 PDF(1942 KB)
PDF(1942 KB)


Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on root phosphorus acquisition strategy in Larix gmelinii and Fraxinus mandshurica plantations
YIN Tianlong, LIU Zhi, REN Hao, MA Yaoyuan, GU Jiacun
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 150-159.
 PDF(1942 KB)
PDF(1942 KB)
 PDF(1942 KB)
PDF(1942 KB)
Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on root phosphorus acquisition strategy in Larix gmelinii and Fraxinus mandshurica plantations
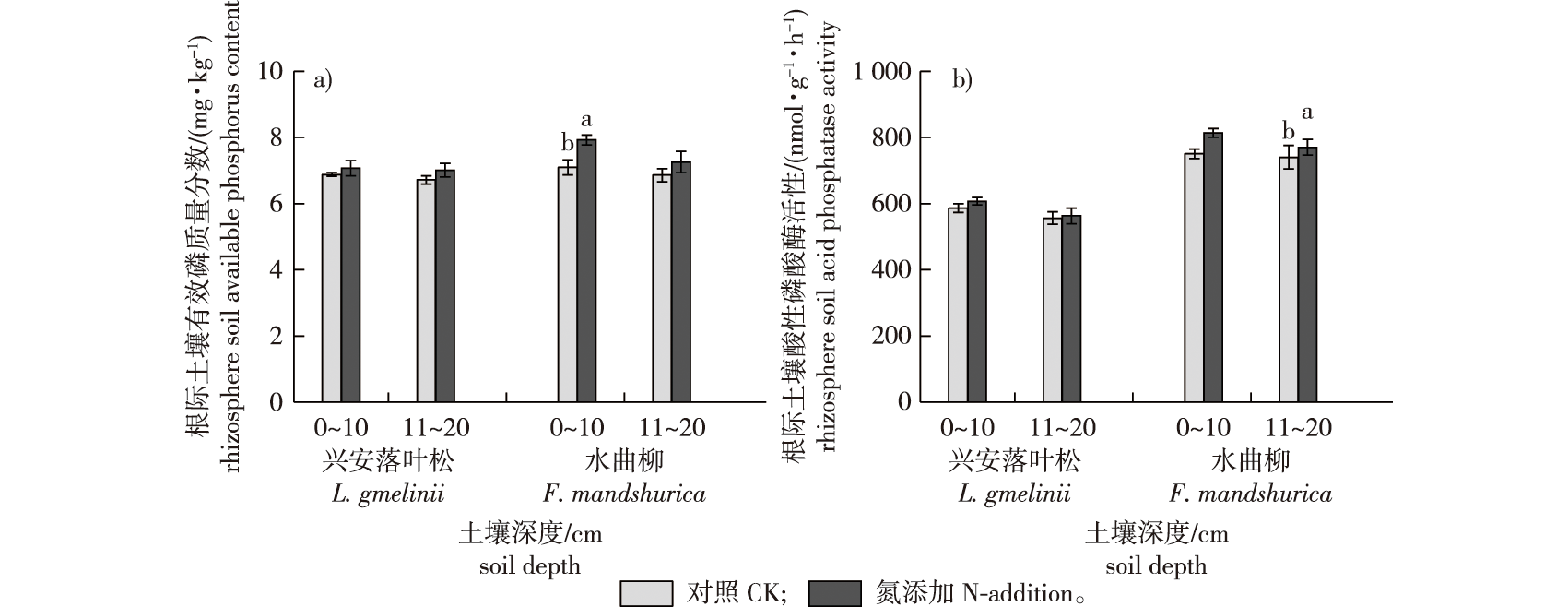
【Objective】 The objective of this study was to reveal the effects of long-term nitrogen (N) addition on root phosphorus (P) acquisition strategies of plantations in northeast China, providing a fundamental understanding in the framework of root economics space. 【Method】Following a 20-year N-addition manipulation in Larix gmelinii and Fraxinus mandshurica plantations in Maoershan, Heilongjiang Province, China, we investigated the effect of long-term N addition on root phosphatase activity (RPA) in the surface (0-10 cm) and subsurface (11-20 cm) soils, and explored the relationship between RPA and root morphology, mycorrhizal colonization rate, and rhizosphere soil properties. 【Result】Long-term nitrogen (N) addition promoted an increasing trend in rhizosphere soil available phosphorus and phosphatase activity for both L. gmelinii and F. mandshurica. Root phosphatase activity (RPA) progressively declined from first-to third-order roots in both species, though no significant differences were observed between soil layers. Within the same root order, F. mandshurica consistently exhibited higher RPA than L. gmelinii. Prolonged N addition significantly reduced the total RPA of absorptive roots (first three orders) in both species, with the most pronounced reduction occurring in the first-order roots of F. mandshurica. Additionally, absorptive roots displayed morphological adjustments under N enrichment, including finer root diameters and lower tissue density. Principal component analysis revealed multidimensional coordination of root functional traits, highlighting negative correlations between RPA and mycorrhizal colonization rate, rhizosphere available phosphorus, and bulk soil phosphatase activity, but positive correlations with specific root length and surface area. These patterns collectively indicate that RPA aligns with a “do-it-yourself” phosphorus acquisition strategy along the fungal collaboration gradient, favoring enzymatic investment over symbiotic dependency under N-enriched conditions. 【Conclusion】Collectively, after long-term N addition, the P acquisition strategies of the two trees changed, roots became slender, RPA and the mycorrhizal colonization rate decreased, which were more obvious in F. mandshurica plantations.
Larix gmelinii / Fraxinus mandshurica / plantations / nitrogen addition / phosphatase / absorptive root / root order
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
王文娜, 王燕, 王韶仲, 等. 氮有效性增加对细根解剖、形态特征和菌根侵染的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(4):1294-1302.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
耿鹏飞. 氮添加对红松人工林细根功能性状及生长动态的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2022.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
何敏, 许秋月, 夏允, 等. 植物磷获取机制及其对全球变化的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(3):291-305.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
贾淑霞, 王政权, 梅莉, 等. 施肥对落叶松和水曲柳人工林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(3):372.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
赵凯歌, 周正虎, 金鹰, 等. 长期氮添加对落叶松和水曲柳人工林土壤碳、氮、磷含量和胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5):177-184.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
于立忠, 丁国泉, 史建伟, 等. 施肥对日本落叶松人工林细根直径、根长和比根长的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(5):957-962.
|
| [50] |
刘金梁, 梅莉, 谷加存, 等. 内生长法研究施氮肥对水曲柳和落叶松细根生物量和形态的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(1):1-6.
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |