 PDF(4408 KB)
PDF(4408 KB)


Research on forest fire video recognition based on improved Vision Transformer
ZHANG Min, XIN Ying, HUANG Tianqi
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 186-194.
 PDF(4408 KB)
PDF(4408 KB)
 PDF(4408 KB)
PDF(4408 KB)
Research on forest fire video recognition based on improved Vision Transformer
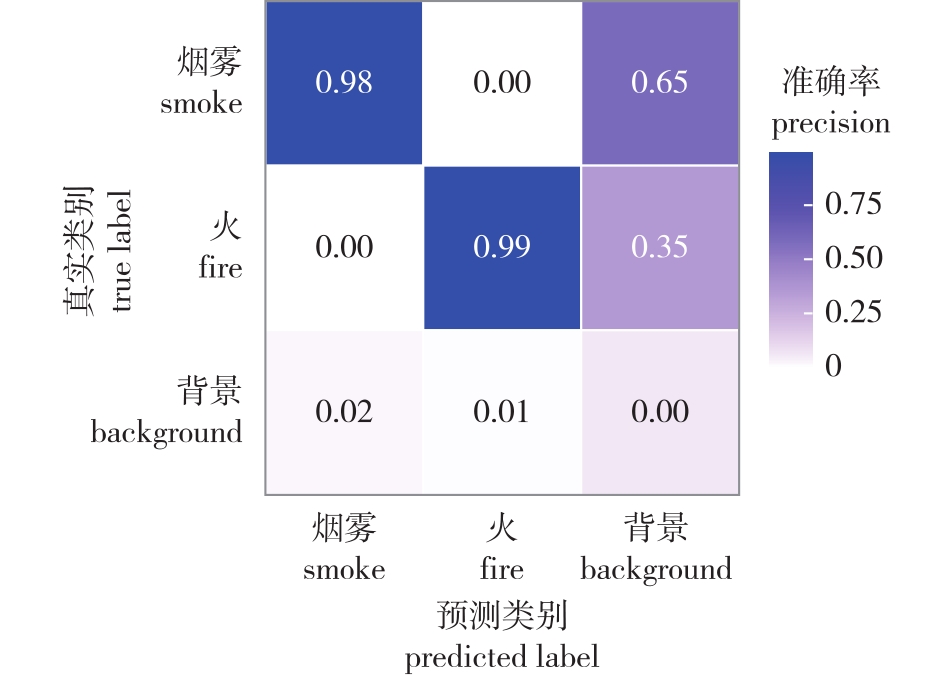
【Objective】This research aims to resolve the limitations of existing forest fire recognition algorithms in temporal feature utilization and computational efficiency, this study proposes a video-based recognition model (C3D-ViT) to enhance both detection accuracy and operational efficiency in practical forest monitoring scenarios.【Method】We presented a hybrid architecture integrating 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (3DCNN) with Vision Transformer (ViT). The framework emploied 3D convolution kernels to extract spatiotemporal features from video sequences, which were subsequently tokenized into vector representations. Vision Transformer’s self-attention mechanism then globally models feature relationships across temporal and spatial dimensions, with final classification achieved through the MLP Head layer. Comprehensive ablation studied and comparative experiments were conducted against ResNet50, LSTM, YOLOv5, and baseline 3DCNN, ViT models.【Result】The C3D-ViT achieves 96.10% accuracy, outperforming ResNet50 (89.07%), LSTM (93.26%), and YOLOv5 (91.46%), and has improved compared to the accuracy of the original 3DCNN and Vision Transformer (93.91%, 90.43%). The improved C3D-ViT model performs better in recognition performance, with high recognition accuracy and stability under unfavorable conditions such as occlusion, long distance, and thin smoke. The demand for real-time detection can be realized.【Conclusion】The C3D-ViT framework effectively addresses spatiotemporal modeling challenges in wildfire detection through synergistic CNN-Transformer interaction, providing a technically viable solution for next-generation forest fire early warning systems.
forest fire / deep learning / object detection / 3DCNN / Vision Transformer (ViT)
| [1] |
罗环敏. 基于极化干涉SAR的森林结构信息提取模型与方法[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2011.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
牛弘健, 刘文萍, 陈日强, 等. 基于Resnet的林地无人机图像去雾改进算法[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(2):175-181.
|
| [4] |
林高华. 基于动态纹理和卷积神经网络的视频烟雾探测方法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018.
|
| [5] |
薛震洋, 林海峰, 焦万果. 基于卷积神经网络的林火小目标和烟雾检测模型[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(1):225-234.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
石争浩, 李成建, 周亮, 等. Transformer驱动的图像分类研究进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2023, 28(9):2661-2692.
|
| [18] |
赵凤, 耿苗苗, 刘汉强, 等. 卷积神经网络与视觉Transformer联合驱动的跨层多尺度融合网络高光谱图像分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5):2237-2248.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |