 PDF(3369 KB)
PDF(3369 KB)


Characteristics of volatile components of representative forests of Baimashan Forest Park in Suichang County,Zhejiang Province
JIA Jing, LEI Linghua, YE Jianchao, LIU Yutian, LIANG Ziyi, ZHUANG Liyan
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 215-224.
 PDF(3369 KB)
PDF(3369 KB)
 PDF(3369 KB)
PDF(3369 KB)
Characteristics of volatile components of representative forests of Baimashan Forest Park in Suichang County,Zhejiang Province
【Objective】This research aims to analyze the volatile component characteristics of eight representative forests in Baimashan Forest Park, Suichang County, Zhejiang Province, and explore the potential health benefits of their volatile components. This will provide a pure ecological, low-cost, and side-effect-free ecological prevention and treatment path for populations with chronic diseases or sub-health in the new era, and provide a theoretical reference for ecological natural healing and forest health base construction.【Method】Forest volatile components were collected from eight representative forest areas in Baimashan Forest Park, at human respiratory height using adsorption tube sampling. The components were analyzed using thermal desorption gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (TD-GC/MS) technology. Volatile component mass spectrometry was retrieved from the NIST standard spectrum library, and relevant data were matched based on mass spectrometry fragmentation rules. Qualitative and relative mass analysis of volatile components in each forest stand was conducted.【Result】The order of the richness of forest volatile components in the eight representative forest areas from high to low was Cupressus funebris pure forest, Cunninghamia lanceolata + Houpoea officinalis + Liquidambar formosana + Liriodendron chinense mixed forest, Cunninghamia lanceolata+Pinus hwangshanensis + Schima superb mixed forest, Cryptomeria japonica pure forest, Cunninghamia lanceolata+Cryptomeria japonica mixed forest, Phyllosatachys edulis pure forest, Cunninghamia lanceolata pure forest, Cunninghamia lanceolata+Pinus hwangshanensis mixed forest. The study isolated 59, 101, 46, 60, 100, 77, 62 and 52 chromatographic peaks from the eight representative forest areas, identifying 38, 62, 37, 22, 52, 43, 33 and 39 compounds respectively. Among the eight forest areas, a total of 12 compounds were identified, including benzaldehyde, nonanal, decanal, npropyl acetate, sec-butyl acetate, acetophenone, benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, acetic acid, and benzonitrile. The relative content of benzaldehyde, nonanal, decanal, and acetophenone in each forest area was above 12%, with the highest being 53.95%. The eight forest regions all have typical pollutants with relative contents ranging from 1.09% to 21.78%, of which the mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata + Pinus hwangshanensis + S. superb mixed forest has the highest pollutant content, and the mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata + Pinus hwangshanensis has the lowest pollutant content. In addition to Cupressus funebris pure forests and C. lanceolata + Houpoea officinalis + Liquidambar formosana + Liriodendron chinense mixed forest, all forest areas in Baimashan Forest Park contain more than 26% of aldehydes, ketones, and esters, and Cupressus funebris pure forest release four terpenes.【Conclusion】The types of forest volatile components in the representative forest areas of Baimashan Forest Park are rich, and the main volatile components released from the eight forest areas all contain aromatic cyclohydrocarbons and alkanes. Among them, the total relative content of healthy volatile components released from the mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata + Pinus hwangshanensis, such as terpenes, aldehydes, ketones, esters and alcohols, is the highest. In early autumn, four forest areas with community structure of mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata + Pinus hwangshanensis, pure forest of Cupressus fortunei, pure forest of Chinese fir and pure forest of Phyllostuchys edulis are suitable for carrying out forest health care activities. Mixed forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata + Pinus hwangshanensis is most conducive to carrying out forest health care activities for sub healthy people with chronic cardiovascular diseases, followed by Cupressus japonica, Cunninghamia lanceolata and P. pubescens pure forest.
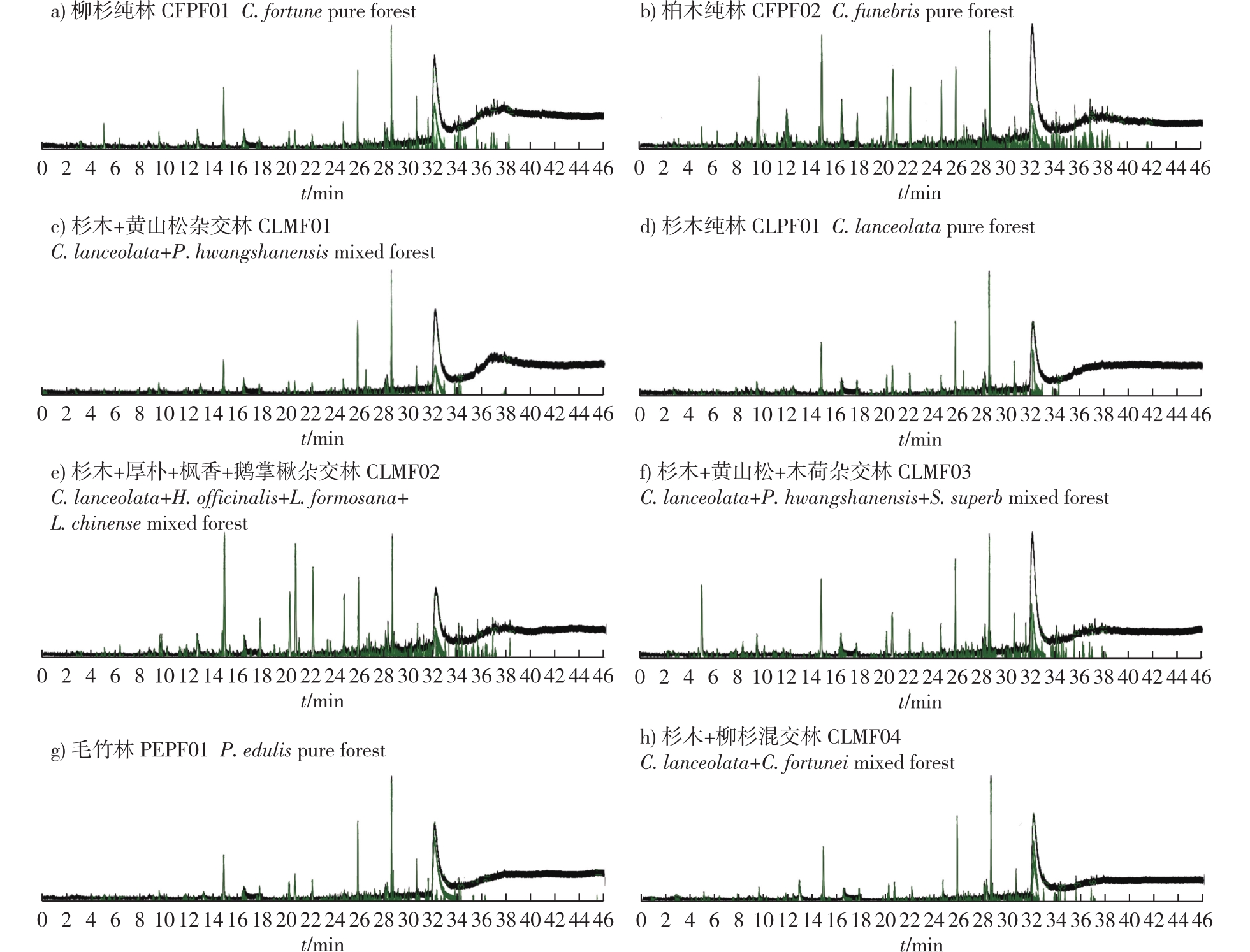
forest community / stand structure / volatile components of forest / thermal desorption gas chromato graphy/mass spect-metry(TD-GC/MS) / forest-based health and wellness / Baimashan Forest Park
| [1] |
彭巍, 李明文, 杜鹏飞. “天然杀菌素”植物精气国内外研究进展[J]. 防护林科技, 2020(12):69-71.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
吴章文, 吴楚材, 陈奕洪, 等. 8种柏科植物的精气成分及其生理功效分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2010, 30(10):1-9.
|
| [4] |
吕杨. 3种绿化树种的挥发物对小鼠行为的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2019.
|
| [5] |
张薇, 程政红, 刘云国, 等. 植物挥发性物质成分分析及抑菌作用研究[J]. 生态环境, 2007, 16(5):1455-1459.
|
| [6] |
雷凌华, 朱强根, 夏更寿, 等. 黄心夜合不同组织挥发油成分分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(1):193-199.
|
| [7] |
孙丽娟, 柯闲, 王俊俊, 等. 森林芬多精类成分及其生物活性的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(22):7032-7043.
|
| [8] |
商天其. 短时高温、CO2浓度倍增以及叶片生长阶段对香樟(Cinnamomum camphora)单萜释放和光合生理的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2018.
|
| [9] |
靳明慧, 赵起. 薰衣草精油对皮肤光老化作用机制研究进展[J]. 西南医科大学学报, 2017, 40(1):94-96.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
熊唯琛. 合欢花减轻对乙酰氨基酚诱导的急性肝损伤的有效成分及其作用机制研究[D]. 武汉: 湖北中医药大学, 2020.
|
| [12] |
谢小洋. 西安市主要绿化树种VOCs组成及释放规律研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016.
|
| [13] |
闫秋菊, 王海鸥, 朱华, 等. 冻干水蜜桃挥发性风味成分的变化及迁移[J]. 食品与机械, 2019, 35(7):20-25.
|
| [14] |
卢昌利, 欧阳春平, 王超军, 等. 异佛尔酮合成技术研究进展[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(13):83-84,92.
|
| [15] |
杨水萌. 十三种药用植物挥发性成分的SHS/GC-MS研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2018.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
许金钗, 刘建阳, 徐桂花, 等. 香薰疗法联合愉快因子刺激对乳腺癌化疗患者焦虑及依从性的影响[J]. 中国乡村医药, 2020, 27(22):11-12.
|
| [18] |
范培珍, 潘铖, 王梦馨, 等. 内山六安瓜片4个等级茶叶香气的组成及其差异[J]. 茶叶科学, 2020, 40(5):665-675.
|
| [19] |
李少宁, 陶雪莹, 李绣宏, 等. 植物释放有益挥发性有机物研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1):187-195.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
雷凌华, 李胜华, 曾军英, 等. 黄心夜合不同季节鲜叶挥发性成分研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 2017, 35(1):107-114.
|
| [22] |
李桂香, 马莎, 崔庆德, 等. GC-MS分析核桃花中的挥发性成分[J]. 大理大学学报, 2021, 6(12):55-58.
|
| [23] |
雷凌华, 于晓英, 李炎林. 不同季节黄心夜合鲜嫩枝挥发性成分的差异[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 42(3):296-300.
|
| [24] |
刘圆圆, 彭玮瑶, 张健, 等. 3个不同地区山胡椒的果、茎、叶挥发性成分分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2022, 43(8):1703-1715.
|
| [25] |
李素欣, 姜清彬, 张晖, 等. 醉香含笑不同树高处心边材挥发性成分的差异[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2024, 52(1):128-136.
|
| [26] |
吴沁娇, 宋艳冬, 陶士杰, 等. 丽水白云国家森林公园5种典型林分挥发性有机化合物释放特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2023, 40(5):930-939.
|
| [27] |
徐晨, 章尧想, 吴迪, 等. 北京市3种典型森林类型林内植物源挥发性有机物变化特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(5):130-139.
|
| [28] |
文娟, 常明山, 郝建, 等. 马尾松、杉木纯林及其混交林挥发性有机物成分分析[J]. 广西科学, 2023, 30(2):251-258.
|
| [29] |
吴楚材, 吴章文, 罗江滨. 植物精气研究[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社,2006:264.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |