JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY ›› 2021, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 13-20.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202010024
Special Issue: 青钱柳培育与选优专题
Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Na1( ), ZHU Peilin2, FENG Cai1, WEN Minxue3, FANG Shengzuo1, SHANG Xulan1,*(
), ZHU Peilin2, FENG Cai1, WEN Minxue3, FANG Shengzuo1, SHANG Xulan1,*( )
)
Received:2020-10-17
Accepted:2020-11-15
Online:2021-01-30
Published:2021-02-01
Contact:
SHANG Xulan
E-mail:1519811872@qq.com;shangxulan@njfu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LI Na, ZHU Peilin, FENG Cai, WEN Minxue, FANG Shengzuo, SHANG Xulan. Variations in physiological characteristics of rootstock-scion and its relationship to graft compatibility during the grafting union process of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(1): 13-20.
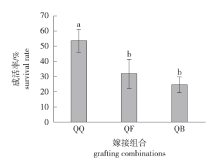
Fig.1
Variations in the grafting survival rate of C. paliurus at various grafting combinations QQ indicate the grafting combination of C. paliurus and C. paliurus, QF indicate the grafing combination of C. paliurus and P. stenoptera, and QB indicate the grafing combination of C. paliurus and C. illinoinensis. The same below. Different letters indicate the significant difference of survival rates grafting at various grafting combinations at the same time(P<0.05)."
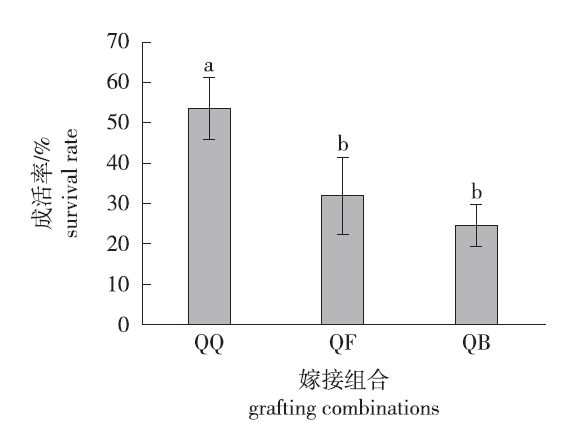
Table 1
Variations in soluble sugar and soluble protein contents of rootstocks and scions at various grafting combinations"
| 类别 item | 取样时间/d sampling time | 可溶性糖质量分数/% soluble sugar content | 可溶性蛋白质量分数/% soluble protein content | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QF | QB | QF | QB | |||||||||
| 接穗 scion | 0 | 1.89±0.08 b | 1.79±0.09 b | 1.90±0.14 b* | 4.54±0.29 b | 4.54±0.24 b | 4.54±0.41 b | |||||
| 40 | 1.27±0.07 c* | 1.64±0.07 b | 1.81±0.06 b* | 5.48±0.27 a* | 5.53±0.32 a | 5.44±0.29 a | ||||||
| 70 | 2.20±0.07 a | 2.43±0.10 a | 3.42±0.15 a | 5.63±0.27 a | 5.67±0.18 a | 6.05±0.38 a | ||||||
| 砧木 rootstock | 0 | 1.89±0.08 b | 1.59±0.08 c | 1.30±0.08 c | 4.54±0.29 c | 4.30±0.30 b | 4.25±0.23 b | |||||
| 40 | 1.59±0.06 c | 1.74±0.08 b | 2.36±0.14 b | 6.46±0.30 a | 5.58±0.23 a | 6.00±0.41 a | ||||||
| 70 | 2.14±0.11 a | 2.51±0.12 a | 3.56±0.14 a | 5.65±0.28 b | 5.42±0.34 a | 5.74±0.20 a | ||||||
Table 2
Variations in starch and tannin contents of rootstocks and scions at various grafting combinations"
| 类别 item | 取样时间/d sampling time | 淀粉质量分数/% starch content | 单宁质量分数/% tannin content | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QF | QB | QF | QB | |||||||||
| 接穗 scion | 0 | 1.39±0.07 b | 1.39±0.07 c* | 1.39±0.08 b* | 1.60±0.24 b | 1.46±0.11 c | 1.62±0.13 b | |||||
| 40 | 1.05±0.07 c | 1.53±0.09 b | 1.77±0.08 a* | 2.10±0.20 a | 2.68±0.21 a | 2.93±0.25 a* | ||||||
| 70 | 1.81±0.11 a* | 1.78±0.06 a* | 1.85±0.11 a* | 1.77±0.18 ab | 2.24±0.23 b* | 2.72±0.25 a | ||||||
| 砧木 rootstock | 0 | 1.39±0.07 b | 1.63±0.08 b | 2.43±0.10 b | 1.65±0.20 b | 1.40±0.15 b | 1.80±0.09 c | |||||
| 40 | 1.03±0.11 c | 1.57±0.10 b | 2.12±0.17 c | 2.26±0.20 a | 2.78±0.15 a | 3.60±0.22 a | ||||||
| 70 | 2.52±0.09 a | 2.40±0.10 a | 3.55±0.05 a | 1.97±0.16 ab | 2.68±0.14 a | 3.05±0.25 b | ||||||
Table 3
Variations in POD and PPO activity of rootstocks and scions at various grafting combinations"
| 类别 item | 取样时间/d sampling time | POD活性/(U·g-1) POD activity | PPO活性/(U·g-1) PPO activity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QF | QB | QF | QB | |||||||||
| 接穗 scion | 0 | 36.40±3.31 b | 36.06±2.83 b* | 36.40±1.75 b* | 10.55±0.65 b | 10.55±0.84 c | 10.55±0.74 c | |||||
| 40 | 112.60 ±5.85 a* | 86.20±3.53 a* | 65.80±0.21 a* | 6.95±0.63 c | 19.10±1.64 b | 17.20±1.55 b* | ||||||
| 70 | 31.00±3.08 b | 22.40±1.50 c* | 15.50±1.15 c* | 17.10±175 a | 22.25±1.81 a | 25.15±1.90 a | ||||||
| 砧木 rootstock | 0 | 36.40±3.31 b | 101.30±4.17 b | 120.80±3.50 b | 10.55±0.65 b | 10.60±0.87 c | 11.50±1.05 b | |||||
| 40 | 174.80 ±3.89 a | 117.50±3.20 a | 140.20±0.60 a | 7.85±0.79 c | 16.10±1.55 b | 21.65±1.17 a | ||||||
| 70 | 34.30±2.55 b | 30.30±2.20 c | 35.10±2.26 c | 14.10±1.66 a | 20.25±1.85 a | 24.20±1.77 a | ||||||
Table 4
The correlation analysis between the grafting survival rate and physiological indicators of scions and rootstocks at different sampling times"
| 取样时间/d sampling time | 因子 factors | 可溶性糖含量 soluble sugar content | 可溶性蛋白含量 soluble protein content | 淀粉含量 starch content | 单宁含量 tannin content | POD活性 POD activity | PPO活性 PPO activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 接穗 | -0.812** | 0.426 | -0.900** | -0.844** | 0.864** | -0.850** |
| 砧木 | -0.743* | 0.492 | -0.848** | -0.883** | 0.686* | -0.900** | |
| |接穗指标-砧木指标| | -0.052 | 0.184 | -0.620 | 0.510 | -0.381 | -0.728* | |
| 70 | 接穗 | -0.724* | -0.491 | -0.142 | -0.832** | 0.854** | -0.846** |
| 砧木 | -0.789* | -0.110 | -0.561 | -0.883** | 0.027 | -0.867** | |
| |接穗指标-砧木指标| | -0.368 | -0.544 | -0.554 | -0.196 | -0.818** | 0.069 |
| [1] | 凌岩, 秦健, 尚旭岚, 等. 施氮量对青钱柳幼苗生长和总酚积累的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2020,29(4):45-51. |
| LING Y, QIN J, SHANG X L, et al. Effect of applying amount of nitrogen on growth and total phenolic accumulation in Cyclocarya paliurus seedling[J]. J Plant Resour Environ, 2020,29(4):45-51.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2020.04.06. | |
| [2] | 曹燕妮, 茆慧敏, 尚旭岚, 等. 冲泡条件对青钱柳茶主要内含物浸出规律的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,41(4):19-24. |
| CAO Y N, MAO H M, SHANG X L, et al. Effect of brewing conditions on the leaching rate of Cyclocarya paliurus tea compounds[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2017,41(4):19-24. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201609044. | |
| [3] | 林源, 陈培, 周明明, 等. 天然居群青钱柳叶主要生物活性物质及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020,44(2):10-16. |
| LIN Y, CHEN P, ZHOU M M, et al. Key bioactive substances and their antioxidant activities in Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja leaves collected from natural populations[J]. J Nanjing For Univ(Nat Sci Ed), 2020,44(2):10-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201901045. | |
| [4] | 尚旭岚, 李琼琼, 邓波, 等. 光照和施肥对青钱柳幼苗叶片性状与解剖结构的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2014,34(6):9-15. |
| SHANG X L, LI Q Q, DENG B, et al. Effects of light intensity and fertilization on leaf traits and anatomical structure of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. J Southwest For Univ, 2014,34(6):9-15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1914.2014.06.002. | |
| [5] |
CHEN X L, WANG Y, ZHAO H, et al. Localization and dynamic change of saponins in Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja[J]. PLoS One, 2019,14(10):e0223421. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223421.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223421 pmid: 31613931 |
| [6] |
ZHOU M M, LIN Y, FANG S Z, et al. Phytochemical content and antioxidant activity in aqueous extracts of Cyclocarya paliurus leaves collected from different populations[J]. PeerJ, 2019,7:e6492. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.6492.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.6492 pmid: 30809459 |
| [7] | 张金凤, 方升佐, 尚旭岚, 等. 青钱柳幼胚愈伤组织的诱导[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,36(5):47-50. |
| ZHANG J F, FANG S Z, SHANG X L, et al. Callus induction from young embryos of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2012,36(5):47-50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2012.05.008. | |
| [8] | MELNYK C W, MEYEROWITZ E M. Plant grafting[J]. Curr Biol, 2015,25(5):183-188. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.01.029. |
| [9] | 马绍英, 刘元卫, 苏李维, 等. 葡萄离体嫁接部位的生理生化变化[J]. 果树学报, 2016,33(2):179-186. |
| MA S Y, LIU Y W, SU L W, et al. Physiological and biochemical changes in the graft site after in vitro grafting in grape[J]. J Fruit Sci, 2016,33(2):179-186. DOI: 10.13925/j.cnki.gsxb.20150278. | |
| [10] | 冯金玲, 杨志坚, 陈辉, 等. 油茶芽苗砧嫁接体的亲和性生理[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2011,40(1):24-30. |
| FENG J L, YANG Z J, CHEN H, et al. Physiological affinity of nurse seed grafted union of Camellia oleifera[J]. J Fujian Agric For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2011,40(1):24-30. DOI: 10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).2011.01.014. | |
| [11] |
LÓPEZ-GÓMEZ E, SAN JUAN M A, DIAZ-VIVANCOS P, et al. Effect of rootstocks grafting and boron on the antioxidant systems and salinity tolerance of loquat plants (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.)[J]. Environ Exp Bot, 2007,60(2):151-158. DOI: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.10.007.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.10.007 |
| [12] | 严毅. 葡萄柚砧穗愈合过程中酶类活性研究[D]. 昆明:西南林业大学, 2012. |
| YAN Y. The enzymes activity research on the process of grapefruit grafting on stock-scion[D]. Kunming:Southwest Forestry University, 2012. | |
| [13] | 石雪晖, 王淑英, 吴艳纯, 等. 葡萄叶片中生理生化物质含量与嫁接亲和力关系的研究[J]. 果树学报, 2001,18(1):24-27. |
| SHI X H, WANG S Y, WU Y C, et al. Study on the effects of the content of physiological and biochemical substances in the rootstock leaves to the graft compatibility[J]. J Fruit Sci, 2001,18(1):24-27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9980.2001.01.006. | |
| [14] | 张燕, 邓思, 沈峰杰, 等. 青钱柳砧穗及品系嫁接亲和力初探[J]. 南方农业, 2017,11(1):39-40,43.DOI: 10.19415/j.cnki.1673-890x.2017.1.013. |
| [15] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| LI H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. | |
| [16] | 张晓, 田纪春. 不同小麦多酚氧化酶活性检测方法的比较[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2008,39(1):15-18. |
| ZHANG X, TIAN J C. The comparison of different assays of wheat polyphenol oxidase activity[J]. J Shandong Agric Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2008,39(1):15-18. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2008.01.004. | |
| [17] | 韩卫娟, 李加茹, 梁玉琴, 等. 柿果实和叶片中可溶性单宁含量的年变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015,39(6):61-66. |
| HAN W J, LI J R, LIANG Y Q, et al. Annual variation of soluble tannin in the fruits and leaves of persimmon[J]. J Nanjing For Univ(Nat Sci Ed), 2015,39(6):61-66. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2015.06.012. | |
| [18] | GOLDSCHMIDT, ELIEZER E. Plant grafting:new mechanisms, evolutionary implications[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014,5(3) :727. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00727. |
| [19] |
MANOS P S, SOLTIS P S, SOLTIS D E, et al. Phylogeny of extant and fossil Juglandaceae inferred from the integration of molecular and morphological data sets[J]. Systematic Biology, 2007,56(3):412-30. DOI: 10.1080/10635150701408523.
doi: 10.1080/10635150701408523 pmid: 17558964 |
| [20] | 胡昳恒. 基于基因组学与转录组学的胡桃科植物系统进化及群体遗传学研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2018. |
| HU Y H. Phylogenetic and population genetics of Juglandaceae baced on genomics and transcriptomics[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2018. | |
| [21] | 朱晓慧, 杨途熙, 魏安智, 等. 无刺花椒嫁接愈合过程中相关生理指标的变化[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2015,30(2):134-138. |
| ZHU X H, YANG T X, WEI A Z, et al. Changes of relative physiological indices involved in the graft union development of Zanthoxylum bungeanum[J]. J Northwest For Univ, 2015,30(2):134-138. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2015.02.23. | |
| [22] | 马攀, 龚榜初, 江锡兵, 等. 不同砧木嫁接甜柿苗期生长生理特性及亲和性评价[J]. 林业科学研究, 2015,28(4):518-523. |
| MA P, GONG B C, JIANG X B, et al. Evaluation on affinity,growth trait and physiology indicators of persimmon grafted on different stocks[J]. For Res, 2015,28(4):518-523. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2015.04.010. | |
| [23] | 杨邵, 束庆龙, 姚小华, 等. 油茶不同芽苗砧嫁接组合的亲和性生理[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015,43(7):19-22,46. |
| YANG S, SHU Q L, YAO X H, et al. Physiological affinity of different nurse seed grafted union of Camellia oleifera[J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2015,43(7):19-22,46. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.07.005. | |
| [24] | 苗丽, 李衍素, 范兴强, 等. 植物嫁接体接口愈合机制的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017,53(1):17-28. |
| MIAO L, LI Y S, FAN X Q, et al. Research advances on mechanism of interface healing of plant grafting[J]. Plant Physiol Commun, 2017,53(1):17-28.DOI: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2016.0413. | |
| [25] | 王瑞, 陈永忠, 王湘南, 等. 油茶芽苗砧嫁接愈合过程中砧穗相关生理指标的研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,42(1):46-50. |
| WANG R, CHEN Y Z, WANG X N, et al. Dynamic changes in physiological indexes of Camellia oleifera nurse seed graft in the grafting and recovering process[J]. J Northwest A&F Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2014,42(1):46-50. DOI: 10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2014.01.026. | |
| [26] |
LEE K M, LIM C S, MUNEER S, et al. Functional vascular connections and light quality effects on tomato grafted unions[J]. Sci Hortic, 2016,201:306-317. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.02.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.02.013 |
| [27] | 曹建华, 林位夫, 陈俊明. 砧木与接穗嫁接亲合力研究综述[J]. 热带农业科学, 2005,25(4):64-69. |
| CAO J H, LIN W F, CHEN J M. Studies of affinity between rootstock and scion[J]. Chin J Trop Agric, 2005,25(4):64-69. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2196.2005.04.018. | |
| [28] | 孙华丽, 宋健坤, 李鼎立, 等. 梨不同嫁接组合嫁接愈合过程中生理动态变化研究[J]. 北方园艺, 2013(16):25-29. |
| SUN H L, SONG J K, LI D L, et al. Study on the physiological dynamic change of different graft combinations in pear during the grafted healing process[J]. North Hortic, 2013(16):25-29. | |
| [29] | 魏菊, 董胜君, 刘明国, 等. 山杏良种嫁接愈合过程中生理生化特性研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2017,48(3):304-310. |
| WEI J, DONG S J, LIU M G, et al. Physiological and biochemical characteristics in grafted healing process of Armeniaca sibirica seed[J]. J Shenyang Agric Univ (Soc Ed), 2017,48(3):304-310. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2017.03.008. | |
| [30] |
张力平, 孙长霞, 李俊清, 等. 植物多酚的研究现状及发展前景[J]. 林业科学, 2005,41(6):157-162.
doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20050627 |
| ZHANG L P, SUN C X, LI J Q, et al. The present conditions and development trend of plant polyphenols research[J]. Sci Silvae Sin, 2005,41(6):157-162. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2005.06.027. | |
| [31] | 苏文川. 薄壳山核桃嫁接愈合的解剖学和生理生化特性研究[D]. 南京:南京林业大学, 2016. |
| SU W C. Research on anatomical, physiological and biochemical traits of union of Carya illinoensis bud grafting[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Forestry University, 2016. | |
| [32] |
USENIK V, KRŠKA B, VIČAN M, et al. Early detection of graft incompatibility in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) using phenol analyses[J]. Sci Hortic, 2006,109(4):332-338. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2006.06.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2006.06.011 |
| [33] | 张小红, 赵依杰, 林强, 等. 不同砧木嫁接对甜瓜生理和品质的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2012,2(9):32-35. |
| ZHANG X H, ZHAO Y J, LIN Q, et al. Influence of physiological indicators and fruit quality on grafted muskmelon of different stocks[J]. Chin Countrys Well-Off Technol, 2012,2(9):32-35.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7774.2012.09.008. | |
| [34] | 杨冬冬, 黄丹枫. 西瓜嫁接体发育中木质素合成及代谢相关酶活性的变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 2006,26(2):290-294. |
| YANG D D, HUANG D F. Lignin contents and the activities of enzymes related to lignin biosynjournal in the stock and scions of watermelon after grafting[J]. Acta Bot Boreali-Occidentalia Sin, 2006,26(2):290-294. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2006.02.011. | |
| [35] | 白雪. 薄皮甜瓜嫁接体砧穗愈合过程中的亲和生理机制研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2019. |
| BAI X. Study on affinity physiological mechanisms during rootstock healing of thin-skinned melon grafting[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University, 2019. | |
| [36] |
IRISARRI P, BINCZYCKI P, ERREA P, et al. Oxidative stress associated with rootstock-scion interactions in pear/quince combinations during early stages of graft development[J]. J Plant Physiol, 2015,176:25-35. DOI: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.10.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.10.015 pmid: 25543953 |
| [37] |
GRIMA-PETTENATI J, GOFFNER D. Lignin genetic engineering revisited[J]. Plant Sci, 1999,145(2):51-65. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00051-5.
doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00051-5 |
| [38] |
DOUGLAS C J. Phenylpropanoid metabolism and lignin biosynjournal:from weeds to trees[J]. Trends Plant Sci, 1996,1(6):171-178. DOI: 10.1016/1360-1385(96)10019-4.
doi: 10.1016/1360-1385(96)10019-4 |
| [39] | 杨瑞. 葡萄砧穗组合生理物质变化与嫁接亲和力的关系[J]. 西北农业学报, 2012,21(12):108-111. |
| YANG R. Relationship between the physiological and biochemical substances and the graft affinity of grape rootstock-scion combination[J]. Acta Agric Boreali-Occidentalis Sin, 2012,21(12):108-111. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2012.12.021. | |
| [40] | 姚焕英, 唐静成, 张鞍灵, 等. 核桃属植物化学成分及生物活性研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2003,23(9):1650-1655. |
| YAO H Y, TANG J C, ZHANG A L, et al. Advances in research of the chemistry and bioactivity of Juglans plants[J]. Acta Bot Boreali-Occidentalia Sin, 2003,23(9):1650-1655. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2003.09.036. | |
| [41] | 苏美玲. 四种砧木对沃柑嫁接亲和性和生长结果比较研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2019. |
| SU M L. Comparisons of grafting compatibility and growth fruit of oran on the four rootstock[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University, 2019. | |
| [42] | 张蜀秋, 杨世杰, 马龙彪. 嫁接组合形成过程中两种酶活性的动态变化[J]. 北京农业大学学报, 1990(2) :149-152. |
| ZHANG S Q, YANG S J, MA L B. The changes of two enzyme activities during the developmental processes of the graft unions[J]. Journal of Beijing Agricultural University, 1990(2) :149-152. | |
| [43] | 史俊燕, 樊金拴, 严江. 酚类物质及其相关酶对核桃嫁接成活的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2005,20(1):80-83. |
| SHI J Y, FAN J S, YAN J. The effect of polyphenol and relative enzyme on walnut grafting[J]. J Northwest For Univ, 2005,20(1):80-83. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2005.01.021. | |
| [44] | 黄曼娜, 孙华丽, 宋健坤, 等. ‘杏叶梨/杜梨’嫁接愈合过程的解剖学与生理学研究[J]. 青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,31(3) :177-182. |
| HUANG M N, SUN H L, SONG J K, et al. Study on anatomy and physiology of graft healing process in ‘P. armeniaeaefolia/P. betulaefolia’[J]. J Qingdao Agric Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2014,31(3) :177-182. DOI: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1674-148X.2014.03.005. |
| [1] | CHEN Hui, WANG Gaiping, PENG Fangren, ZHU Yunfen, ZHANG Yu, WANG Han. Soil quality assessment for Carya illinoensis-Paeonia ostii under various patterns [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 177-183. |
| [2] | LIU Xiaofang, YUE Xiliang, FANG Shengzuo, LI Qing, SUN Xin. Effects of various ratios of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on the growth and contents of leaf bioactive substances in Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 57-66. |
| [3] | LIU Li, QU Yinquan, YU Yanhao, WANG Qian, FU Xiangxiang. Analysis of SSR locus based on the whole genome sequences of Cyclocarya paliurus and the development of polymorphic primers [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 67-75. |
| [4] | LIU Xialan, SONG Ziqi, HU Fengrong, SHANG Xulan. A comparative study on leaf characters between diploid and tetraploid of Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 76-84. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zanpei, GU Yueying, SHANG Xulan, WANG Ji, FANG Shengzuo. An evaluation on the cold tolerance of twenty-three Cyclocarya paliurus families under natural low temperatures [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 85-92. |
| [6] | SONG Ziqi, BIAN Guoliang, LIN Feng, HU Fengrong, SHANG Xulan. Establishment and application of a flow cytometry method for chromosome ploidy identification of Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(2): 61-68. |
| [7] | GUO Congcong, SHEN Yongbao, SHI Fenghou. Effects of temperature on stored substance metabolism and enzyme activity during germination of Pinus bungeana seeds [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(6): 25-34. |
| [8] | WANG Ji, FANG Shengzuo. Effects of different anti-browning agents on enzyme activity and growth in callus of Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(6): 167-174. |
| [9] | JIA Ruirui, ZHU Yanyan, YANG Xiulian, FU Yu, YUE Yuanzheng, WANG Lianggui. Effects of different rootstocks on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of grafted seedlings of Catalpa bungei [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(5): 97-106. |
| [10] | HUANG Ziliang, XU Ziheng, SUN Caowen. Study on seasonal dynamics of seed rain and characteristics of soil seed banks in Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(2): 18-26. |
| [11] | FANG Shengzuo. A review on the development history and the resource silviculture of Cyclocarya paliurus industry [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(6): 115-126. |
| [12] | LIU Qianqian, PENG Xiaonan, LIU Xin, WANG Shutian, DAI Kanglong, XU Haibin, DONG Li’na, ZHANG Jinchi. Seasonal variation characteristics of soil quality in Zijin Mountain under the disturbance of trample [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(3): 185-193. |
| [13] | XU Zhanhong, ZHU Ying, JIN Huiying, SUN Caowen, FANG Shengzuo. Variations in the contents of leaf pigments and polyphenols and photosynthesis traits in Cyclocarya paliurus with different leaf colors [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(2): 103-110. |
| [14] | SUN Caowen, ZHONG Wenwen, FU Xiangxiang, SHANG Xulan, FANG Shengzuo. A study on growth and aboveground biomass production of juvenile Cyclocarya paliurus plantations [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(1): 138-144. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xiaorong, DUAN Guangde, HAO Longfei, LIU Tingyan, ZHANG You, ZHANG Shengxi. Responses of the non-structural carbohydrates and rhizosphere soil enzymes of Clematis fruticosa to nitrogen deposition and inoculation mycorrhizal fungi [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(1): 171-178. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||