 PDF(2343 KB)
PDF(2343 KB)


Effects of Miscanthus on soil physicochemical characteristics and microbial community composition in saline-alkali soil
ZHANG Zhe, ZONG Junqin, LI Ling, LU Hailong, XUE Jianhui
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 50-57.
 PDF(2343 KB)
PDF(2343 KB)
 PDF(2343 KB)
PDF(2343 KB)
Effects of Miscanthus on soil physicochemical characteristics and microbial community composition in saline-alkali soil
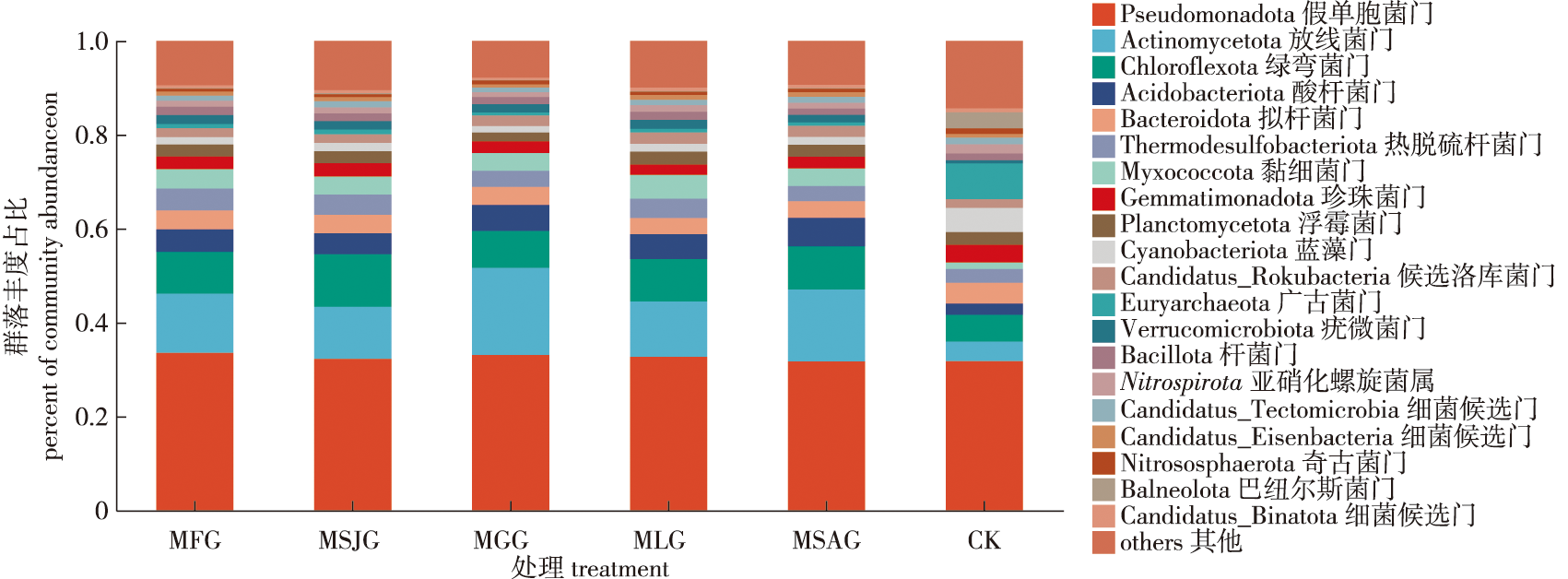
【Objective】 To investigate the effects of planting different Miscanthus species on the physicochemical properties of saline-alkali soil and the composition and structure of the microbial community, thus providing a basis for selecting suitable Miscanthus species for ecological restoration of saline-alkali land.【Method】Rhizosphere soil, non-rhizosphere soil, and bare land (CK) soil samples were collected from the planting sites of five Miscanthus species: Miscanthus sinensis, Miscanthus sacchariflorus, Miscanthus floridulus, Miscanthus lutarioriparius, and Miscanthus × longiberbis. Soil physicochemical properties were measured, and high-throughput sequencing technology was employed to analyze the composition of the soil microbial community.【Result】Compared with bare land soil, planting Miscanthus significantly improved the soil environment: soil water content increased in the planting sites of all five Miscanthus species, with a significant increase of 40.4% in the Miscanthus sinensis planting site. Soil pH and total salt content decreased, with a 2.6% reduction in pH in the M. × longiberbis planting site compared to CK, and a significant 83.9% reduction in total salt content in the M. sacchariflorus planting site. The contents of organic carbon, total nitrogen, and available phosphorus increased. While no significant differences were observed in microbial community α diversity, the community composition and structure underwent significant changes, with Pseudomonadota being the dominant phylum. The relative abundances of Acidobacteriota, Actinobacteriota, and Chloroflexota significantly increased, whereas those of Gemmatimonadota and Cyanobacteria significantly decreased. 【Conclusion】Planting Miscanthus effectively ameliorates the physicochemical properties of saline-alkali soil, enhances soil fertility, and optimizes microbial community structure. Among the tested species, M. sacchariflorus exhibited the best overall improvement effects. The findings of this study provide a theoretical basis and practical guidance for selecting Miscanthus species in the ecological restoration of saline-alkali land.
Miscanthus spp. / saline land / soil physical and chemical properties / microbial community composition
| [1] |
王佳丽, 黄贤金, 钟太洋, 等. 盐碱地可持续利用研究综述[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(5):673-684.
|
| [2] |
李彬, 王志春, 孙志高, 等. 中国盐碱地资源与可持续利用研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2005, 23(2):154-158.
|
| [3] |
王伟, 解建仓, 黄俊铭, 等. 盐碱地治理新模式研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2009, 20(5):117-119,122.
|
| [4] |
何蕾, 李国胜, 崔林林, 等. 江苏沿海滩涂围垦与社会经济发展的耦合关系[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(23):9228-9238.
|
| [5] |
马国辉, 郑殿峰, 母德伟, 等. 耐盐碱水稻研究进展与展望[J]. 杂交水稻, 2024, 39(1):1-10.
|
| [6] |
孙盛楠, 严学兵, 尹飞虎. 我国沿海滩涂盐碱地改良与综合利用现状与展望[J]. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(2):1-13.
|
| [7] |
赵英, 王丽, 赵惠丽, 等. 滨海盐碱地改良研究现状及展望[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(3):67-74.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
欧阳旭, 张亚茹, 李跃林. 基于生物质能的芒属(Miscanthus)植物碳动态和收支研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(9):1633-1638.
|
| [13] |
詹伟君, 任君霞, 金松恒, 等. 能源植物芒草的农学特性研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2012, 29(1):119-124.
|
| [14] |
于延冲, 易自力, 周功克. 能源植物芒草研究进展与综合利用现状[J]. 生命科学, 2014, 26(5):474-480.
|
| [15] |
郑铖, 易自力, 肖亮, 等. NaCl胁迫对芒属种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(3):37-42.
|
| [16] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M].3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [17] |
邱莉萍, 张兴昌. 黄土高原沟壑区小流域不同植被覆被对土壤性质的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2010, 17(3):64-68.
|
| [18] |
段鹏飞, 陈彦, 张菲, 等. 芒草种植对土壤细菌群落结构和功能的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(6):2030-2038.
|
| [19] |
王光华, 刘俊杰, 于镇华, 等. 土壤酸杆菌门细菌生态学研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(2):14-20.
|
| [20] |
鲜文东, 张潇橦, 李文均. 绿弯菌的研究现状及展望[J]. 微生物学报, 2020, 60(9):1801-1820.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
耿德洲, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 等. 黄土高原半干旱区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿人工草地土壤微生物和线虫群落特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(4):1365-1377.
|
| [24] |
杨阳, 李海亮, 马凯丽, 等. 放线菌及其代谢产物研究进展:基于CiteSpace可视化分析[J]. 微生物学报, 2022, 62(10):3825-3843.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
靳新影, 张肖冲, 金多, 等. 腾格里沙漠东南缘不同生物土壤结皮细菌多样性及其季节动态特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6):718-726.
|
| [27] |
姚丽茹, 李伟, 朱员正, 等. 施用生物炭对麦田土壤细菌群落多样性和冬小麦生长的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6):3396-3407.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
杜昊楠, 兰国玉, 吴志祥, 等. 海南热带雨林土壤细菌组成与多样性分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2022, 53(3):840-849.
|
| [32] |
张丽, 闫倩, 王保莉, 等. 不同土地利用方式下滨海盐土细菌多样性变化[J]. 西北农业学报, 2011, 20(8):163-167,198.
|
| [33] |
李寒, 张晓黎, 郭晓红, 等. 滨海盐渍化土壤中蓝细菌多样性及分布[J]. 微生物学通报, 2015, 42(5):957-967.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |