 PDF(1800 KB)
PDF(1800 KB)


Study on the control of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus by trunk injection with three kinds of agents
XIANG Fan, LIU Yuzhuo, YE Jianren, ZHANG Wanjun
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6) : 95-101.
 PDF(1800 KB)
PDF(1800 KB)
 PDF(1800 KB)
PDF(1800 KB)
Study on the control of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus by trunk injection with three kinds of agents
【Objective】This study aimed to evaluate the conduction residues and disease prevention efficacy of different chemicals in pine trees following trunk injection and identify trunk injections with strong persistence and effective control, providing a theoretical basis for the use of trunk injections to prevent pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus).【Method】The insecticidal efficacy of 5% emamectin benzoate soluble liquid, 5% avermectin emulsifiable concentrate, and 1% emamectin benzoate-9% imidacloprid soluble liquid on B. xylophilus was assessed using the dipping method. The sublethal concentration (LC20) of each pesticide was applied to Botrytis cinerea and inoculated with B. xylophilus to assess their effects on nematode feeding and reproduction. Subsequently, these pesticides were injected into the trunks of Pinus massoniana in the forest, and the translocation of residues within the trees was analyzed one year and 660 days after injection. In June of the second year (2022), P. massoniana was artificially inoculated with B. xylophilus, and the disease prevention effect was observed and statistically analyzed one year after the injection.【Result】After 24 hours of treatment, the LC50 values for the three agents were determined to be 10.879 8 mg/L, 57.008 7 mg/L, and 93.693 9 mg/L, respectively. When B. cinerea was inoculated with nematodes and treated with sublethal concentrations (LC20) of these pesticides, all three significantly inhibited nematode feeding rates and reduced nematode populations (333, 466, and 500 nematodes, respectively, compared to 47 766 nematodes/dish in the control). One year after injection, the pesticides were found to translocate upward from the injection sites in P. massoniana. Residual amounts were detected in the upper branches, except for the 5% avermectin emulsifiable concentrate. Among the treatments, the 5% emamectin benzoate soluble liquid exhibited the lowest residual concentration at 0.006 3 mg/kg, while the mixed formulation showed the highest residual concentrations of imidacloprid (0.213 0 mg/kg) and emamectin benzoate (0.082 3 mg/kg). These compounds accumulated at higher levels in areas 2.0 m and 0.5 m from the injection points, with concentrations of 12.863 6 mg/kg and 128.395 2 mg/kg, respectively. After 660 days, residual concentrations of all formulations decreased, although residues remained detectable in the upper branches. The highest residual compound concentration was 0.125 1 mg/kg, followed by 5% emamectin benzoate soluble liquid at 0.074 1 mg/kg, and 5% avermectin emulsifiable concentrate at 0.012 4 mg/kg. Unlike the results after one year, where certain areas exhibited the highest residual concentrations for the 5% emamectin benzoate soluble liquid and the mixed formulation, the residual concentrations decreased with height over time. Pine trees inoculated with B. xylophilus 450 days post-injection and analyzed 75 days after inoculation showed a 100% disease prevention rate with all three pesticides. Continuous observation revealed that 5% avermectin emulsifiable concentrate had a significantly better preventive effect.【Conclusion】The three agents-5% emamectin benzoate soluble liquid, 5% avermectin emulsifiable concentrate, and 1% emamectin benzoate-9% imidacloprid soluble liquid—not only exhibit strong toxicity to B. xylophilus but also demonstrate good translocation and persistence in P. massoniana following trunk injection. Additionally, these injections maintain a strong preventive effect against pine wood nematode infection even into the second year. Among the agents tested, 5% avermectin emulsifiable concentrate shows the best overall control efficacy and should be considered for large-scale application in forest management.
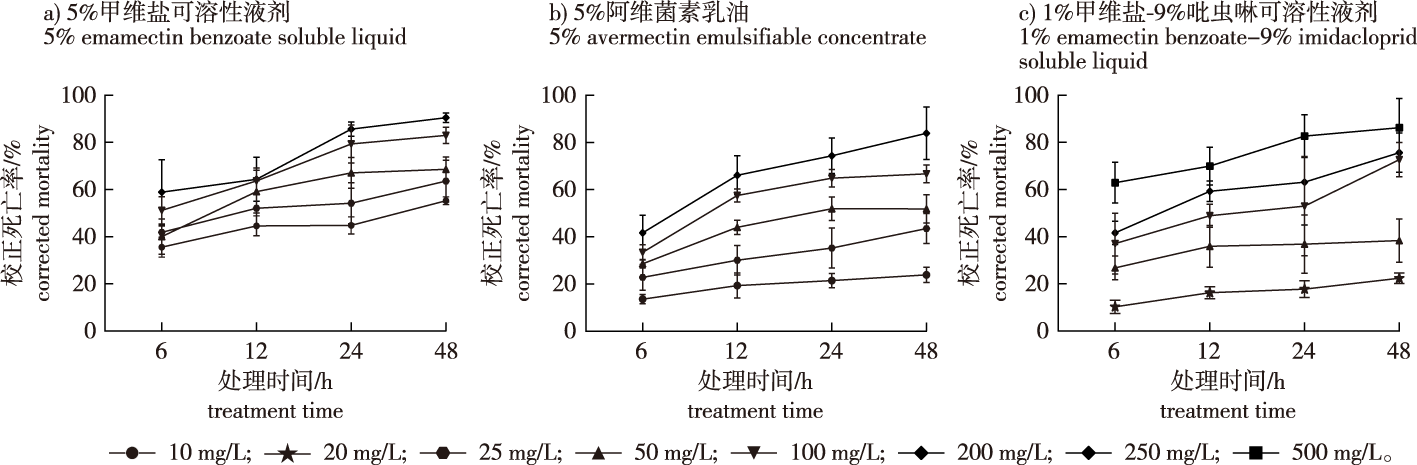
pine wilt disease / trunk injection / agent residues / effect of disease prevention / nematicide / emamectin benzoate / avermectin emulsifiable concentrate / emamectin benzoate-imidacloprid
| [1] |
史兴文, 陈绍银. 金寨县松材线虫病防治探究[J]. 南方农业, 2020, 14(23):66-67.
|
| [2] |
孙永春. 南京中山陵发现松材线虫[J]. 江苏林业科技, 1982(4):27-47.
|
| [3] |
苗力, 王禹, 李瑞红, 等. 松材线虫病的危害、传播途径和防控措施[J]. 吉林林业科技, 2023, 52(1):44-45.
|
| [4] |
葛迎春, 韩冰, 张华伟, 等. 树干注射施药技术的应用分析[J]. 现代农村科技, 2020(10):30-31.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
李长强, 叶建仁, 张婉君, 等. 注干施用甲维盐防治松材线虫病的研究[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2022, 42(3):16-19.
|
| [8] |
林茂松, 周明国. 2%阿维菌素乳油对松材线虫的生物活性测定[J]. 农药学学报, 2001(3):40-44.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
艾辉建, 刘志明, 黄金玲, 等. 几种杀线剂对南方根结线虫的田间药效试验[J]. 南方农业学报, 2012, 43(7):961-964.
|
| [11] |
谈家金, 杨荣铮, 吴慧平. 不同地理种群的松材线虫对马尾松的致病力差异[J]. 植物检疫, 2000(6):324-325.
|
| [12] |
张扬, 杨鼎超, 李正昀, 等. 高效新型杀松材线虫剂的筛选及其林间防效[J]. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(5):856-862.
|
| [13] |
张印海. 树干注药技术对松材线虫病的预防效果[J]. 现代园艺, 2023, 46(4):10-11, 30.
|
| [14] |
朱丽华, 林丽, 蒋鹏, 等. 不同致病力松材线虫的繁殖能力和移动能力比较[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(12):76-79.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
孙薇, 张立华, 王勇军, 等. 注干施药后黄山松体内甲维盐含量检测及残留动态分析[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2022, 42(4):83-87.
|
| [18] |
张娇, 叶建仁, 陈婷婷, 等. 松材线虫高效复配制剂的药效分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(3):73-80.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |