 PDF(4431 KB)
PDF(4431 KB)


Response of plant diversity under Platycladus orientalis plantation to canopy density in Xuzhou
SUI Xiran, ZHAO Qingjun, ZHOU Xiaoqing, CHEN Juan, CHEN Jing, PENG Qian, ZHANG Zengxin
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 219-226.
 PDF(4431 KB)
PDF(4431 KB)
 PDF(4431 KB)
PDF(4431 KB)
Response of plant diversity under Platycladus orientalis plantation to canopy density in Xuzhou
【Objective】This study explored the species diversity of the understory plant community of a Platycladus orientalis plantation across 50 years in Quanshan Mountain and Yunlong Mountain, Xuzhou City. We then investigated the response of the understory plant diversity to the canopy density.【Method】The canopy density of the plantation was measured using a standard sample plot survey method and divided into five canopy density grades ([0.9,1.0], [0.8,0.9),[0.7,0.8),[0.6,0.7),and [0, 0.6) according to the current field stand conditions. The plant species composition and diversity characteristics were then evaluated for different canopy density forests.【Result】The results identified 129 species of trees, shrubs, and grasses in 65 families and 116 genera in the P. orientalis plantation. As the canopy density decreased, the number of plant species initially increased and subsequently decreased, and the understory species exhibited a gradual transition from shade-tolerant to sun-tolerant succession pattern. Plant life forms were generally complex and stable. Moreover, the Shannon-Wiener diversity index initially increased and subsequently decreased with the decrease in canopy closure. The canopy closure values of canopy density categories [0.6, 0.7) and [0.7, 0.8) were significantly higher than those of categories [0.9,1.0],[0.8,0.9) and [0,0.6). No significant differences were observed in the Margalef richness and Pielou evenness indexes among the five canopy densities (P > 0.05). The Simpson dominance index initially increased and subsequently decreased with the decrease in canopy density, and was the highest at the canopy density [0.6, 0.7). Correlation analysis between the canopy density and the plant species diversity index of the P. orientalis plantation revealed a negative correlation between canopy density and the Shannon-Wiener diversity, Margalef richness, and Pielou evenness indexes. Furthermore, the canopy closure was a very weak negative correlated with the Simpson dominance index.【Conclusion】In summary, the plant diversity in the P. orientalis plantation was optimal under medium canopy density [0.6, 0.7). Higher or lower canopy densities may lead to the relative reduction of the species composition and diversity of the plants in the plantation, which is harmful to the maintenance of the P. orientalis plantation.
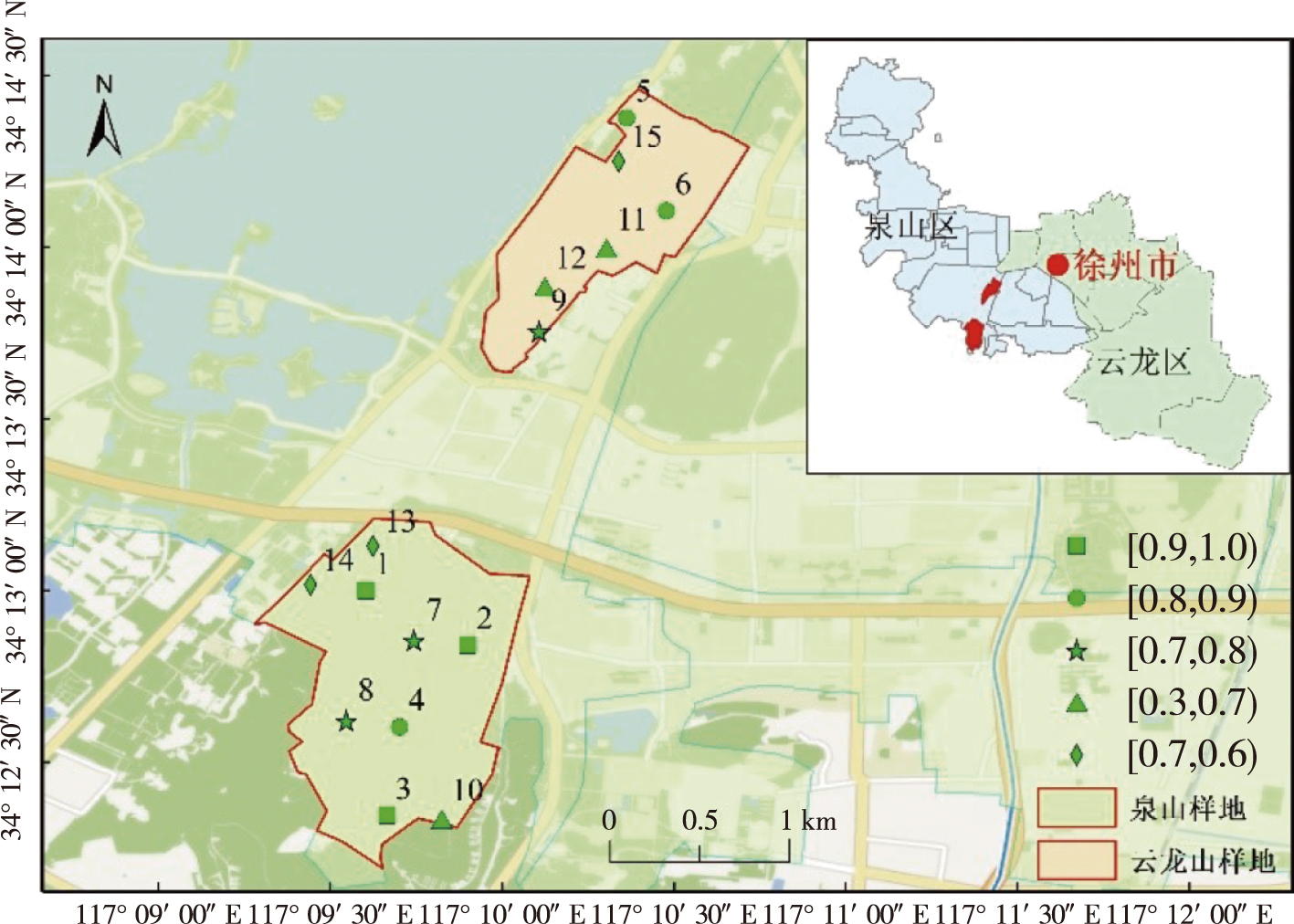
Platycladus orientalis / canopy closure / plant diversity / understory plants
| [1] |
张勇强, 李智超, 厚凌宇, 等. 林分密度对杉木人工林下物种多样性和土壤养分的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(1):239-250.
|
| [2] |
金亚宁, 管增艳, 石松林, 等. 川西云杉人工林与天然林群落空间分布格局及种间关联性[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(3):495-504.
|
| [3] |
田佳歆, 刘盛, 冯万斌, 等. 间伐强度对长白落叶松人工林冠层结构和草本物种多样性的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(3):30-34,50.
|
| [4] |
何司彦. 亚热带山地森林群落结构多样性与热量分布的生境关联[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2017.
|
| [5] |
赵苏亚. 抚育间伐对杉木人工林土壤微生物和理化性质的影响[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2021.
|
| [6] |
付凯婷. 无人机遥感技术估算桉树蓄积量的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2015.
|
| [7] |
潘惠均. 林分郁闭度对杉木林下浙江楠和红豆树幼苗生长的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2014, 55(8):1206-1208.
|
| [8] |
李双喜, 朱建军, 张银龙, 等. 人工马褂木林下草本植物物种多样性与林分郁闭度的关系[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2009, 25(2):20-24.
|
| [9] |
郭弘婷, 纪小芳, 汪成, 等. 我国人工林林下灌木层植物多样性空间变异及影响要素[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(4):144-152.
|
| [10] |
张捷. 郁闭度控制对林下植被发育及马尾松人工林凋落叶分解的影响[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2018.
|
| [11] |
颜成正, 郑文革, 贾剑波, 等. 控水条件下侧柏冠层气孔导度对土壤水的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(12):4017-4026.
|
| [12] |
汤茜, 尤海梅, 王梦君. 徐州市人工侧柏林的群落结构及物种多样性分析[J]. 淮阴师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2006, 5(2):168-172.
|
| [13] |
梁波, 于艳华, 翟爱进. 徐州市侧柏林分改造措施[J]. 华东森林经理, 2001, 15(3):22-23.
|
| [14] |
陈平. 徐州石灰岩山地退化植被特征及恢复重建研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2010.
|
| [15] |
刘畅. 徐州石灰岩山地4种典型林分保健功能的研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2019.
|
| [16] |
赵燕波, 张丹桔, 张健, 等. 不同郁闭度马尾松人工林林下植物多样性[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2016, 22(6):1048-1054.
|
| [17] |
庞圣江, 张培, 贾宏炎, 等. 不同造林模式对桉树人工林林下植物物种多样性的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(9):44-52.
|
| [18] |
曾伟, 谭一凡, 曹华, 等. 深圳市马占相思过熟林群落组成及物种多样性分析[J]. 生态科学, 2020, 39(6):112-119.
|
| [19] |
德永军, 姜佳岷, 王小军, 等. 基于两个标准的内蒙古造林抚育精准设计研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(1):121-127.
|
| [20] |
石福习, 赵成章, 任珩, 等. 祁连山北坡自然恢复杨桦林地植物功能型组成及其影响因素[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2012, 18(4):546-552.
|
| [21] |
冯艳琼. 荒漠草原区盐生草甸湿地土壤理化特性、盐分阈值及微生物响应研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2020.
|
| [22] |
陈露蔓, 吕倩, 刘思泽, 等. 柏木低效人工林开窗初期草本层植物多样性及生态位[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2021, 27(5):1178-1185.
|
| [23] |
李晓鹏. 城市化环境下公园自生植物的多样性与公众感知研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020.
|
| [24] |
周爽爽. 不同林型下幼苗更新对近自然森林经营初期的响应及促进措施[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2022.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
高天, 李永生, 陈泓, 等. 生物多样性指示因子在我国森林景观应用中的有效性强度研究[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2017(11):66-76.
|
| [27] |
赵燕波. 不同郁闭度马尾松人工林林下植物多样性及5种主要林下植物化学计量学特征[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2017.
|
| [28] |
赵成章, 石福习, 董小刚, 等. 祁连山北坡退化林地植被群落的自然恢复过程及土壤特征变化[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(1):115-122.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |