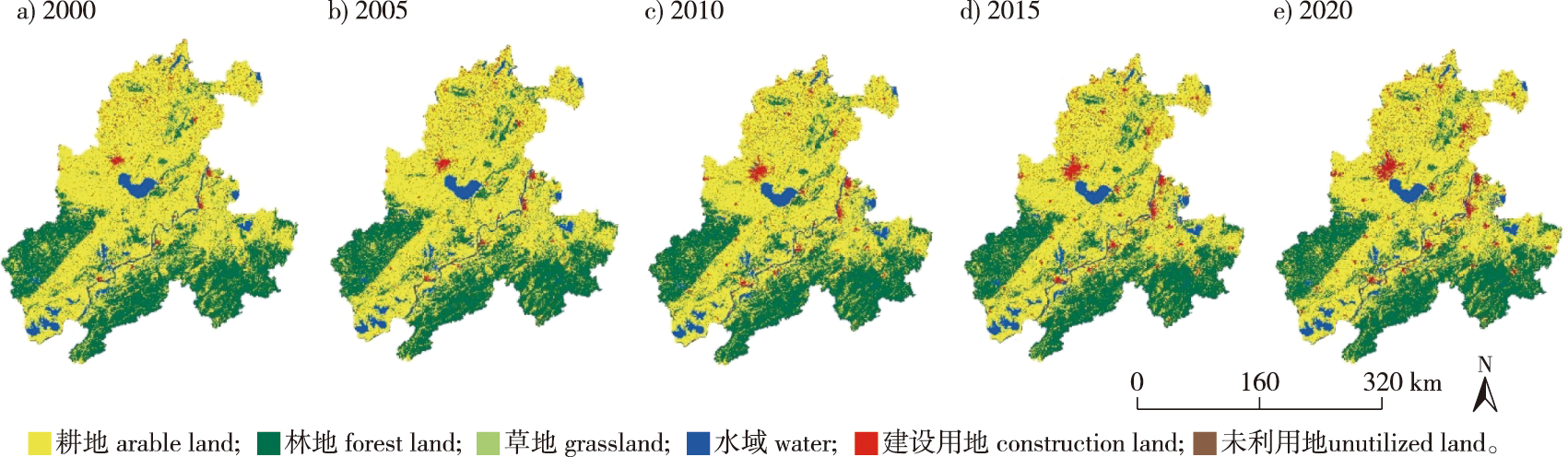
patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model / Wanjiang urban belt / land use change / multi-scenario simulation / driving factors
| [1] |
范树平, 程从坤, 刘友兆, 等. 中国土地利用/土地覆盖研究综述与展望[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2017, 36(2):94-101.
|
| [2] |
杜习乐, 吕昌河, 王海荣. 土地利用/覆被变化(LUCC)的环境效应研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2011, 43(3):350-360.
|
| [3] |
林坚, 周琳, 张叶笑, 等. 土地利用规划学30年发展综述[J]. 中国土地科学, 2017, 31(9):24-33.
|
| [4] |
曹祺文, 顾朝林, 管卫华. 基于土地利用的中国城镇化SD模型与模拟[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(4):1062-1084.
|
| [5] |
李世锋, 洪增林, 薛旭平, 等. 基于Logistic-CA-Markov耦合模型的彬州市LUCC多情景模拟[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(4):292-299.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
牛统莉, 熊立华, 陈杰, 等. 基于PLUS模型的长江流域土地利用变化模拟与多情景预测[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2024, 57(2):129-141,151.
|
| [10] |
罗芳, 潘安, 陈忠升, 等. 四川省宜宾市1980—2018年耕地时空格局变化及其驱动因素[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(6):336-344.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
孙雷, 崔育宝, 刘桂建. 产业转移区域经济-社会-环境协调发展研究:以皖江城市带承接产业转移示范区为例[J]. 电子科技大学学报(社科版), 2020, 22(5):50-59.
|
| [14] |
李鼎, 郭贯成, 史洋洋. 区域建设用地利用效率时空分异及驱动因素研究:以皖江城市带为例[J]. 江苏师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(4):66-72.
|
| [15] |
刘瑞, 朱道林. 基于转移矩阵的土地利用变化信息挖掘方法探讨[J]. 资源科学, 2010, 32(8):1544-1550.
|
| [16] |
王秀兰. 土地利用/土地覆盖变化中的人口因素分析[J]. 资源科学, 2000, 22(3):39-42.
|
| [17] |
李俊, 杨德宏, 吴锋振, 等. 基于PLUS与InVEST模型的昆明市土地利用变化动态模拟与碳储量评估[J]. 水土保持通报, 2023, 43(1):378-387.
|
| [18] |
李长爱, 刘玲, 邱冰, 等. 安徽省土地利用/覆被时空变化及其驱动因素分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(5):213-223.
|
| [19] |
杨朔, 苏昊, 赵国平. 基于PLUS模型的城市生态系统服务价值多情景模拟:以汉中市为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(10):86-95.
|
| [20] |
王保盛, 廖江福, 祝薇, 等. 基于历史情景的FLUS模型邻域权重设置:以闽三角城市群2030年土地利用模拟为例[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(12):4284-4298.
|
| [21] |
孙方虎, 方凤满, 洪炜林, 等. 基于PLUS和InVEST模型的安徽省碳储量演化分析与预测[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(1):151-158.
|
| [22] |
孙欣欣, 薛建辉, 董丽娜. 基于PLUS模型和InVEST模型的南京市生态系统碳储量时空变化与预测[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2023, 39(1):41-51.
|
| [23] |
吴先雯, 郭风成. 基于Invest模型和Flus模型的江苏省碳储量变化模拟与预测[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2024, 32(2):230-239.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
李帅呈, 龚健, 杨建新, 等. 兰西城市群土地利用/覆被变化模式特征:基于强度分析框架[J]. 资源科学, 2023, 45(3):480-493.
|
| [26] |
周振宏, 周敏, 刘东义, 等. 皖江城市带近20年土地利用变化及其生态环境效应[J]. 曲阜师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 50(1):112-118.
|
| [27] |
刘纪远, 宁佳, 匡文慧, 等. 2010—2015年中国土地利用变化的时空格局与新特征[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(5):789-802.
|
| [28] |
匡文慧, 张树文, 杜国明, 等. 2015—2020年中国土地利用变化遥感制图及时空特征分析[J]. 地理学报, 2022, 77(5):1056-1071.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
汪勇政, 徐雅利, 余浩然. 基于PLUS-InVEST模型的安徽省碳储量时空变化预测[J]. 水土保持通报, 2023, 43(3):277-289.
|
| [31] |
智菲, 周振宏, 赵铭, 等. 基于PLUS和InVEST模型的合肥市生态系统碳储量时空演变特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2024, 38(2):205-215.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |