 PDF(1971 KB)
PDF(1971 KB)


Effects of different nitrogen forms on the growth and physiological characteristics of Carya illinoensis
QIAO Zhenbing, CHEN Mengyun, ZHU Jiaju, LU Longtao, ZHU Kaikai, TAN Pengpeng, PENG Fangren
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 160-169.
 PDF(1971 KB)
PDF(1971 KB)
 PDF(1971 KB)
PDF(1971 KB)
Effects of different nitrogen forms on the growth and physiological characteristics of Carya illinoensis
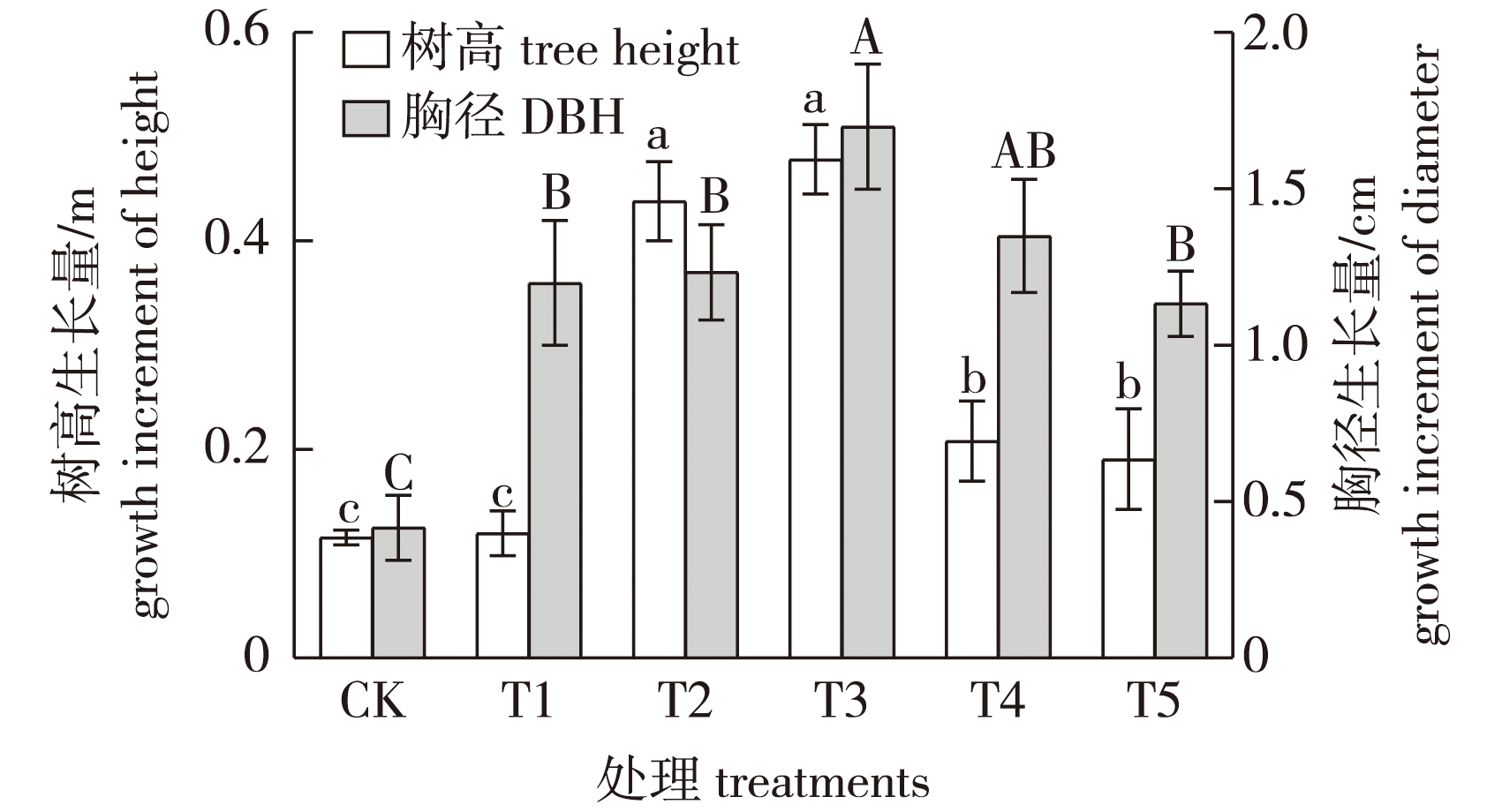
【Objective】 Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3--N) are the two primary inorganic nitrogen forms absorbed by plants and play crucial roles in plant growth and development. Screening the optimal nitrogen form ratio for pecan (Carya illinoinensis) growth can provide a theoretical basis for improving its nitrogen use efficiency.【Method】The experiment used 14-year-old pecan trees of the C. illinoinensis ‘Pawnee’ cultivar as plant materials. Six treatments were established with NO3--N to NH4+-N mass ratios of 100∶0 (T1), 72∶25 (T2), 50∶50 (T3), 25∶75 (T4), 0∶100 (T5), and a no-nitrogen fertilizer control (CK). Variance analysis, correlation analysis, and principal component analysis were conducted on the growth and physiological characteristics of pecan under different nitrogen form treatments to preliminarily determine the optimal nitrogen form ratio.【Result】The results showed that the T2 treatment significantly increased the contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total chlorophyll in pecan leaves, as well as the free amino acid and crude fat contents in the kernels. Under T3 treatment, tree height and diameter at breast height growth were significantly enhanced, ammonium nitrogen content in roots and kernels was significantly reduced, while ammonium nitrogen content in leaves was significantly increased. T4 treatment significantly increased the soluble sugar content in roots and leaves, as well as the soluble protein and free amino acid contents in both roots and kernels. The T5 treatment significantly increased the soluble sugar content in the kernels. Correlation analysis indicated positive relationships between the majority of the measured parameters in pecan. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation revealed that the T4 treatment was most conducive to promoting the growth and development of pecan. 【Conclusion】Through the analysis of growth and physiological characteristics, correlation analysis, and principal component analysis of pecan under different nitrogen form ratio treatments, it was found that the T4 treatment had the best promoting effect on the growth and development of pecan. This provides a theoretical foundation for improving nitrogen use efficiency in pecan.
Carya illinoensis(pecan) / nitrogen forms / growth and physiological characteristics / nitrogen use efficiency
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
赵喆, 王菲, 胡甜, 等. 薄壳山核桃脂肪酸研究进展[J]. 食品科技, 2023, 48(2): 173-178.
|
| [3] |
黄梅, 任华东, 姚小华, 等. 薄壳山核桃主要生物活性成分及其作用研究进展[J]. 中国油脂, 2023, 48(6): 99-104.
|
| [4] |
周樊, 陈文静, 曹凡, 等. 配比施肥对薄壳山核桃幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(9): 96-103.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
吕浩楠, 周晓嘉, 吴金鹏, 等. 控释氮肥在稻麦轮作体系上应用的研究进展[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 54(6): 923-929.
|
| [7] |
杨林森. 薄壳山核桃容器播种苗培育关键技术研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2024.
|
| [8] |
杨学峰. 施肥对薄壳山核桃幼苗生长的影响[J]. 安徽林业科技, 2022, 48(1): 21-24.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
杜洋文, 邓先珍, 程军勇. 不同尿素施肥量对薄壳山核桃嫁接苗光合作用日变化的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(1): 27-35.
|
| [11] |
邹英武, 杜洋文, 黄发新, 等. 不同氮肥浓度对薄壳山核桃苗木光合特性影响[J]. 湖北林业科技, 2021, 50(5): 1-7.
|
| [12] |
冯英, 赵悦竹, 戚晶, 等. 氮、磷、钾优化配比在薄壳山核桃果实及叶片中分配效应研究[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2023, 50(5): 798-801.
|
| [13] |
周米生, 王陆军, 肖正东, 等. 叶面肥对薄壳山核桃幼苗生长的影响[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2021, 67(7): 51-56.
|
| [14] |
尚杨娟, 谭鹏鹏, 范平桦, 等. 薄壳山核桃叶面喷锌效果的评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(6): 1071-1079.
|
| [15] |
沈超. 氮钾对薄壳山核桃幼苗生理生化特性的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2018.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
郑天晨. 氮供应及氮形态对油松幼苗生长的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2023.
|
| [18] |
陈昕钰. 小麦根系的生长发育及其对氮素和干旱的响应机理研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2024.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
段永康. 黑莓氮素形态偏好性及其相关机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2024.
|
| [21] |
薛泽政. 氮素形态对核桃幼苗生长特性的影响[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2022.
|
| [22] |
闫小莉, 胡文佳, 马远帆, 等. 异质性供氮环境下杉木、马尾松、木荷氮素吸收偏好及其根系觅氮策略[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(2): 1-11.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
王华顺, 张玲芳, 刘华银, 等. 串联索氏提取法快速测定烟草种子中油脂含量研究[J]. 云南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 34(1): 1-8.
|
| [25] |
罗学平, 李腊, 张丽, 等. 乙醇浸泡法测定绿茶叶绿素含量的试验研究[J]. 现代食品, 2023, 29(1): 148-154.
|
| [26] |
张述伟, 宗营杰, 方春燕, 等. 蒽酮比色法快速测定大麦叶片中可溶性糖含量的优化[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2020, 41(7): 196-200.
|
| [27] |
焦洁. 考马斯亮蓝G-250染色法测定苜蓿中可溶性蛋白含量[J]. 农业工程技术, 2016, 36(17): 33-34.
|
| [28] |
吴有勤. 氮素形态对樟树幼苗生长及光合生理特性的影响[J]. 陕西林业科技, 2024, 52(2): 21-25.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
蔡东升, 杨文洁, 段伊佩, 等. 不同氮素形态及配比对番茄幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(16): 113-118.
|
| [31] |
马超, 李雪, 马瑞杰, 等. 铵硝配比对樱桃番茄生长发育、产量、品质及氮素吸收的影响[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2024, 37(3): 121-127.
|
| [32] |
王瑞. 氮素对油茶苗木生长的影响研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2021.
|
| [33] |
沈谦, 梁正川, 余泽岑, 等. 不同施氮水平对桑树幼苗非结构性碳水化合物及其抗旱能力的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2023, 32(3): 402-410.
|
| [34] |
郝凯, 贾立国, 秦永林, 等. 氮素对马铃薯源-库关系影响研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 2020(3): 22-26.
|
| [35] |
高俊飞. 不同施肥配方对榉树幼苗生长和生理的影响[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2014.
|
| [36] |
花蕊, 郁万文, 李婷婷, 等. 硝铵配比对银杏苗生长和叶品质及产量的影响[J]. 经济林研究, 2021, 39(3): 1-9.
|
| [37] |
马秀玲, 蒋与刚. 精氨酸和一氧化氮合成的关系及其在免疫调节中的作用[J]. 氨基酸和生物资源, 2002(1): 46-50.
|
| [38] |
汪建飞, 董彩霞, 沈其荣. 氮素不同形态配比对菠菜体内游离氨基酸含量和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007(4): 664-670.
|
| [39] |
许如意, 别之龙, 黄丹枫. 不同氮素形态配比对网纹甜瓜干物质分配和氮代谢的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2005(S2): 147-150.
|
| [40] |
梁娟, 叶漪, 杨伟. 不同氮素形态及配比对天门冬生长和品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018(1): 28-31.
|
| [41] |
郭华. 铵态氮和硝态氮对矮牵牛生长发育及花瓣氨基酸代谢的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022.
|
| [42] |
徐新娟. 氮素形态对番茄果实生长和有机酸代谢动态变化的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011.
|
| [43] |
刘威, 刘旭, 蔡卫佳, 等. 六个薄壳山核桃单株果实脂肪酸组成和营养成分比较分析[J]. 北方园艺, 2022(23): 46-53.
|
| [44] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |