 PDF(3342 KB)
PDF(3342 KB)


Simulation and prediction of habitat quality in the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve
ZHANG Ying, WANG Ranghui, LIU Chunwei, ZHOU Limin
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 135-144.
 PDF(3342 KB)
PDF(3342 KB)
 PDF(3342 KB)
PDF(3342 KB)
Simulation and prediction of habitat quality in the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve
【Objective】 To explore the potential problems and conflicts of habitat quality in the Qilianshan Nature Reserve as per future land use changes; to respond to the regional ecological environmental protection policy per the concept of “Mountain, Water, Forest, Field, Lake, Grass, and Sand”, and to provide a scientific basis for regional ecological management and sustainable development. 【Method】 Based on five phases of land use data from 2000 to 2020, the PLUS model was used to simulate land use under different scenarios in the future through 2030. The InVEST model was coupled to assess and predict the current and future habitat quality of the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve. 【Results】 Land use in the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve was dominated by grassland, forest land, and unused land, and an increase in the area of ecological land. The increase in the area of ecological land under the ecological protection scenario was significantly higher than under the natural development scenario for 2030. Habitat quality showed a spatial distribution pattern of “low in the northwest and high in the southeast,” with the mean value of habitat quality from 2000 to 2020 as follows: 0.656 2, 0.656 3, 0.665 8, 0.664 6, and 0.665 7, respectively. This showed a fluctuating trend of increasing, decreasing, and increasing values. The average value of habitat quality in 2030 was 0.667 9 under the ecological protection scenario and 0.665 6 under the natural development scenario. The total habitat contribution under the ecological protection scenario was greater than that under the natural development scenario. The degree of habitat degradation increased and then decreased from 2000 to 2030, showed a spatial distribution from weak to strong circles from the center outwards, with the most degraded areas located at the edges of grassland adjacent to unused land—the areas most affected by human activities. 【Conclusion】 The habitat quality of the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve is developing in a positive direction; the habitat quality under the future ecological protection scenario is significantly better than that under the natural development scenario; strengthening the protection of ecological land such as woodland and grassland is conducive to the improvement of habitat quality.
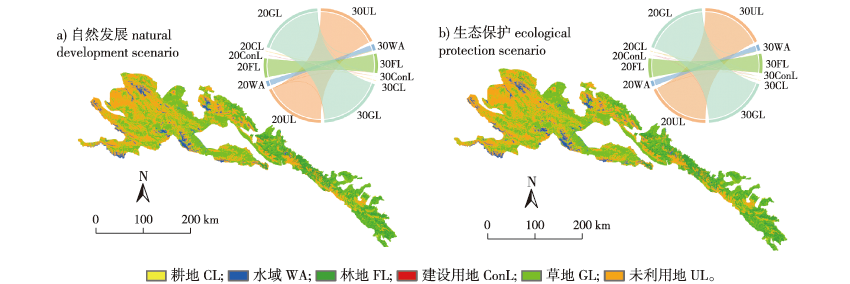
habitat quality / land use / PLUS model / InVEST model / the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve
| [1] |
王建华, 田景汉, 吕宪国. 挠力河流域河流生境质量评价[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(2):481-486.
|
| [2] |
钟莉娜, 王军. 基于InVEST模型评估土地整治对生境质量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(1):250-255.
|
| [3] |
吴健生, 毛家颖, 林倩, 等. 基于生境质量的城市增长边界研究:以长三角地区为例[J]. 地理科学, 2017, 37(1):28-36.
|
| [4] |
郑宇, 张蓬涛, 汤峰, 等. 基于InVEST模型的昌黎县土地利用变化对生境质量的影响研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(7):121-128.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
褚琳, 张欣然, 王天巍, 等. 基于CA-Markov和InVEST模型的城市景观格局与生境质量时空演变及预测[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(12):4106-4118.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
陈霆, 徐伟铭, 吴升, 等. 国土空间规划视角下的城镇开发边界划定和空间管控体系构建[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2022, 24(2):263-279.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
徐洁, 谢高地, 肖玉, 等. 国家重点生态功能区生态环境质量变化动态分析[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(9):3039-3050.
|
| [16] |
王让会, 赵文斐, 彭擎, 等. 气候变化及景观格局与生态系统碳储存的耦合关系:以祁连山为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(1):250-257.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
张大川, 刘小平, 姚尧, 等. 基于随机森林CA的东莞市多类土地利用变化模拟[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2016, 32(5):29-36,127.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
张学儒, 周杰, 李梦梅. 基于土地利用格局重建的区域生境质量时空变化分析[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75(1):160-178.
|
| [24] |
包玉斌, 刘康, 李婷, 等. 基于InVEST模型的土地利用变化对生境的影响:以陕西省黄河湿地自然保护区为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2015, 32(3):622-629.
|
| [25] |
李潇, 杨加猛, 陈禹衡, 等. 基于土地利用变化的江苏盐城湿地自然保护区生境质量评估[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5): 169-176.
|
| [26] |
和娟, 师学义, 付扬军, 等. 汾河源头区域土地利用及生境质量时空演变的多情景模拟[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(5):250-258.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |