 PDF(4436 KB)
PDF(4436 KB)


Research on forest change detection based on fully convolutional network and low resolution label
XIANG Jun, YAN Enping, JIANG Jiawei, SONG Yabin, WEI Wei, MO Dengkui
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 187-195.
 PDF(4436 KB)
PDF(4436 KB)
 PDF(4436 KB)
PDF(4436 KB)
Research on forest change detection based on fully convolutional network and low resolution label
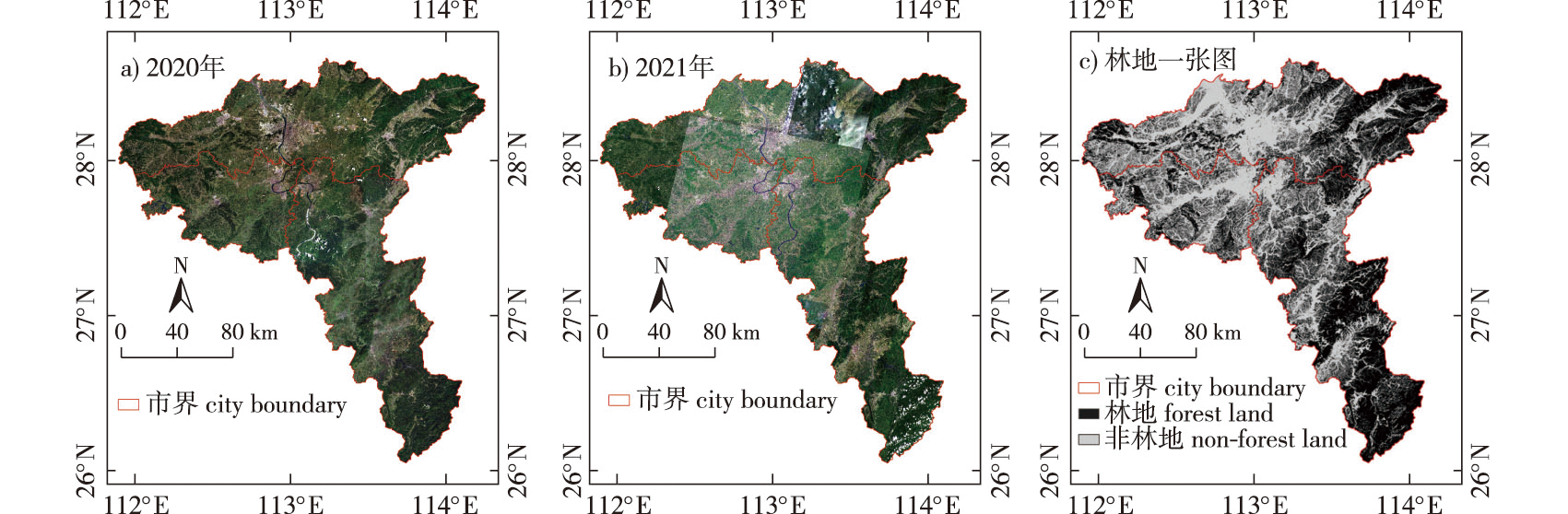
【Objective】A forest change detection method based on fully convolutional networks and low resolution labels is proposed to address the problem of missing or insufficient high-precision label samples in current forest change detection, with the goal of achieving simple and rapid extraction of forest changes in forest areas. 【Method】First, the gathered data was de-clouded, screened and labeled, and then the fully convolutional network model was used to extract the forests in high-scoring remote sensing photos in the study area in 2020 and 2021, respectively, and the model accuracy was evaluated. The forest change area was calculated using the post-classification comparison method, and the findings were compared with visual interpretation results. The pixel area was used to calculate evaluation indicators, such as forest change detection accuracy. 【Result】Experiments reveal that the F1 score of the model employed in this research is 97.09% in 2020 forest extraction results and 95.96% in 2021 forest extraction results, which was the best among segmentation network models (U-Net, FPN, LinkNet). The total change precision rate of forest increase and forest decline was 73.30%, the recall rate was 77.37%, and the F1 score was 75.28% when comparing the forest extraction data from the two periods to obtain the changed area. 【Conclusion】Based on low resolution labeling, this method allows for the speedy and precise capture of forest change regions from high-resolution remote sensing pictures. To accomplish forest change detection, a small number of low-resolution labels are used, which can also serve as a reference for large-scale forestland change inquiries.
low resolution label / fully convolutional network / deep learning / forest changes detection
| [1] |
魏安世, 杨志刚. 森林资源年度监测小班数据自动更新技术[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 34(4):123-128.
|
| [2] |
刘羿, 佘光辉, 刘安兴, 等. 森林资源系统自组织特征研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 32(5):51-55.
|
| [3] |
李春干, 梁文海. 基于面向对象变化向量分析法的遥感影像森林变化检测[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2017, 29(3):77-84.
|
| [4] |
张丽云, 赵天忠, 夏朝宗, 等. 遥感变化检测技术在林业中的应用[J]. 世界林业研究, 2016, 29(2):44-48.
|
| [5] |
张祖宇, 滕永核, 秦元丽, 等. 基于U-Net模型的无人机影像数据地表覆被信息自动提取研究[J]. 广西林业科学, 2022, 51(4):516-519.
|
| [6] |
王利民, 刘佳, 杨玲波, 等. 基于无人机影像的农情遥感监测应用[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(18):136-145.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
郭颖, 李增元, 陈尔学, 等. 一种改进的高空间分辨率遥感影像森林类型深度学习精细分类方法:双支FCN-8s[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(3):48-60.
|
| [10] |
覃先林, 李晓彤, 刘树超, 等. 中国林火卫星遥感预警监测技术研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2020, 24(5):511-520.
|
| [11] |
杨雷, 禹定峰, 高皜, 等. Sentinel-2的胶州湾水体透明度遥感反演[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(12):515-521.
|
| [12] |
陈锐志, 王磊, 李德仁, 等. 导航与遥感技术融合综述[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(12):1507-1522.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
业巧林, 许平, 张冬. 基于深度学习特征和支持向量机的遥感图像分类[J]. 林业工程学报, 2019, 4(2):119-125.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
王昶, 张永生, 王旭, 等. 基于深度学习的遥感影像变化检测方法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2020, 54(11):2138-2148.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
马润, 胡斯勒图, 尚华哲, 等. 基于葵花-8卫星大气产品的地表下行短波辐射计算[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(5):924-934.
|
| [26] |
伟乐斯, 尚华哲, 胡斯勒图, 等. GF-5 DPC数据的云检测方法研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(10):2053-2066.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
吴胜义, 张方圆, 王飞. 林地变更调查技术方法分析与研究[J]. 林业科技, 2021, 46(2):38-41,45.
|
| [35] |
徐新良, 刘纪远, 庄大方, 等. 中国林地资源时空动态特征及驱动力分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2004, 26(1):41-46.
|
| [36] |
夏传福, 李静, 柳钦火. 植被物候遥感监测研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2013, 17(1):1-16.
|
| [37] |
范德芹, 赵学胜, 朱文泉, 等. 植物物候遥感监测精度影响因素研究综述[J]. 地理科学进展, 2016, 35(3):304-319.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |