JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 33-40.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202311030
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Ziwei1( ), RUAN Honghua1,*(
), RUAN Honghua1,*( ), YANG Yan2, XIE Youchao2, SHEN Caiqin3, XU Yaming3, CAO Guohua3
), YANG Yan2, XIE Youchao2, SHEN Caiqin3, XU Yaming3, CAO Guohua3
Received:2023-11-22
Accepted:2024-03-26
Online:2025-05-30
Published:2025-05-27
Contact:
RUAN Honghua
E-mail:z1442527446@163.com;hhruan@njfu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
ZHAO Ziwei, RUAN Honghua, YANG Yan, XIE Youchao, SHEN Caiqin, XU Yaming, CAO Guohua. Effects of drought on the soil microbial biomass C, N, P ecological stoichiometric characteristics of poplar plantation[J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(3): 33-40.
Fig. 1
Changes of soil microbial biomass C,N,P in different drought treatments Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments in the same seasons; different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different seasons under the same treatment. The same below."
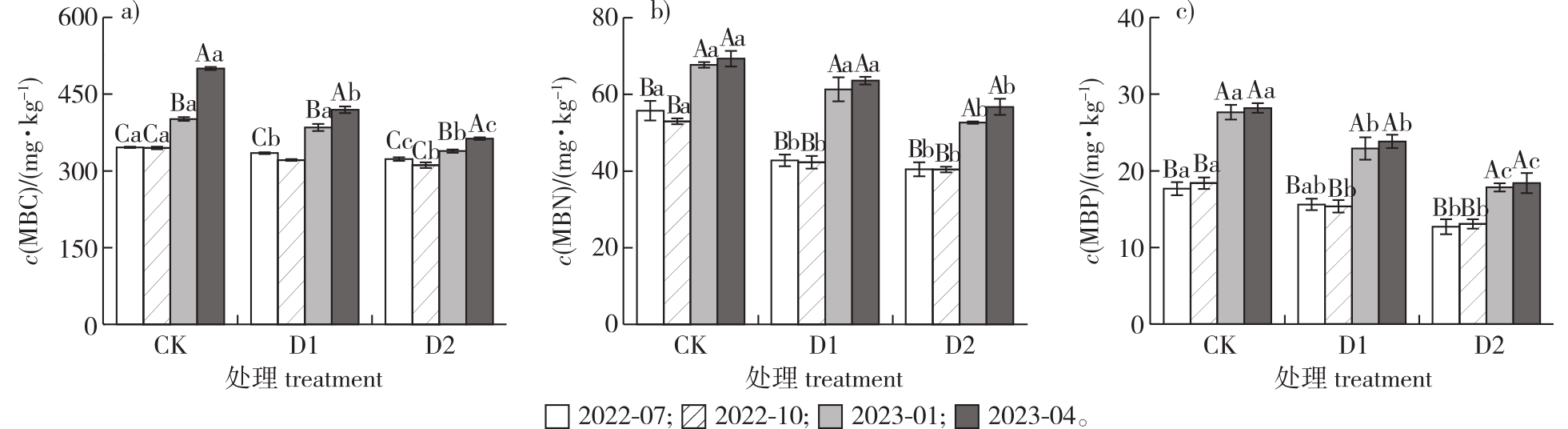
Table 1
Changes in soil physicochemical properties according to different drought treatments"
| 指标index | CK | D1 | D2 | 指标index | CK | D1 | D2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤含水率/% SWC | 26.79±0.70 a | 24.96±0.80 ab | 23.83±0.80 b | c(SOC)/(g·kg-1) | 11.67±0.42 a | 11.00±0.31 a | 10.58±0.26 a |
| pH | 8.25±0.01 b | 8.34±0.02 a | 8.38±0.02 a | c(AP)/(mg·kg-1) | 5.17±0.32 a | 3.66±0.34 b | 3.63±0.21 b |
| 土壤容重/ (g·cm-3) BD | 1.19±0.02 a | 1.14±0.03 a | 1.20±0.02 a | c(TC)/(g·kg-1) | 17.11±0.13 a | 17.63±0.18 a | 17.27±0.17 a |
| c($\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$)/ (mg·kg-1) | 0.93±0.16 b | 2.30±0.23 a | 2.75±0.25 a | c(TN)/(g·kg-1) | 1.25±0.03 a | 1.21±0.02 a | 1.18±0.03 a |
| c($\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$)/ (mg·kg-1) | 1.46±0.21 a | 0.73±0.28 b | 0.46±0.04 b | c(TP)/(mg·kg-1) | 883.73±27.04 a | 840.66±24.21 ab | 819.63±25.91 b |
| c(DOC)/ (mg·kg-1) | 510.80±30.21 a | 413.70±43.50 ab | 343.42±39.54 b | C/N | 14.10±0.34 a | 14.43±0.32 a | 14.64±0.40 a |
Table 2
Correlation analysis of soil microbial biomass, its stoichiometric characteristics and soil physicochemical properties"
| 指标index | MBC | MBN | MBP | MBC/MBN | MBC/MBP | MBN/MBP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBN | 0.844** | ||||||||||
| MBP | 0.873** | 0.920** | |||||||||
| MBC/MBN | -0.281 | -0.744** | -0.545** | ||||||||
| MBC/MBP | -0.562** | -0.786** | -0.869** | 0.697** | |||||||
| MBN/MBP | -0.533** | -0.422* | -0.727** | 0.055 | 0.750** | ||||||
| SWC | 0.556** | 0.714** | 0.722** | -0.602** | -0.718** | -0.464** | |||||
| pH | -0.028 | -0.147 | -0.225 | 0.216 | 0.313 | 0.252 | |||||
| BD | 0.587 | 0.587 | 0.560 | -0.413 | -0.492 | -0.395 | |||||
| $\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$ | -0.070 | 0.026 | -0.025 | -0.159 | -0.064 | 0.074 | |||||
| $\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$ | -0.639** | -0.660** | -0.657** | 0.378* | 0.498** | 0.353* | |||||
| DOC | -0.012 | -0.081 | -0.081 | 0.137 | 0.143 | 0.084 | |||||
| SOC | -0.379* | -0.587** | -0.534** | 0.612** | 0.651** | 0.319 | |||||
| AP | -0.009 | -0.015 | 0.063 | 0.072 | -0.020 | -0.103 | |||||
| TC | -0.289 | -0.356* | -0.282 | 0.303 | 0.186 | -0.019 | |||||
| TN | 0.520** | 0.655** | 0.624** | -0.513** | -0.620** | -0.395* | |||||
| TP | 0.122 | 0.246 | 0.345* | -0.299 | -0.449** | -0.376* | |||||
| C/N | -0.571** | -0.735** | -0.662** | 0.600** | 0.596** | 0.595* | |||||
| [1] | LEE J Y, MAROTZKE J, BALA G, et al. IPCC (The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change).Climate change 2021:the physical science basis. Future global climate:scenario-based projections and near-term information[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,2021: 553-672. DOI: 10.1017/9781009157896.006. |
| [2] | 朴世龙, 张新平, 陈安平, 等. 极端气候事件对陆地生态系统碳循环的影响[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2019, 49(9):1321-1334. |
| PIAO S L, ZHANG X P, CHEN A P, et al. The impacts of climate extremes on the terrestrial carbon cycle:a review[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2019, 49(9):1321-1334. | |
| [3] | KNAPP A K, HOOVER D L, WILCOX K R, et al. Characterizing differences in precipitation regimes of extreme wet and dry years:implications for climate change experiments[J]. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21(7):2624-2633.DOI: 10.1111/gcb.12888. |
| [4] | WELTZIN J F, LOIK M E, SCHWINNING S, et al. Assessing the response of terrestrial ecosystems to potential changes in precipitation[J]. BioScience,2003, 53(10):941-952.DOI: 10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[0941:ATROTE]2.0.CO;2. |
| [5] | 姚庭玉, 陈小梅, 何俊杰, 等. 模拟干旱对鼎湖山季风常绿阔叶林土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2017, 37(1):104-109. |
| YAO T Y, CHEN X M, HE J J, et al. Effects of drought on the C/N/P stoichiometry in the soil of a subtropical monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2017, 37(1):104-109.DOI: 10.11929/j.issn.2095-1914.2017.01.017. | |
| [6] | GIMBEL K F, FELSMANN K, BAUDIS M, et al. Drought in forest understory ecosystems-a novel rainfall reduction experiment[J]. Biogeosciences, 2015, 12(4):961-975.DOI: 10.5194/bg-12-961-2015. |
| [7] | SUN Y, CHEN H Y H, JIN L, et al. Drought stress induced increase of fungi:bacteria ratio in a poplar plantation[J]. CATENA, 2020,193:104607.DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104607. |
| [8] | 许华, 何明珠, 唐亮, 等. 荒漠土壤微生物量碳、氮变化对降水的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4):1295-1304. |
| XU H, HE M Z, TANG L, et al. Response of changes of microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen to precipitation in desert soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4):1295-1304.DOI: 10.5846/stxb201901020014. | |
| [9] | 许淼平, 任成杰, 张伟, 等. 土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷与土壤酶化学计量对气候变化的响应机制[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(7):2445-2454. |
| XU M P, REN C J, ZHANG W, et al. Responses mechanism of C∶N∶P stoichiometry of soil microbial biomass and soil enzymes to climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(7):2445-2454.DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201807.041. | |
| [10] | 李品, 木勒德尔·吐尔汗拜, 田地, 等. 全球森林土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷化学计量的季节动态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(6):532-542. |
| LI P, Muledeer Tuerhanbai, TIAN D, et al. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial biomass carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across global forest ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2019, 43(6):532-542.DOI: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0075. | |
| [11] | 李帅军, 郭剑芬, 吴东梅, 等. 隔离降雨对米槠天然林土壤微生物生物量和酶活性的影响[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2018, 13(1):17-25. |
| LI S J, GUO J F, WU D M, et al. Effects of throughfall exclusion on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a natural Castanopsis carlesii forest in subtropical China[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2018, 13(1):17-25.DOI: 10.19687/j.cnki.1673-7105.2018.01.003. | |
| [12] | WAN X H, CHEN X L, HUANG Z Q, et al. Global soil microbial biomass decreases with aridity and land-use intensification[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2021, 30(5):1056-1069.DOI: 10.1111/geb.13282. |
| [13] | HESSEN D O, ELSER J J. Elements of ecology and evolution[J]. Oikos, 2005, 109(1):3-5.DOI: 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.14055.x. |
| [14] | 王绍强, 于贵瑞. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8):3937-3947. |
| WANG S Q, YU G R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus elements[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(8):3937-3947.DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.08.054. | |
| [15] | ANDERSON T R, BOERSMA M, RAUBENHEIMER D. Stoichiometry:linking elements to biochemicals[J]. Ecology, 2004, 85(5):1193-1202.DOI: 10.1890/02-0252. |
| [16] | 哈斯其美格, 杨嘉琪, 汪珊珊, 等. 土壤微生物生物量的生态化学计量特征[J]. 甘肃科技纵横, 2022, 51(1):12-14,19. |
| Haschinegger, YANG J Q, WANG S S, et al. Ecological stoichiometry of soil microbial biomass[J]. Scientific & Technical Information of Gansu, 2022, 51(1):12-14,19. | |
| [17] | 朱湾湾, 许艺馨, 王攀, 等. 降水量及N添加对荒漠草原植物和土壤微生物C∶N∶P生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(4):676-687. |
| ZHU W W, XU Y X, WANG P, et al. Effects of precipitation and N addition on plant and microbial C∶N∶P ecological stoichiometry in a desert steppe of northwestern China[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(4):676-687. | |
| [18] | CHEN L Y, GAO Y H. Global climate change effects on soil microbial biomass stoichiometry in alpine ecosystems[J]. Land, 2022, 11(10):1661.DOI: 10.3390/land11101661. |
| [19] | 王凯, 邢仕奇, 张日升, 等. 科尔沁沙地杨树人工林植物-土壤C、N、P化学计量变化[J]. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(1):162-169. |
| WANG K, XING S Q, ZHANG R S, et al. Changes in C,N,and P stoichiometry of soil and plant of poplar plantations in Horqin sandy land[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43(1):162-169.DOI: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202401.023. | |
| [20] | MAO Y, WU Z Y, HE H, et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of drought in a typical plain region based on the soil moisture anomaly percentage index[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2017, 576:752-765.DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.116. |
| [21] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社,2000:1-51. |
| BAO S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press,2000:1-51. | |
| [22] | 王国兵, 王瑞, 徐瑾, 等. 生物炭对杨树人工林土壤微生物生物量碳、氮、磷及其化学计量特征的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(2):1-6. |
| WANG G B, WANG R, XU J, et al. Effects of biochar application on microbial biomass C,N,P and stoichiometry characteristics of poplar plantation soil[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 43(2):1-6.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201803022. | |
| [23] | 吴金水, 林启美, 黄巧云, 等. 土壤微生物生物量测定方法及其应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社,2006:79-84. |
| WU J S, LIN Q M, HUANG Q Y, et al. Determination method of soil microbial biomass and its application[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press,2006:79-84. | |
| [24] | 黄菊莹, 余海龙, 刘吉利, 等. 控雨对荒漠草原植物、微生物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(15):5362-5373. |
| HUANG J Y, YU H L, LIU J L, et al. Effects of precipitation levels on the C:N:P stoichiometry in plants,microbes,and soils in a desert steppe in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(15):5362-5373. | |
| [25] | LIU Y W, ZOU X M, CHEN H Y H, et al. Fungal necromass is reduced by intensive drought in subsoil but not in topsoil[J]. Global Change Biology, 2023, 29(24):7159-7172.DOI: 10.1111/gcb.16978. |
| [26] | 许艺馨, 余海龙, 李春环, 等. 模拟降水量变化对荒漠草原土壤酶活性的影响及其相关因素分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(11):1912-1923. |
| XU Y X, YU H L, LI C H, et al. Effects of simulated precipitation on soil enzyme activities in a desert steppe of northwest China and their related influencing factors[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(11):1912-1923.DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2021.11.1912. | |
| [27] | BROOKES P, OCIO J, WU J S. The soil microbial biomass: its measurement, properties and role in soil nitrogen and carbon dynamics following substrate incorporation[J]. Soil Microorganisms, 1990, 35:39-51. DOI: 10.18946/jssm.35.0_39. |
| [28] | GARCIA F O, RICE C W. Microbial biomass dynamics in tallgrass prairie[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1994, 58(3):816-823.DOI: 10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800030026x. |
| [29] | 王国兵, 阮宏华, 唐燕飞, 等. 森林土壤微生物生物量动态变化研究进展[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2009, 36(1):100-104. |
| WANG G B, RUAN H H, TANG Y F, et al. A review on the dynamics of soil microbial biomass in forest ecosystems[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2009, 36(1):100-104.DOI: 10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.2009.01.026. | |
| [30] | WARREN M, ZOU X M. Seasonal nitrogen retention in temperate hardwood forests[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2003, 27(1):11-15.DOI: 10.17521/cjpe.2003.0002. |
| [31] | XU X F, THORNTON P E, POST W M. A global analysis of soil microbial biomass carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2013, 22(6):737-749.DOI: 10.1111/geb.12029. |
| [1] | CAO Lili, RUAN Honghua, LI Yuanyuan, NI Juanping, WANG Guobing, CAO Guohua, SHEN Caiqin, XU Yaming. Variations of surface soil macrofauna in different aged Metasequoia glyptostroboides plantations [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(2): 91-98. |
| [2] | JIANG Xiaozeng, ZHU Yan, ZHOU Hengwei, HUANG Xingzhao, FU Longlong, WAN Fangfang. Effects of drought on nitrogen uptake and distribution in Camellia oleifera root under nitrogen addition [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(1): 95-102. |
| [3] | YE Yuyan, DING Fangjun, WU Peng, ZHOU Hua, LI Yuanyong, ZHOU Ting, CUI Yingchun. Effects of hydraulics and anatomical structure on sap flow of nine tree species in Karst primary forest [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(6): 111-120. |
| [4] | SONG Zihe, ZHEN Yan. Advancements in the research of miRNAs associated with plant drought and salt stress responses [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 1-11. |
| [5] | MA Tan, TIAN Ye, WANG Shujun, LI Wenhao, DUAN Qiying, ZHANG Qingyuan. Sex-specific leaf physiological responses of southern-type poplar to short-term intermittent soil drought [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(3): 172-180. |
| [6] | SHEN Yang, DI Jingjing, CHEN Ying, FENG Kai, LU Jinling, HU Yuchen. Effects of H2S donor NaHS on the adaptability and antioxidant properties of Agave americana plantlets under an in vitro culture of osmotic stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(2): 121-128. |
| [7] | DU Jincheng, LI Xinxin, WANG Zeliang, LIU Si, ZHONG Yi, WANG Lihua. Response of physiological indexes of three Olea europaea cultivars to PEG stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(2): 137-143. |
| [8] | WANG Zhipu, LI Zhuorong, LUO Zhibin, DENG Shurong. Mechanisms of PagAPY1 in regulating drought tolerance in Populus alba × P. glandulosa [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(6): 105-112. |
| [9] | MU Hongna, WANG Wei, FAN Lei, WU Chu, GUO Xiaohua, SUN Taoze. Effects of Piriformospora indica on growth and drought resistance in Osmanthus fragrans under water deficit stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(2): 101-106. |
| [10] | XU Chen, RUAN Honghua, WU Xiaoqiao, XIE Youchao, YANG Yan. Progresses in drought stress on the accumulation and turnover of soil organic carbon in forests [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(6): 195-206. |
| [11] | WANG Bixia, DU Xiaoqi, DENG Yan, CAI Xiaomei, SU Guangcan. Seasonal variations of the nutrients and phenols from olive leaves in main cultivation varieties at Liangshan, Sichuan Province [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(4): 169-176. |
| [12] | LI Mengjuan, ZHU Liming, HUO Junnan, ZHANG Jingbo, SHI Jisen, CHENG Tielong. Cloning and expression analyses of NtCBL1,NtCBL2 gene of Nitraria tangutorum [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(3): 93-99. |
| [13] | HONG Zhen, LIU Shuxin, HONG Conghao, LEI Xiaohua. Resistance response of five afforestation tree species under drought stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(2): 111-119. |
| [14] | SHI Xinlong, YANG Yueqin, XUE Xian, LIU Wei, SONG Chengwei, GUO Lili, HOU Xiaogai. Effects of chitooligosaccharide on the growth physiology of Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ seedlings under drought stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(2): 120-126. |
| [15] | YU Linlin, HU Haibo, YU Wei. Effects of urban green spaces on PM2.5 concentrations in atmosphere [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(3): 179-184. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||