 PDF(2376 KB)
PDF(2376 KB)


The dynamic characteristics of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) stands after strip-shaped clear-cutting
ZHANG Xuan, GUAN Fengying, FAN Shaohui, ZHENG Yaxiong, ZHOU Xiao
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 29-36.
 PDF(2376 KB)
PDF(2376 KB)
 PDF(2376 KB)
PDF(2376 KB)
The dynamic characteristics of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) stands after strip-shaped clear-cutting
【Objective】This study aimed to examine the dynamic characteristics of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) stands subjected to strip-shaped clear-cutting and to provide insights into the development of appropriate scientific management strategies for moso bamboo forests.【Method】A strip-shaped clear-cutting experiment was conducted in pure moso bamboo stands within the Forest Farm of Yixing, Jiangsu Province. The size of strip-shaped clear-cutting plots (SC) is 20 m×8 m for each. In addition, three reserved plots (RB) of the same dimensions were positioned on both sides of the clear-cutting plots. For comparison, three 20 m ×20 m control plots (CK) were set up under traditional management practices. The study investigated the dynamics of moso bamboo shoot development, the growth of new bamboo, and changes in soil nutrient content across the different treatment plots over five years following the strip-shaped clear-cutting. Pearson correlation analysis was applied to assess the relationship between soil nutrient factors and stand characteristics.【Result】(1) In the first year following clear-cutting, the number of bamboo shoots in the SC plots increased by 71.17% compared with RB and by 62.21% compared to CK, while the number of new bamboo grew by 38.97% in SC relative to RB and 55.07% relative to CK. (2) In the first year, the mean diameter at breast height (DBH), mean height to crown base (CBH), and mean height (H) of new bamboo in SC were significantly lower than those in CK (P<0.05). By the fifth year after clear-cutting, the DBH, CBH, and H of new bamboo in SC surpassed those in CK, with a significant increase in CBH (P<0.05). (3) Strip-shaped clear-cutting significantly reduced the total soil nutrient content in SC plots (P<0.05), while enhancing the content of quick-acting nutrients in both SC and RB plots; however, these differences were not statistically significant. The soil organic carbon content in SC was lower than in CK and RB, although the difference was not significant. By the fifth year after clear-cutting, there was no significant difference in soil nutrient content between SC and RB when compared to CK. (4) Correlation analysis revealed a highly significant negative relationship between the number of shoots in SC and the soil’s alkaline nitrogen (AN) and quick-acting potassium (AP) content (P<0.01). Similary, the number of new bamboo exhibited significant negative correlations with both soil AN and AP content (P<0.05). Conversely, the quality characteristics of the new bamboo were significantly positively correlated with soil total potassium content (P<0.05).【Conclusion】Strip-shaped clear-cutting enhances bamboo shoot density and the formation of new bamboo in moso bamboo forests but negatively impacts the quality of new bamboo. It leads to a reduction in total soil nutrient levels and an increase in quick-acting nutrients. As the bamboo stands recover, the quality of the new bamboo gradually improves, and soil fertility is restored. By the fifth year after clear-cutting, the stand characteristics of the moso bamboo forest in the SC plots return to levels similar to those in the CK plots.
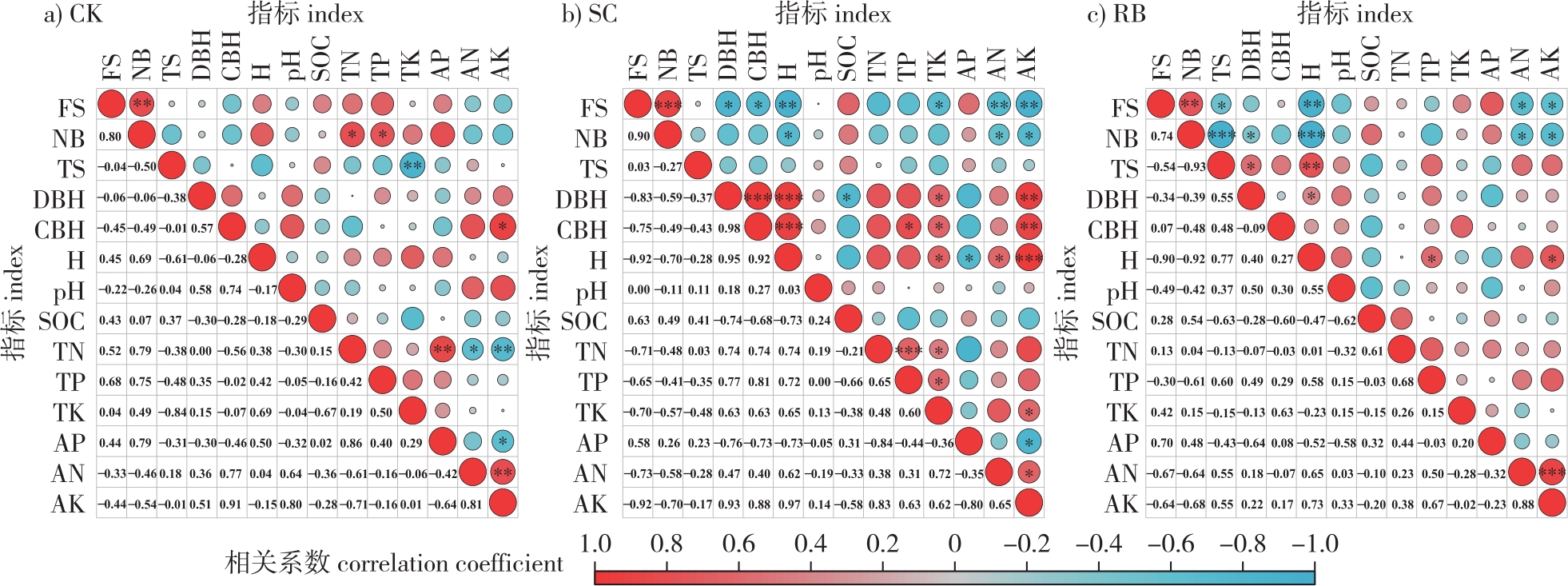
Phyllostachys edulis forests / strip-shaped clear-cutting / stand characteristics / soil nutrient
| [1] |
叶翰舟, 王戈, 程海涛, 等. 发挥“以竹代塑”潜力引领全球绿色可持续发展[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2023, 21(2):1-8.
|
| [2] |
胡玉安, 黄慧, 贺磊, 等. 建筑建材领域“以竹代塑”工程材料研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 林业工程学报, 2024, 9(6):1-11.
|
| [3] |
范少辉, 刘广路, 苏文会, 等. 竹林培育研究进展[J]. 林业科学研究, 2018, 31(1):137-144.
|
| [4] |
詹美春, 官凤英, 晏颖杰, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹林林下植被物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(12):4169-4179.
|
| [5] |
王树梅, 范少辉, 官凤英, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹林土壤理化性质、酶活性及优势菌群的短期影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(1):46-51.
|
| [6] |
曾宪礼, 苏文会, 范少辉, 等. 带状采伐毛竹林恢复的质量特征研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(5):917-924.
|
| [7] |
申景昕, 范少辉, 刘广路, 等. 毛竹林采伐林窗近地层温度时空分布特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(11):3549-3557.
|
| [8] |
吴昌明, 范少辉, 冯云, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹林土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(7):42-51.
|
| [9] |
王树梅, 王波, 范少辉, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹林土壤细菌群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(2):60-68.
|
| [10] |
曾宪礼, 苏文会, 范少辉, 等. 带状采伐毛竹林土壤质量评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(10):3015-3023.
|
| [11] |
申景昕, 范少辉, 刘广路, 等. 毛竹林带采伐宽度对土壤碳氮磷含量及计量比的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(8):1851-1857.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
庄明浩, 李迎春, 陈双林. 竹子生理整合作用的生态学意义及研究进展[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 2011, 30(2):5-9.
|
| [16] |
童亮, 李平衡, 周国模, 等. 竹林鞭根系统研究综述[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(1):183-192.
|
| [17] |
张幼法, 林世奎, 张世渊. 毛竹林地下鞭动态生长的研究[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 1999, 18(3):62-65.
|
| [18] |
张韫. 土壤·水·植物理化分析教程[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2011.
|
| [19] |
罗学刚, 董鸣. 蛇莓克隆构型对光照强度的可塑性反应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2001, 25(4):494-497.
|
| [20] |
黄慧敏, 董蓉, 向运蓉, 等. 不同群落冠层环境下紫耳箭竹笋期生长发育研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 2018, 36(5):696-704.
|
| [21] |
蔡宗明, 邓智文, 李秉钧, 等. 带状采伐宽度对毛竹林地下竹鞭结构特征的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2023, 59(4):79-87.
|
| [22] |
王树梅. 带状采伐毛竹林地下鞭根系统与地面成竹响应特征的研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2021.
|
| [23] |
周成军, 巫志龙, 周新年, 等. 采伐强度对杉阔混交人工林凋落物及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(1):145-151.
|
| [24] |
张洋洋, 凡莉莉, 王敏, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹林土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2020, 40(3):234-242.
|
| [25] |
刘宗悦, 吕时新, 徐钧杰, 等. 毛竹林皆伐和剩余物保留对土壤质量的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(6):1289-1295.
|
| [26] |
宋贤芬, 赵各进, 严夏帆, 等. 土壤养分、林分结构和地形因子对毛竹更新的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(3):7-12.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
苏文会. 基于生长和养分积累规律的毛竹林施肥理论与实践研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2012.
|
| [29] |
郑素芸, 林雨薇, 黄怡, 等. 长周期母竹留养模式的毛竹林土壤养分状况评价[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(12):97-103.
|
| [30] |
谭宏超, 谭汝强, 张翼飞. 3种皆伐方式对毛竹林更新生长的影响[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2017, 15(3):52-55.
|
| [31] |
黄翔, 洪桢华, 张晓萍, 等. 带状采伐后施肥对毛竹林恢复的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(5):14-19,29.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
李翀, 周国模, 施拥军, 等. 毛竹林老竹水平和经营措施对新竹发育质量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(8):2243-2254.
|
| [34] |
张洋洋, 凡莉莉, 徐文达, 等. 带状采伐后不同时期毛竹林恢复和土壤养分特征[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(8):1407-1413.
|
| [35] |
王树梅, 范少辉, 肖箫, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹地上生物量分配及异速生长的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(5):19-24.
|
| [36] |
苏文会, 曾宪礼, 范少辉, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹非结构性碳与生物量分配的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(10):2934-2940.
|
| [37] |
施建敏, 叶学华, 陈伏生, 等. 竹类植物对异质生境的适应——表型可塑性[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(20):5687-5695.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
蔡宗明, 邓智文, 李东宝, 等. 带状采伐对毛竹生物量和根系非结构性碳水化合物的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(4):33-42.
|
| [40] |
李承基, 官凤英, 周潇, 等. 配比施肥对带状采伐毛竹林立竹数量和质量恢复的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(2):79-85.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |