 PDF(2706 KB)
PDF(2706 KB)


Extraction and construction of a QSM-based model of first-order branches of Larix gmelinii plantations
PENG Wenyue, JIA Weiwei, WANG Fan, LI Xin, LI Dandan
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 185-193.
 PDF(2706 KB)
PDF(2706 KB)
 PDF(2706 KB)
PDF(2706 KB)
Extraction and construction of a QSM-based model of first-order branches of Larix gmelinii plantations
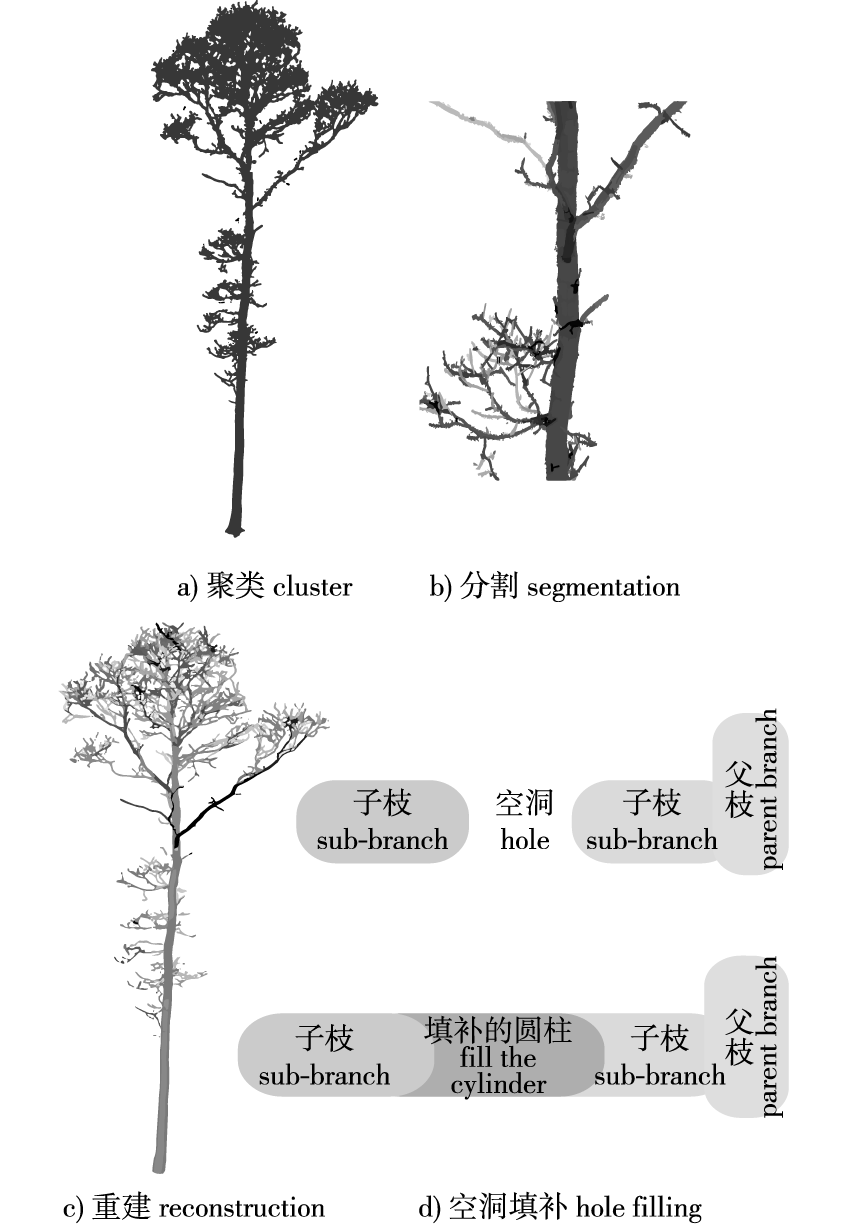
【Objective】The quantitative structural model (QSM) algorithm was used to extract the number of first-order branches at different relative branch depths using a fully automatic strategy based on terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) point cloud data. A linear mixed prediction model of first-order branch density was constructed to provide a theoretical basis for research studies on Larix gmelinii plantation canopies. 【Method】 The TLS data of 30 L. gmelinii plantations and the QSM algorithm were used to obtain parameters pertaining to tree structure, and the extracted and measured values were subjected to regression analysis for exploring the accuracy of modeling based on point cloud data. The extraction accuracy of the method used for determining the number of first-order branches at different relative branch depths was assessed using the point cloud layering method. The optimal mixing model of the first-order branch density of the sample tree effect was constructed using the Poisson regression model, and the model was evaluated. 【Result】 The average extraction accuracy of the model constructed based on 30 L. gmelinii plantation branches was 80.71%, and the RMSE was 6.959 4. There were differences among the number of first-order branches extracted from different canopies, and the best results were obtained when the relative branch depth ranged from 0.7 to 0.8. The average accuracy was 87.78%, and a mixed model based on the sample tree effect was found to be optimal for determining the first-order branch density. The optimal model of branch density was a linear mixed model based on three random effect parameters, namely natural logarithm of the relative branching depth [ln(RDINC)], square of the relative branching depth (RDINC2), and ratio of tree height to breast diameter [HT/DBH], and the values of R2 and RMSE were 0.745 4 and 0.229, respectively. 【Conclusion】 The parameters pertaining to the branch structure of individual trees were obtained based on the ground-based laser radar scanning data, using the quantitative structure model that was applicable or reliable. Based on the effects observed in the sample wood, the density mixed model of the first-order branches of L. gmelinii plantations not only reflects the changes in the distribution density of the primary branches in the canopy, but can also predict the overall growth trend of the crown.
Larix gmelinii / point cloud data / number of first-order branches / quantitative structural model (QSM) / linear mixed model
| [1] |
刘兆刚, 刘继明, 李凤日, 等. 樟子松人工林树冠结构的分形分析[J]. 植物研究, 2005, 25(4):465-470.
|
| [2] |
陈东升, 金钟跃, 李凤日, 等. 樟子松节子的大小及分布[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2007, 35(5):19-21.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
夏明鹏, 官凤英, 范少辉, 等. TLS技术在森林资源调查中的应用现状与展望[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2018, 33(3):238-244.
|
| [6] |
曹伟, 陈动, 史玉峰, 等. 激光雷达点云树木建模研究进展与展望[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021, 46(2):203-220.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
梁晓军, 庞勇, 陈博伟. 基于地基激光雷达胸径提取的单木位置精确测量[J]. 林业科学研究, 2020, 33(4):67-74.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
刘芳, 冯仲科, 杨立岩, 等. 基于三维激光点云数据的树冠体积估算研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(3):328-334.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
刘兆刚, 李凤日. 樟子松人工林树冠内一级枝条空间的分布规律[J]. 林业科学, 2007, 43(10):19-27.
|
| [19] |
苗铮, 董利虎, 李凤日, 等. 基于GLMM的人工林红松二级枝条分布数量模拟[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(4):121-128.
|
| [20] |
王曼霖, 董利虎, 李凤日. 基于Possion回归混合效应模型的长白落叶松一级枝数量模拟[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(11):45-55.
|
| [21] |
贾炜玮, 罗天泽, 李凤日. 基于抚育间伐效应的红松人工林枝条密度模型[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(2):10-21.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
李春明. 基于纵向数据非线性混合模型的杉木林优势木平均高研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2011, 24(1):68-73.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
张颖, 贾炜玮. 基于地基激光雷达的落叶松人工林枝条因子提取和建模[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(7):2505-2513.
|
| [30] |
王帆, 贾炜玮, 唐依人, 等. 基于TLS的红松树冠半径提取及其外轮廓模型构建[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(1):13-22.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |