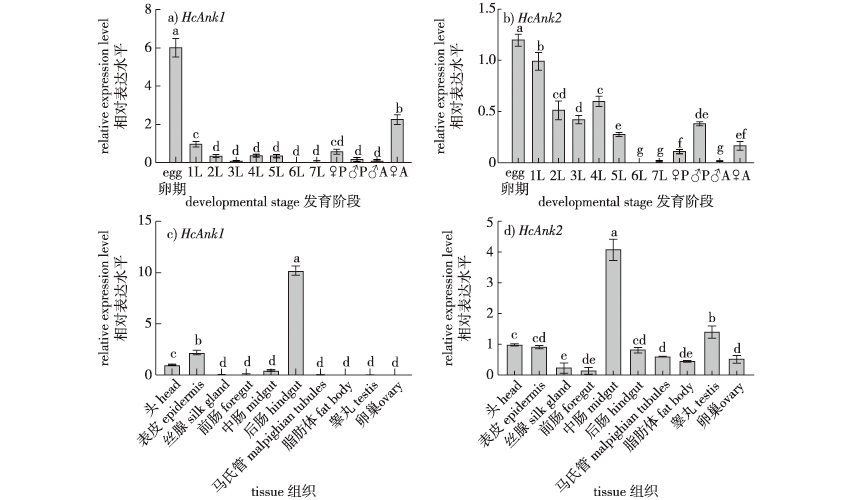
【Objective】 Ankyrin is a family of adaptor proteins that connect the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane. However, the functions of insect ankyrin are poorly understood. In this study, the Ankyrin genes of Hyphantria cunea were cloned and their expression characteristics were determined in different developmental stages and tissues of H. cunea. The mortality rate of H. cunea was measured under the stress of exposure to nucleopolyhedrosis virus, which provided a theoretical basis for further developing synergists for NPV-based control strategies. 【Method】 The Ankyrin1 (HcAnk1) and Ankyrin2 (HcAnk2) genes were screened by a transcriptome library, and the characteristics of the two Ankyrin genes were determined using bioinformatics. Using qRT-PCR, the expression of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 genes were determined at different developmental stages and in different tissues, and under different HcNPV concentrations. The survival rate of H. cunea larvae under HcNPV stress was investigated after the gene silencing of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 using an RNAi technique. 【Result】 The open reading frames of the HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 genes were 1392 and 1866 bp, encoding 463 and 621 amino acids, respectively. The molecular weights of the HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 proteins were 59.18 and 69.19 ku, respectively, and the theoretical isoelectric points were 5.74 and 8.66, respectively. A phylogenetic analysis showed that HcAnk1 was closely related to Trichoplusia ni and was clustered into one group. HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 were expressed at all developmental stages, with the highest expression in the egg stage and the lowest expression in the sixth instar larva. The highest expression of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 was observed in the midgut and hindgut, respectively, but HcAnk1 was not detected in the ovary or testis, while HcAnk2 was mainly expressed in the midgut and testis. In tests with different levels of HcNPV stress, the transcription levels of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 were induced at low concentrations and inhibited at high concentrations. The relative growth rate and food conversion efficiency (ECD) were significantly decreased after silencing HcAnks in H. cunea larvae. Additionally, the H. cunea with HcAnks silencing were significantly less resistant to HcNPV. 【Conclusion】 HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 play an important role in the resistance to HcNPV. HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 can be used as HcNPV synergists for the pollution-free control of H. cunea.
 PDF(2364 KB)
PDF(2364 KB)


 PDF(2364 KB)
PDF(2364 KB)
 PDF(2364 KB)
PDF(2364 KB)