 PDF(1695 KB)
PDF(1695 KB)


Analysis of composition and diversity of plant communities in the lake shore zone of Taihu Lake
LI Sumei, WANG Qing, XUE Jianhui, GAO Lulu, SONG Chunfeng, LI Ya, WANG Peng, WANG Shu’an
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 58-64.
 PDF(1695 KB)
PDF(1695 KB)
 PDF(1695 KB)
PDF(1695 KB)
Analysis of composition and diversity of plant communities in the lake shore zone of Taihu Lake
【Objective】 Vegetation is a vital component of the lake shore zone ecosystems. A comprehensive analysis of plant community composition and diversity characteristics is essential for evaluating the ecological health and service functions of the lake shore zone of Taihu Lake. 【Method】We systematically investigated the plant community around the lake shore zone of Taihu Lake using a transect-quadrat survey method to analyze the species composition and diversity. 【Result】(1) The lake shore zone harbored 226 plant species from 179 genera and 76 families, predominantly wetland and aquatic herbaceous plants. Alien invasive plants were numerous and widely distributed. (2) Distinct, regionally characteristic plant communities formed based on habitat conditions, each containing at least one alien invasive species. (3) The important value of the dominant alien invasive species (ranked by the highest important value, IV) exhibited a negative correlation with the plant community’s diversity index. 【Conclusion】Alien plant invasion poses a serious threat to the lake shore ecosystem of Taihu Lake, undermining biodiversity stability. Enhanced monitoring and management are urgently required.
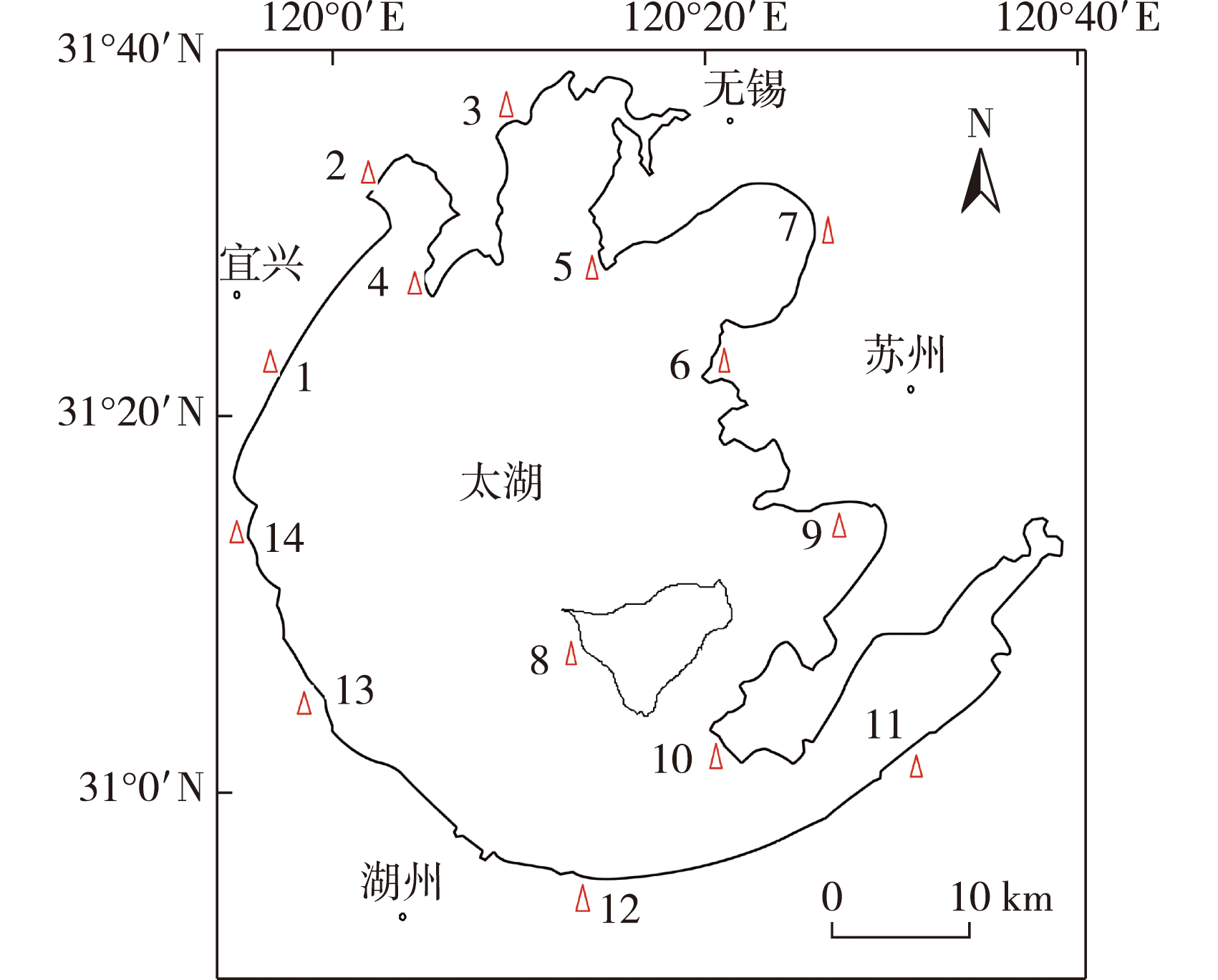
lake shore zone of Taihu Lake / plant community / biodiversity / invasive alien plant
| [1] |
叶春, 李春华, 邓婷婷. 论湖滨带的结构与生态功能[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(2):171-181.
|
| [2] |
田玉清, 陈欣, 吕超超, 等. 洱海湖滨带水生植物多样性及分布现状[J]. 湖泊科学, 2023, 35(3):941-949.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
叶春, 李春华, 吴蕾, 等. 湖滨带生态退化及其与人类活动的相互作用[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(3):401-407.
|
| [5] |
赵凯. 太湖水生植被分布格局及演变过程[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2017.
|
| [6] |
赵凯, 周彦锋, 蒋兆林, 等. 1960年以来太湖水生植被演变[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(2):351-362.
|
| [7] |
耿荣妹, 胡小贞, 许秋瑾, 等. 太湖东岸湖滨带水生植物特征及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(12):17-23.
|
| [8] |
谢洪民, 李启升, 刘帅领, 等. 环太湖地区河道和湖泊沿岸带水生植物多样性现状调查[J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(3):735-744.
|
| [9] |
姚程, 胡小贞, 姜霞, 等. 太湖贡湖湾人工湖滨带水生植物恢复及其富营养化控制[J]. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(6):1626-1638.
|
| [10] |
刘倩, 李超, 徐军, 等. 太湖流域湖荡湿地水生植物的分布特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(1):244-251.
|
| [11] |
徐德瑞, 周杰, 张建华, 等. 东太湖沉水植物现状及影响因子分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 2020, 38(4):64-67,94.
|
| [12] |
蔡天祎, 叶春, 李春华, 等. 太湖湖滨带水向辐射带水生植物多样性及生境因子分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(1):164-170.
|
| [13] |
叶春, 李春华, 陈小刚, 等. 太湖湖滨带类型划分及生态修复模式研究[J]. 湖泊科学, 2012, 24(6):822-828.
|
| [14] |
刘启新. 江苏植物志-2,2[M]. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 2013.
|
| [15] |
马金双. 中国入侵植物名录[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013.
|
| [16] |
王伯荪. 植物群落学实验手册[M]. 广州: 广东高等教育出版社, 1996.
|
| [17] |
张鑫, 胡海波, 吴秋芳, 等. 基于挂网喷播绿化的岩质边坡植物多样性及影响因素分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(3):131-138.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
贺坤, 张紫菀, 宋桉楠, 等. 海岸带生态修复工程对鸟类多样性及群落动态变化的影响分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023(3):158-166.
|
| [20] |
高海龙, 程寒飞, 詹茂华, 等. 太湖水生植物研究进展[J]. 湿地科学, 2019, 17(1):9-15.
|
| [21] |
王友文, 徐杰, 李继影, 等. 东太湖围网全面拆除前后水生植被及水质变化[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2022, 38(1):104-111.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
柳晓燕, 朱金方, 李飞飞, 等. 豚草入侵对新疆伊犁河谷林下本地草本植物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(24):9613-9620.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
张紫妍, 张致杰, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对遮荫的可塑性反应:入侵地与原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(1):18-22.
|
| [26] |
黄河燕, 朱政财, 吴纪华, 等. 喜旱莲子草对模拟全天增温的可塑性:引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4):419-427.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
于良瑞, 朱政财, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对同基因型邻体根系的表型可塑性:入侵地和原产地的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6):651-657.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
何新雄. 警惕“生态杀手”:加拿大一枝黄花[J]. 林业与生态, 2025(1):40-41.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |