 PDF(2145 KB)
PDF(2145 KB)


A comprehensive evaluation of fruit characteristics of 46 blueberry cultivars
ZHAO Huifang, ZHAO Fengyi, LIU Hongxia, WU Wenlong, WU Yaqiong, LI Weilin
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 52-62.
 PDF(2145 KB)
PDF(2145 KB)
 PDF(2145 KB)
PDF(2145 KB)
A comprehensive evaluation of fruit characteristics of 46 blueberry cultivars
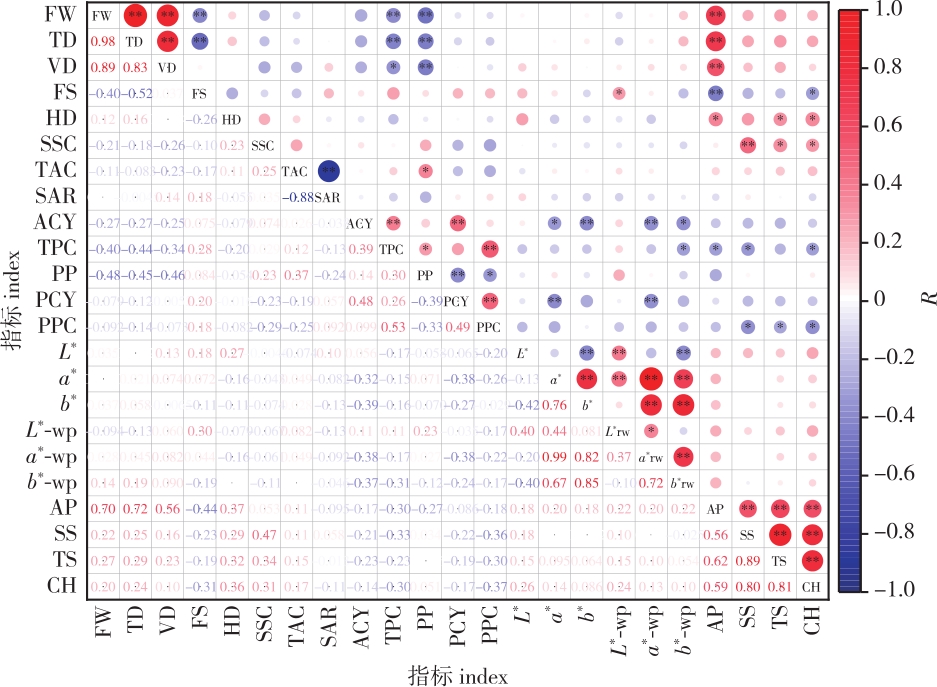
【Objective】This research aims to evaluate the fruit characteristics of 46 blueberry cultivars for selection and breeding purposes. 【Method】The fruit appearance, inner quality and sensory properties of 46 blueberry cultivars were investigated, then classified and evaluated by correlation, principal component and cluster analyses. 【Result】The northern highbush blueberry exhibited the largest fruit size, highest and acidity levels, and achieved the highest sensory score. The fruit of southern highbush blueberry was the smallest, with the lowest hardness and sensory score, the highest sweetness and total polyphenol content. The fruit of rabbit eye blueberry was larger than southern highbush blueberry, with the highest pericarp ratio and total anthocyanin content. Among appearance indices, the chromaticity a* of fruit with epicuticular powder removed exhibited the highest coefficient of variation (CV) at 2 926.91%, followed closely by the original fruit chromaticity a* at 370.96%. The CV of solid acid ratio (42.77%) was the highest among quality indices, followed by total anthocyanin content (39.78%), and the CV of sensory score was the lowest (<10%). Correlation analysis revealed that larger fruit size was associated with lower pericarp percentage and total polyphenol content. The acidity had the greatest effect on the solid acid ratio of blueberry fruits. Sensory evaluation indices, including appearance and comprehensive scores, showed significant positive correlations with fruit weight, transverse diameter, and longitudinal diameter, indicating that larger fruit size is a preferred characteristic in sensory evaluation. Cluster analysis showed that the 46 blueberry cultivars were divided into three types, among which the first type had the largest fruit with high hardness and acidity, the second type had the second-largest fruit with the highest sweetness, and the third type had the smallest fruit with high pericarp ratio, belonging to the processing type with high total anthocyanin and polyphenol content. Principal component analysis reduced the 11 appearance and quality indices to four principal components, explaining 75.217% of the total variance. Sensory evaluation revealed that, in addition to differences in size, sweet-sour balance and nutrient content, the 46 blueberry cultivars also varied in wax thickness, texture and fruity aroma, and seven large-fruit cultivars of ‘Primadonna’, ‘Millennia’, ‘Jewel’, ‘Chandler’, ‘Brigitta’, ‘Aurora’ and ‘Prolific’, 3 high sweetness cultivars of ‘Anna’ ‘Sweetheart’ and ‘Brightwell’, and four excellent taste cultivars of ‘Sunshine’, ‘Magnolia’, ‘Brigitta’ and ‘Beckyblue’ were selected. Comprehensive evaluation showed that sensory assessment results were largely consistent with principal component and cluster analyses. 【Conclusion】The 10 cultivars with large fruit size, high sweetness, crisp texture and rich aroma were ‘Prolific’, ‘Chandler’, ‘Sweetheart’, ‘Brigitta’, ‘Millennia’, ‘Beckyblue’, ‘Primadonna’, ‘Brigitta’, ‘Magnolia’ and ‘Pink Lemonade’, which were recommended for fresh consumption, and the 5 cultivars with high total anthocyanins and polyphenols content and high pericarp percent were ‘Gardenblue’, ‘Zhongzhi 4’, ‘Zhaixuan 4’, ‘Baldwin’ and ‘Centurion’, which can be used for processing blueberry products. These cultivars can also serve as parental materials for corresponding breeding objectives.
blueberry(Vaccinum spp.) / germplasm / fruit characteristics / cluster analysis / principal component analysis
| [1] |
李亚东, 吴林, 张志东. 长白山区不同生态条件下引种越桔生长结果研究[J]. 北方园艺, 1996(4):6-8.
|
| [2] |
李亚东, 刘海广, 张志东, 等. 我国蓝莓产业现状和发展趋势[J]. 中国果树, 2008(6):67-69,71.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
梁钰梅, 李可, 林籽汐, 等. 基于主成分分析法的9个品种蓝莓品质评价[J]. 食品工业科技, 2024, 45(9):235-244.
|
| [9] |
张春红, 黄正金, 赵慧芳, 等. 3个南高丛蓝莓品种在南京的引种表现及栽培特性[J]. 现代园艺, 2022, 45(9):64-66.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
乌凤章, 张润梅, 尹泽宇, 等. 基于主成分分析的高丛蓝莓品种果实品质综合评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(22):262-269.
|
| [12] |
董晓雅, 时东方, 赵博雅, 等. 不同品种蓝莓果实品质评价[J]. 长春师范大学学报, 2023, 42(8):109-112.
|
| [13] |
刘丙花, 孙锐, 王开芳, 等. 不同蓝莓品种果实品质比较与综合评价[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(1):70-76.
|
| [14] |
陈昌琳, 孙小钦, 钟程操, 等. 四川地区不同蓝莓品种的品质评价及香气成分分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 48(19):264-271.
|
| [15] |
韩斯, 孟宪军, 汪艳群, 等. 不同品种蓝莓品质特性及聚类分析[J]. 食品科学, 2015, 36(6):140-144.
|
| [16] |
刘笑宏, 王建萍, 顾亮, 等. 不同品种蓝莓果实品质及芳香物质成分分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2019, 45(24):234-240.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
赵慧芳, 吴文龙, 黄正金, 等. 34个蓝莓品种果实品质评价[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2023, 32(4):44-53,72.
|
| [20] |
吴文龙, 赵慧芳, 方亮, 等. 南京地区蓝莓品种(系)果实品质分析与评价[J]. 经济林研究, 2013, 31(4):87-92.
|
| [21] |
赵慧芳, 吴文龙, 闾连飞, 等. 钱德勒等4个北高丛蓝莓品种在南京地区的引种表现[J]. 中国南方果树, 2021, 50(6):105-110,115.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
张晓晓, 黄午阳, 於虹, 等. 不同种植地区蓝莓果中花色苷的分布[J]. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22(10):314-324.
|
| [26] |
文光琴, 赵亮清, 周荧, 等. 6个高丛蓝莓在贵州不同海拔生态区的生长及果实特性差异[J]. 中国南方果树, 2023, 52(4):145-150.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
蒋强, 钟勇, 马涛, 等. 4个蓝莓品种在广西百色市种植表现及品质特性分析[J]. 中国南方果树, 2024, 53(3):270-275.
|
| [34] |
蒋芯, 颜丽菊. 27个蓝莓品种在浙江临海的果实性状表现初探[J]. 中国南方果树, 2022, 51(1):144-149.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
李嘉琦, 刘有春, 王兴东, 等. 基于电子鼻的蓝莓重要亲本及杂交后代香气物质研究[J]. 北方果树, 2024(4):6-12,20.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |