JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY ›› 2023, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 226-233.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202111008
Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Wei1( ), WANG Bin2,*(
), WANG Bin2,*( ), CHU Xiuli3, WANG Xiuhua4, ZHANG Dongbei4, WU Xiaolin4, ZHOU Zhichun2
), CHU Xiuli3, WANG Xiuhua4, ZHANG Dongbei4, WU Xiaolin4, ZHOU Zhichun2
Received:2021-11-03
Accepted:2022-02-22
Online:2023-01-30
Published:2023-02-01
Contact:
WANG Bin
E-mail:lhsunwei@163.com;ylwangbin@sina.com
CLC Number:
SUN Wei, WANG Bin, CHU Xiuli, WANG Xiuhua, ZHANG Dongbei, WU Xiaolin, ZHOU Zhichun. Response and association of the growth and nutrient traits of Pinus massoniana container seedlings to phosphorus addition and inoculation of mycorrhizal fungi[J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(1): 226-233.
Table 1
Variance analysis of growth traits of Pinus massoniana container seedlings"
| 项目index | 苗高/cm seedling height | 地径/mm caliper | 高径比 height- diameter ratio | 单株总生物量/ (g·株-1) total biomass | 总根长/cm total root length | 根系直径 /mm root diameter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不接种non-inoculated(NM) | 18.457±1.654 | 3.081±0.355 | 60.191±4.164 | 1.364±0.232 | 158.154±32.950 | 0.137±0.009 | |
| 接种inoculated(LM) | 19.076±1.550 | 3.385±0.366 | 56.590±3.508 | 1.930±0.424 | 122.622±14.739 | 0.154±0.013 | |
| 接菌处理(M)mycorrhizal | 2.198 | 16.519*** | 12.077** | 40.052*** | 19.557*** | 22.265*** | |
| F | 添加P处理(P)P addition | 4.157** | 9.324*** | 3.595** | 2.858* | 1.04 | 1.15 |
| M × P | 0.533 | 0.7 | 0.501 | 1.76 | 0.7 | 0.418 | |
Table 2
Variance analysis of nutrient traits of Pinus massoniana container seedlings"
| 项目 index | N含量/ (g·kg-1) N content | P含量/ (g·kg-1) P content | N吸收量/ (g·株-1) N uptake | P吸收量/ (g·株-1) P uptake | N利用指数/g N utilization index | P利用指数/g P utilization index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不接种non-inoculated(NM) | 12.918±1.312 | 2.292±0.229 | 17.563±2.986 | 3.124±0.573 | 0.836±0.188 | 5.473±1.130 | |
| 接种inoculated(LM) | 9.693±1.121 | 2.034±0.294 | 18.450±3.147 | 3.906±0.930 | 1.675±0.561 | 9.333±3.088 | |
| 接菌处理(M)mycorrhizal | 103.137*** | 20.619*** | 1.351 | 26.200*** | 54.238*** | 33.815*** | |
| F | 添加P处理(P)P addition | 2.778* | 6.941*** | 3.852** | 9.224*** | 2.128 | 1.667 |
| M×P | 1.927 | 2.086 | 1.744 | 2.337 | 1.755 | 1.457 | |
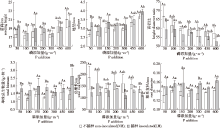
Fig.1
Growth difference of Pinus massoniana container seedlings under phosphorus addition and inoculation of mycorrhizal fungi Different uppercase letters indicated significant differences between different mycorrhizal fungi treatment under the same P addition treatment (P < 0.05), while different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between different P addition treatment under the same mycorrhizal fungi treatment (P < 0.05). The same below."
Table 3
Correlation analysis of growth and nutrient traits of Pinus massoniana container seedlings"
| 处理 treatment | 性状 traits | 苗高 seedling height | 地径 caliper | 高径比 height- diameter ratio | 总生物量 total biomass | 总根长 total root length | 根系直径 root diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不接种 non-inoculated (NM) | N含量N content | -0.307 | -0.249 | -0.011 | -0.202 | -0.185 | -0.073 |
| P含量P content | -0.077 | 0.248 | -0.560** | -0.039 | -0.248 | -0.115 | |
| N吸收量N uptake | 0.425 | 0.446* | -0.236 | 0.820** | -0.400 | 0.130 | |
| P吸收量P uptake | 0.535* | 0.679** | -0.489* | 0.863** | -0.400 | 0.084 | |
| N利用指数N utilization index | 0.614** | 0.555** | -0.141 | 0.873** | -0.164 | 0.160 | |
| P利用指数P utilization index | 0.395 | 0.228 | 0.130 | 0.718** | -0.168 | 0.316 | |
| 接种 inoculated (LM) | N含量N content | -0.505* | -0.437* | 0.051 | -0.565** | 0.358 | -0.421 |
| P含量P content | -0.097 | 0.073 | -0.270 | -0.167 | 0.152 | -0.368 | |
| N吸收量N uptake | 0.681** | 0.741** | -0.404 | 0.831** | -0.099 | 0.217 | |
| P吸收量P uptake | 0.674** | 0.807** | -0.508* | 0.803** | -0.167 | 0.140 | |
| N利用指数N utilization index | 0.757** | 0.761** | -0.307 | 0.934** | -0.440* | 0.553** | |
| P利用指数P utilization index | 0.640** | 0.583** | -0.164 | 0.776** | -0.421 | 0.665** |
| [1] |
WANG C Y, XIAO H G, LIU J, et al. Insights into the effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on leaf functional traits of Rhus typhina[J]. Pol J Environ Stud, 2016, 25(3):1279-1284.DOI:10.15244/pjoes/61788.
doi: 10.15244/pjoes/61788 |
| [2] | 刘晓娟, 马克平. 植物功能性状研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2015, 45(4):325-339. |
|
LIU X J, MA K P. Plant functional traits:concepts,applications and future directions[J]. Sci Sin Vitae, 2015, 45(4):325-339.DOI:10.1360/N052014-00244.
doi: 10.1360/N052014-00244 |
|
| [3] | 王先之, 蒋海亮, 许可旺, 等. 磷添加对紫花苜蓿幼苗地上部及根系生长模式的影响[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(1):87-91,99. |
|
WANG X Z, JIANG H L, XU K W, et al. Influence of phosphorus addition on shoot and root growth patterns of Medicago sativa L.[J]. J Lanzhou Univ (Nat Sci), 2013, 49(1):87-91,99.DOI:10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2013.01.006.
doi: 10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2013.01.006 |
|
| [4] | 郑亚萍, 王春晓, 郑祖林, 等. 磷对花生根系形态特征的影响[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2019, 41(4):622-628. |
|
ZHENG Y P, WANG C X, ZHENG Z L, et al. Effect of phosphorus(P) on root morphology characteristics of peanut[J]. Chin J Oil Crop Sci, 2019, 41(4):622-628.DOI:10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2019.04.017.
doi: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2019.04.017. |
|
| [5] |
KIRKBY C A, SMYTHE L J, COX J W, et al. Phosphorus movement down a toposequence from a landscape with texture contrast soils[J]. Soil Res, 1997, 35(2):399.DOI:10.1071/s96045.
doi: 10.1071/s96045 |
| [6] | 薛小平, 杨勇, 黄建国. 外生菌根促进植物磷素营养研究进展[J]. 中国食用菌, 2006, 25(6):3-4. |
|
XUE X P, YANG Y, HUANG J G. Advancement on the research of improvement of plant’s phosphorus nutrition by ectomycorrhizal[J]. Edible Fungi China, 2006, 25(6):3-4.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-8310.2006.06.001.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8310.2006.06.001 |
|
| [7] |
杨青, 张一, 周志春, 等. 异质低磷胁迫下马尾松家系根构型和磷效率的遗传变异[J]. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(12):1226-1235.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2011.01226 |
|
YANG Q, ZHANG Y, ZHOU Z C, et al. Genetic variation in root architecture and phosphorus efficiency in response to heterogeneous phosphorus deficiency in Pinus massoniana families[J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2011, 35(12):1226-1235.DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1258.2011.01226.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2011.01226 |
|
| [8] | 杨青, 张一, 周志春, 等. 低磷胁迫下不同种源马尾松的根构型与磷效率[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(9):2339-2345. |
|
YANG Q, ZHANG Y, ZHOU Z C, et al. Root architecture and phosphorus efficiency of different provenance Pinus massoniana under low phosphorous stress[J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2012, 23(9):2339-2345.DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.2012.0324.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.2012.0324 |
|
| [9] | 宋平, 张一, 张蕊, 等. 低磷胁迫下马尾松无性系磷效率性状对氮沉降的响应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(2):502-511. |
|
SONG P, ZHANG Y, ZHANG R, et al. Responses of phosphorus efficiency to simulated nitrogen deposition under phosphorus deficiency in Pinus massoniana clones[J]. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci, 2017, 23(2):502-511.DOI:10.11674/zwyy.16112.
doi: 10.11674/zwyy.16112 |
|
| [10] | 王艺, 丁贵杰. 水分胁迫下外生菌根对马尾松幼苗养分吸收的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2013, 26(2):227-233. |
|
WANG Y, DING G J. Influence of ectomycorrhiza on nutrient absorption of Pinus massoniana seedlings under water stress[J]. For Res, 2013, 26(2):227-233.DOI:10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2013.02.017.
doi: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2013.02.017 |
|
| [11] |
ELBERSE I A M, VAN DAMME J M M, VAN TIENDEREN P H. Plasticity of growth characteristics in wild barley (Hordeum spon-taneum) in response to nutrient limitation[J]. J Ecol, 2003, 91(3):371-382.DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2745.2003.00776.x.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2745.2003.00776.x |
| [12] | 张东北, 王秀花, 周生财, 等. 不同家系马尾松容器苗对基质配比及控释肥的响应[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(5):1044-1050. |
|
ZHANG D B, WANG X H, ZHOU S C, et al. Response of masson pine container seedlings from different families to substrate proportion and control released fertilizer[J]. J Zhejiang A & F Univ, 2019, 36(5):1044-1050.DOI:10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.05.026.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.05.026 |
|
| [13] |
阎秀峰, 王琴. 两种外生菌根真菌在辽东栎幼苗上的混合接种效应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(1):17-23.
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2004.0003 |
|
YAN X F, WANG Q. Effects of co-inoculation with two ectomycorrhizal fungi on Quercus liaotungensis seedlings[J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2004, 28(1):17-23.
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2004.0003 |
|
| [14] | 王艺, 王秀花, 吴小林, 等. 缓释肥加载对浙江楠和闽楠容器苗生长和养分库构建的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(12):57-63. |
|
WANG Y, WANG X H, WU X L, et al. Effects of slow-release fertilizer loading on growth and construction of nutrients reserves of Phoebe chekiangensis and Phoebe bournei container seedlings[J]. Sci Silvae Sin, 2013, 49(12):57-63.DOI:10.11707/j.1001-7488.20131209.
doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20131209 |
|
| [15] |
HAWKINS B J. Family variation in nutritional and growth traits in Douglas-fir seedlings[J]. Tree Physiol, 2007, 27(6):911-919.DOI:10.1093/treephys/27.6.911.
doi: 10.1093/treephys/27.6.911 pmid: 17331909 |
| [16] | 王亚军, 唐明, 郭渊, 等. 外生菌根真菌对杉木的接种效应[J]. 西北植物学报, 2006, 26(9):1900-1904. |
|
WANG Y J, TANG M, GUO Y, et al. Inoculation effect of ectomycorrhizal fungi on Cunninghamia lanceolata[J]. Acta Bot Boreali Occidentalia Sin, 2006, 26(9):1900-1904.DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2006.09.026.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2006.09.026 |
|
| [17] | 何跃军, 钟章成, 刘济明. 接种外生菌根真菌对柏木幼苗生长的影响[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2008, 36(1):67-69. |
|
HE Y J, ZHONG Z C, LIU J M. Effects of ectomycorrhiza fungi on seedling growth of Cupressus funebris[J]. Guizhou Agric Sci, 2008, 36(1):67-69.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2008.01.021.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2008.01.021 |
|
| [18] | 姜磊, 李焕勇, 张芹, 等. AM真菌对盐碱胁迫下杜梨幼苗生长与生理代谢的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6):152-160. |
|
JIANG L, LI H Y, ZHANG Q, et al.Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi on the growth and physiological metabolism of Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge seedlings under saline-alkaline stress[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2020, 44(6):152-160. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.202001045.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.202001045 |
|
| [19] | 贾艳艳, 顾大路, 杨文飞, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对还田麦秆分解及玉米生物量的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2019, 35(3):612-617. |
|
JIA Y Y, GU D L, YANG W F, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonization on wheat-straw decomposition and maize biomass[J]. Jiangsu J Agr Sci, 2019, 35(3):612-617.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2019.03.015.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2019.03.015 |
|
| [20] | 鲍志来. 外生菌根菌接种对白皮松生长的影响[J]. 上海农业科技, 2017(4):99,107. |
|
BAO Z L. Effects of ectomycorrhizal fungi inoculation on the growth of Pinus bungeana[J]. Shanghai Agric Sci Technol, 2017(4): 99,107.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-0106.2017.04.054.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0106.2017.04.054 |
|
| [21] | 宝秋利, 乔宇, 闫伟, 等. 两株乳牛肝菌属外生菌根真菌对沙地云杉幼苗生长的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2020(4):87-92. |
|
BAO Q L, QIAO Y, YAN W, et al. Effect of two Suillus ectomycorrhizal fungus on seedling growth of Picea mongolica[J]. North Hortic, 2020(4):87-92.DOI:10.11937/bfyy.20192033.
doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20192033 |
|
| [22] | 马琼, 黄建国, 蒋剑波. 接种外生菌根真菌对马尾松幼苗生长的影响[J]. 福建林业科技, 2005, 32(2):85-88. |
|
MA Q, HUANG J G, JIANG J B. Effect of inoculating with the ectotrophic mycorrhizal epiphyte on the Pinus massoniana seedling growth[J]. J Fujian For Sci Technol, 2005, 32(2):85-88.DOI:10.13428/j.cnki.fjlk.2005.02.021.
doi: 10.13428/j.cnki.fjlk.2005.02.021 |
|
| [23] | 王艺, 丁贵杰. 外生菌根对马尾松幼苗生长、生理特征和养分的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(2):97-102. WANG Y,DING G J.Effects of ectomycorrhizal on growth,physiological characteristics and nutrition in Pinus massoniana seedlings[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed),2013, 37(2):97-102. |
| [24] | 郝龙飞, 郝文颖, 刘婷岩, 等. 氮添加及接种处理对1年生樟子松苗木根系形态及养分含量的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(4):1-7. |
|
HAO L F, HAO W Y, LIU T Y, et al. Responses of root morphology and nutrient content of Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica seedlings to nitrogen addition and inoculation treatments[J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2021, 43(4):1-7.DOI:10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200071.
doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200071 |
|
| [25] |
刘婷岩, 郝龙飞, 王续富, 等. 氮沉降及菌根真菌对长白落叶松苗木根系构型及根际酶活性的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2021, 41(1):145-151.
doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.01.018 |
|
LIU T Y, HAO L F, WANG X F, et al. Effects of nitrogen deposition and ectomycorrhizal fungi on root architecture and rhizosphere soil enzyme activities of Larix olgensis seedlings[J]. Bull Bot Res, 2021, 41(1):145-151.DOI:10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.01.018.
doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.01.018 |
|
| [26] | 张珍明, 张家春, 何云松, 等. 马尾松外生菌根真菌研究进展[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2016(2):66-68,72. |
|
ZHANG Z M, ZHANG J C, HE Y S, et al. The research progress of ectomycorrhizal fungi in Pinus massoniana[J]. Tillage Cultiv, 2016(2):66-68, 72.DOI:10.13605/j.cnki.52-1065/s.2016.02.027.
doi: 10.13605/j.cnki.52-1065/s.2016.02.027 |
|
| [27] | 李洋, 胥晓雯, 杨凯晴, 等. 一株高效羽毛降解菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 生物加工过程, 2022, 20(3):270-276. |
|
LI Y, XU X W, YANG K Q, et al. Screening of a highly efficient feather degrading bacterium[J]. Chin J Bioprocess Eng, 2022, 20(3):270-276. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2022.03.005.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2022.03.005 |
|
| [28] |
LAN Z C, BAI Y F. Testing mechanisms of N-enrichment-induced species loss in a semiarid Inner Mongolia grassland:critical thresholds and implications for long-term ecosystem responses[J]. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 2012, 367(1606):3125-3134.DOI:10.1098/rstb.2011.0352.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0352 |
| [29] | 毛佳昊, 熊晓辉, 卢一辰. 茉莉酸调控植物应对逆境胁迫作用的研究进展[J]. 生物加工过程, 2021, 19(4):413-419. |
| MAO J H, XIONG X H, LU Y C. Advanves in the regulation of plant strss response by jasmonic acid[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2021, 19(4):413-419. | |
| [30] |
HE J S, WANG L, FLYNN D F B, et al. Leaf nitrogen:Phosphorus stoichiometry across Chinese grassland biomes[J]. Oecologia, 2008, 155(2):301-310.DOI:10.1007/s00442-007-0912-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00442-007-0912-y |
| [31] |
MARKLEIN A R, HOULTON B Z. Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems[J]. New Phytol, 2012, 193(3):696-704.DOI:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03967.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03967.x pmid: 22122515 |
| [32] | 原雅楠, 李正才, 王斌, 等. 不同林龄榧树根、枝、叶的 C、N、P 化学计量及内稳性特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6):135-142. |
|
YUAN Y N, LI Z C, WANG B, et al. Ecological stoichiometry in leaves, branches and roots of Torreya grandis with different forest ages and its stoichiometric homoeostasis[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2021, 45(6):135-142. DOI:10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202003057.
doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202003057 |
| [1] | YANG Mengqing, HUANG Shengyi, WANG Bin, ZHOU Zhichun, XU Xiaoniu, XU Weike, WU Renchao. Response of the growth and root development of Cyclobalanopsis gilva container seedlings to the slow-release fertilizer addition [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(1): 103-111. |
| [2] | CHEN Youmei, XIA Xinrui, YE Jianren, ZHU Lihua. An in vitro evaluation of the resistance traits to pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) in Pinus massoniana embryogenic callus [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(1): 37-45. |
| [3] | LIN Qiang, XU Jin, LI Shangqian, LIN Yunbin, ZHANG Yunqing, OUYANG Lei. The early selection and analysis of genetic variation of Cryptomeria japonica half-sib progeny from seed orchard in Fuding, Fujian Province [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(1): 78-86. |
| [4] | MIAO Conglin, LIU Yamin, YAO Hongyu, LIU Yumin, JI Yuwei, LI Jun’an. An evaluation of the regulatory effects of three organic acids on the antioxidant system of Pinus massoniana under aluminum toxicity [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(1): 112-118. |
| [5] | WU Wenjie, WU Chaoming, ZHU Li, WANG Linqi, GE Yu, ZHANG Tan, LIU Ziqiang. Adaptation of typical mixed forest species in the southern hilly region to precipitation variation via water source changes [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(6): 121-128. |
| [6] | CHEN Leiru, WEN Zhengyu, XU Xiaoniu, YIN Ruoyong, GAO Yu. Effects of long-term nitrogen and phosphorus additions on soil organic carbon storage and its components in a subtropical forest [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(5): 139-146. |
| [7] | WANG Jiaxing, YAN Pingyu, SUN Baifei, LIU Jinhong, FENG Kele, ZHANG Hanguo. Growth variation and superior families early selection of Larix olgensis free-pollinated families [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(5): 81-89. |
| [8] | ZONG Jianwei, LI Cheng, ZHANG Jing, YANG Yuhua. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and physiological characteristics of Xanthoceras sorbifolium under salt stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 168-176. |
| [9] | WU Yan, HUANG Qing, LIU Xun, ZHENG Rui, CEN Jiabao, DING Bo, ZHANG Yunlin, FU Yuhong. Effects of Pinus massoniana plantation age on soil physical and chemical properties in Karst areas in southwest China [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(3): 99-107. |
| [10] | SUN Jinwei, WANG Shengyan, FAN Diwu, ZHU Yongli. Effects of C, N and P additions on soil respiration in woodland under Cd stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(1): 140-146. |
| [11] | FAN Mingyang, HU Meng, YNAG Yuan, FANG Yanming. Community classification, structures and species diversity characteristics of Pinus massoniana and P. hwangshanensis in the eastern China [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(1): 47-58. |
| [12] | WANG Zhangrong, JI Kongshu, XU Li’an, ZOU Bingzhang, LIN Nengqing, LIN Jingquan. New management model of construction techniques, realistic genetic gain and low cost multi-generation improvement in seedling seed orchard of Pinus massoniana [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(6): 9-16. |
| [13] | WANG Yu, YI Yanling, LIU Hai, WEN Xiaochen, LI Tianyi, YIN Haifeng, LI Xianwei, FAN Chuan. Initial impacts of two thinning methods on the spatial structure of Pinus massoniana plantations [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(5): 138-146. |
| [14] | ZHU Lei, XU Junliang, ZHANG Yiping, LUO Pengfei, SHI Zhiqiang, HOU Jiayu, ZHAI Lexin. Analysis on diurnal variation of sap flow in Pinus massoniana and its influencing factors in Luoyang, Henan Province, China [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(1): 92-100. |
| [15] | JI Kongshu, XU Li’an, WANG Dengbao, NI Zhouxian, WANG Zhangrong. Progresses and achievements of genetic improvement on Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) in China [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(6): 10-22. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||